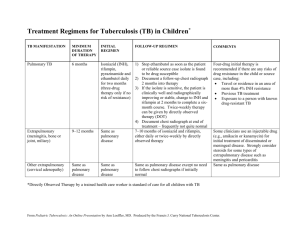
Pulmonary Rehabilitation

King’s Health Partners
Integrated Respiratory Team
PULMONARY REHABILITATION
‘Breathe Better, Feel Good, Do More’
What is it?
Personalised graduated exercise and education programme for patients with long term lung disease who are breathless
Sessions are delivered in a group setting at a range of locations
Who is it for?
Any patient with a long term lung condition whose breathlessness affects their day to day life
Patients with a MRC score 2-5 should be considered for Pulmonary Rehabilitation.
Also think of it after an exacerbation, even if the patient has done PR before. Early PR after an exacerbation reduces readmissions and helps recovery.
The benefits:
There is excellent evidence about the benefits that PR can produce!
PR leads to improvements in health related quality of life, anxiety and depression, exacerbation frequency, functional exercise capacity and maximum exercise capacity 1-12 .
PR includes education sessions focusing on self-management and provides dyspnoea strategies.
Where is it?
Dulwich Leisure Centre SE22 9HB
Brixton Recreation Centre SW9 8QQ
Lambeth Walk SE11 6DU
King’s College Hospital SE5 9RS * Hospital Transport available *
St Thomas’ Hospital SE1 7EH * Hospital Transport available *
How to refer:
Single Point of Referral Southwark specialist GP Noel Baxter
Lambeth Specialist GP Azhar Saleem
What Should Patients expect?
After referral the patient receives a letter offering an appointment for initial assessment.
The PR team will allocate a PR class in a preferred venue for the patient
How to contact us:
If you have any clinical questions and want to speak to a PR physiotherapist please contact us: Tel 020 3299 6039
Email:
kch-tr.pulmonaryrehab1@nhs.net
Lambeth and Southwark Pulmonary Rehab Team,
Dulwich Hospital, East Dulwich Grove, London SE22 8PT
King’s Health Partners
Integrated Respiratory Team
British Lung Foundation- http://www.blf.org.uk/Page/Pulmonary-rehab
IMPRESS – Improving and Integrating Respiratory Services http://www.impressresp.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=38&Ite mid=32
1.
NICE (2010) Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in adults in primary and secondary care. http://www.nice.org.uk/nicemedia/live/13029/49425/49425.pdf
2.
British Thoracic Society Standards of Care Subcommittee on Pulmonary Rehabilitation.
Pulmonary rehabilitation. Thorax. 2001; 56(11):827-834.
3.
Ries AL, Carlin BW, Carrieri-Kohlman V et al. Pulmonary rehabilitation: joint ACCP/AACVPR evidence-based guidelines. Chest. 1997; 112(5):1363-1396.
4.
Salman GF, Mosier MC, Beasley BW et al. Rehabilitation for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Gen Intern Med. 2003;
18(3):213-221.
5.
Toshima MT, Blumberg E, Ries AL et al. Does rehabilitation reduce depression in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease? Journal of Cardiopulmonary Rehabilitation.
1992; 12(4):261-269.
6.
Griffiths TLB. Results at 1 year of outpatient multidisciplinary pulmonary rehabilitation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2000; 355(9201):362-368.
7.
Lacasse Y, Brosseau L, Milne S et al. Pulmonary Rehabilitation for Chronic Obstructive
Pulmonary Disease. The Cochrane Library. 2003; Issue 3(3)
8.
Ries AL, Kaplan RM, Limberg TMK et al. Effects of pulmonary rehabilitation on physiological and psychosocial outcomes in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary-disease. Ann
Intern Med. 1995; 122(11):823-832.
9.
Bestall JC, Paul EA, Garrod R et al. Longitudinal trends in exercise capacity and health status after pulmonary rehabilitation in patients with COPD. Respir Med. 2003; 97(2):173-180.
10.
Griffiths TL, Phillips CJ, Davies S et al. Cost effectiveness of an outpatient multidisciplinary pulmonary rehabilitation programme. Thorax. 2001; 56(10):779-784.
11.
Berry MJ, Rejeski WJ, Adair NE et al. A randomized, controlled trial comparing long-term and short-term exercise in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Journal of
Cardiopulmonary Rehabilitation. 2003; 23(1):60-68.
12.
Foglio K, Bianchi L, Ambrosino N. Is it really useful to repeat outpatient pulmonary rehabilitation programs in patients with chronic airway obstruction? A 2-year controlled study. Chest. 2001; 119(6):1696-1704.
13.
Puhan M, Scharplatz M, Troosters T et al. Pulmonary rehabilitation following exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.
2009;(Scharplatz Madlaina):CD005305.