File - JOrdan Ortiz
advertisement
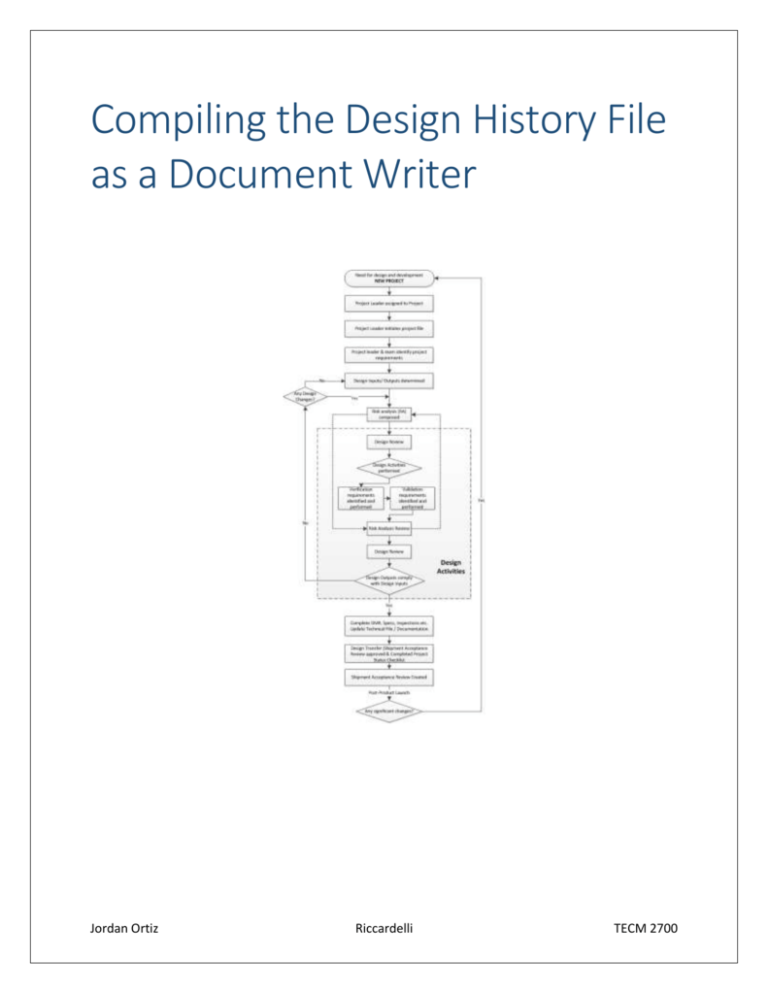
Compiling the Design History File as a Document Writer Jordan Ortiz Riccardelli TECM 2700 ii Compiling the DHF as a Document Writer Table of Contents Table of Contents ................................................................................................................................................... ii Foreword .................................................................................................................................................................. v Chapter 1: Understanding Pre-Design ........................................................................................................... 3 Introduction........................................................................................................................................................ 3 Product Need ...................................................................................................................................................... 3 Project Team ...................................................................................................................................................... 3 Project Leader (PL) ...................................................................................................................................................... 3 Document Writer. ......................................................................................................................................................... 3 Project Plan (R-036-A) .................................................................................................................................... 3 Design Input / Output (R-036-B) ................................................................................................................ 4 Risk Analysis (Risk Management Report) ............................................................................................... 4 Chapter 2: Completing the project Plan (R-036-A) ................................................................................... 7 Introduction........................................................................................................................................................ 7 Gather Data ......................................................................................................................................................... 7 Kick-Off Meeting ................................................................................................................................................ 7 Compilation......................................................................................................................................................... 7 Chapter 3: Writing the Design Input / Output (R-036-B)........................................................................ 9 Introduction........................................................................................................................................................ 9 Gather Data ......................................................................................................................................................... 9 Circulate for Review and signatures ....................................................................................................... 11 Compilation...................................................................................................................................................... 11 Chapter 4: Writing the Risk Analysis (RA) ................................................................................................ 13 Introduction..................................................................................................................................................... 13 Types of RAs..................................................................................................................................................... 13 Gather data....................................................................................................................................................... 13 Risk Assessment ............................................................................................................................................. 13 Risk Mitigation................................................................................................................................................ 15 iii Circulate for Review and Signatures....................................................................................................... 15 Compilation...................................................................................................................................................... 15 Chapter 5: Understanding Product Design ................................................................................................ 17 Introduction..................................................................................................................................................... 17 Design Reviews(R-036-C & R-036-D) ..................................................................................................... 17 Design Activities (R-036-B) ........................................................................................................................ 17 Design Verification (R-036-E) ................................................................................................................... 17 Design Validation (R-036-F) ...................................................................................................................... 17 RA Review (R-036-D).................................................................................................................................... 17 Design Outputs compliance (R-036-H) .................................................................................................. 17 Chapter 6: Composing the Design Review (R-036-D) ............................................................................ 19 Introduction..................................................................................................................................................... 19 DR Meeting ....................................................................................................................................................... 19 Compilation...................................................................................................................................................... 19 Chapter 7: Recording the Design Verification / Validation (R-036-E & R-036-F) ....................... 21 Introduction..................................................................................................................................................... 21 Completion of R-036-E and F ..................................................................................................................... 21 Compilation...................................................................................................................................................... 21 Chapter 8: Filing the Project Change Request (R-036-H) ..................................................................... 23 Introduction..................................................................................................................................................... 23 Signatures ......................................................................................................................................................... 23 Compilation...................................................................................................................................................... 23 Chapter 9: Understanding Post-Design ...................................................................................................... 25 Introduction..................................................................................................................................................... 25 R-036-B Outputs ............................................................................................................................................. 25 Compile the complete DHF ......................................................................................................................... 25 Ship Acceptance (R-036-G) ......................................................................................................................... 25 Chapter 10: Compile the Complete DHF ..................................................................................................... 27 Introduction..................................................................................................................................................... 27 iv Compiling the DHF as a Document Writer Generic DHF Organization .......................................................................................................................... 27 Ship Acceptance (R-036-G) ......................................................................................................................... 27 Chapter 11: Conclusion..................................................................................................................................... 29 v Foreword This manual describes the basic processes for the creation of a Design History File (DHF) for a Document Writer. The Document Writer should ask more questions than stated in this manual and understand the material thoroughly. 2 Compiling the DHF as a Document Writer Figure 1 Pre-Design Flow Chart Chapter 1 3 Chapter 1: Understanding Pre-Design Introduction Pre-design covers the processes prior to Product Design. At this point in development senior management can abort the product design readily. These processes involve cooperation between multiple department and a general recognized need. The Document Writer must complete the Standard Operating Procedures (SOP) throughout the design process to complete the DHF. R-036 and its attachments (A, B, D, E, F, G, and H) serve as the SOP for this company. Product Need A need for a new product arises. Previous products lack a certain marketable characteristics such as translations, outdated Instruction for Use (IFU), or inadequacy of function. If a the need garners the attention of multiple departments, senior management will call a meeting between multiple departments and necessitate a new product development Project Team At the meeting, senior management—CEO, President, CFO or Sr. Vice President—will assign a Project Leader and relate the product need. The Vice President of Product Development usually fulfills this obligation. Together the team can yield an effective product. Project Leader (PL) The Project Leader assigns various employees to positions on the Project Team. This team may number many or none as the Project Leader deems necessary. He or She can offer invaluable advice to the Document. Document Writer. The document writer assigned to the project must compile a Design History File from multiple sources, a Risk Analysis, Meeting Notes and any documents designated to him or her by senior management (PL, Senior Vice President, CFO, President, or CEO). This manual covers only conventional tasks. The Document Writer should compile necessary files into a binder or folder. This manual has “compilation” sections throughout to advise on the general arrangement of the DHF. Chapter 10 contains a complete list of a sample DHF and its parts. Project Plan (R-036-A) The Project Leader will describe the project plan on R-036-A and obtain signatures from the Senior Vice President (SR VP) and at least one of the following: CEO, President, or CFO. The project plan includes the intended start and completion date, a short description, constraints, needed resources, costs, and approval via signatures. The Project Leader can arrange for a meeting, or use email to distribute vital information and obtain signatures individually. Regardless of the method, the document writer must compile notes for the meeting and attach them to R-036-A. If a need arises to change the Project Plan, the Project Leader must complete a Project Plan Change Request. See R-036-H for details in the design Section. 4 Compiling the DHF as a Document Writer Design Input / Output (R-036-B) R-036-B contains both the design Input and the Design Output. The Design Input delineates the initial requirements and specifications of the product The Design Output delineates the Record tasks/testing/documents/etc. completed to show verification of compliance to input. Risk Analysis (Risk Management Report) The Document Writer must compile the Risk Analysis for the project. The document writer can derive a new Risk Analysis from the format of an older, similar Risk Analysis as per R-033. As a result, this manual will use an existing Nursicare Risk Analysis as an example; however, a successful risk analysis will cover all potential risks and risks identified in BS EN ISO 14971:2012 / ISO 14971:2007 and BS EN 62366:2008. 5 6 Figure 3 R-036-A page 1 Compiling the DHF as a Document Writer Figure 2 R-036-A page 2 7 Chapter 2: Completing the project Plan (R-036-A) Introduction The document writer prepares the Project Plan with the PL. The Project Plan lists the goals of the project such as start date, completion date, cost and resources required. The PL or document writer must obtain two signatures: one from the SR. VP and one from either the CFO, CEO or President. Gather Data Ask the PL if he or she wants R-036-A before the kick-off meeting or after. If he or she says before, communicate the idea to several departments and ask for information, such as pricing, and protocols for a previous but similar product. o Use products that undergo similar processes or use identical materials like gamma sterilization, EtO sterilization, or use Exopack liner adhesive. o Communicate the information to the PL If he or she says after, the PL or Document Writer can ask all necessary questions to the meeting’s attendees—granted all those necessary attend. Kick-Off Meeting Create a simple sign in sheet with the meeting type (kick-off) and at least three columns. One for signature, one for department and one for the date. Take notes on any significant topics throughout the meeting including foreseeable setbacks, tentative dates, and special requirements for the project. Type the notes if hand written Use a header to indicate the meeting type (i.e. kick-off), date, list of attendees, and location. Attach the notes to the attendance sheet. Compilation The document writer must obtain the required signatures on the R-036-A for completion. If he or she fails to obtain signatures due to a disagreement about the R-036-A, then he or she must document the meeting with R-036-D. Otherwise the signed R-036-A can replace the R-036-D form. The document writer typically places the meeting notes in an appendix labeled for meeting notes. While the document writer often places the complete R-036-A in a section labeled Standard Operating Procedures (SOP). 8 Figure 4 Design I / O pages 1-2 Figure 5 Design I / O pages 3-4 Compiling the DHF as a Document Writer 9 Chapter 3: Writing the Design Input / Output (R-036-B) Introduction The Document writer must collect data for the Design Input / Output (I / O). This section will explain who to look to for information. Gather Data Locate the Project Leader (PL), VP of Manufacturing (MFG), VP of Clinical Development (CLIN), Senior VP (SR VP), Marketing Director (MKTG), Sales Director (Sales), Chief Engineer (ENGR), Director of Quality (QA), and the Head Chemist (CHEM). Ask each about his or her section of expertise individually, as described below: o Section 1: PL, Clinical o Section 2: MFG, QA o Sections 3: QA, Sr. VP o Section 4: Clinical PL o Section 5: Clinical, Chemistry, QA o Section 6: PL, QA o Section 7: MKTG, QA, ENGR, QA o Section 8: MKTG o Section 9:QA, Chemistry o Section 10: QA, ENGR o Section 11: Sales, MKTG o Section 12: Sales, MKTG o Section 13: QA, Sr. VP o Section 14:Sr. VP o Section 15: QA o Section 16: PL, Clinical o Section 17: PL, QA o Section 18: QA o Section 19: PL, Clinical o 4, 16 and 19 of R-036-B. Use the information in Figure 4, 5 and 6 to form questions (Older copies of the I / O contain relevant information, too). Ask the employee if the information relates to the new product. If irrelevant mark N / A in Design Output column. If relevant disclose ideal completion date for the product (per R-036-A). If the product must meet a new criterion instead, write down the new requirement in the Input column. Determine fastest possible completion date for the task. Check with the employee weekly or biweekly to ensure he or she completes the task. 10 Figure 6 Design I /O page 5-6 Compiling the DHF as a Document Writer 11 Communicate to the PL likely completion dates and call meetings with the PL’s consent (R-036D). Circulate for Review and signatures The Document Writer needs to procure a minimum of 5 signatures for the R-036-B—one from the PL, one from the SR VP, one from MFG, one from QA and one from either MKTG or Sales. Other departments that sign must also review the document for errors. Ask the PL to review and sign first. He or she can best determine the adequacy of the general document and can direct the document writer to the next signee or substitute signee. Email the PL-approved document to all signees. Print several copies of the document for mark ups. Distribute the document copies to all signees except the SR VP for review. Check with the signee’s progress twice a week or weekly; sending reminder emails if necessary. Make changes if necessary. Obtain signature from PL first Obtain signatures from other signees. Take the signed and revised document to the SR VP. If he or she reviews and signs the R-036-B, the document writer can file it in the DHF. If he or she asks for revisions, make the corrections and obtain all the signatures on the revised R-036-B—following the order mentioned above. Compilation The document writer usually files the completed R-036-B in a designated SOP section after R-036-G, R036-A, and R-036-H. The Document writer often indicates the Design I / O with a divider labeled I /O or R-036-B. 12 Compiling the DHF as a Document Writer Figure6 9RA RAPages pages1-2 1-2 Figure Figure 7 RA ISO hazards Figure 8 7 Figure 8 RA Risk Parameters 13 Chapter 4: Writing the Risk Analysis (RA) Introduction The document writer must prepare a Risk analysis with the input of several departments. These departments include Clinical, QA and the PL. The document writer can seek more input from other departments such as CHEM or ENGR if he or she thinks it beneficial. Once the document writer gathers the data about potential risks he or she must compile a report. This report should preferably mimic a previous report. The PL should have the previous reports in older DHFs. Types of RAs The document writer must identify the type of RA in somewhere in the report as demonstrated in Figure 9. The developmental process determines the RA type, so preferably the document Writer must write one RA of each type. Pre-Evaluation Prototype: The RA covers risks that could occur while creating the first or one-off prototype. Post-Evaluation Prototype / Pre-Production: The RA covers risks that could occur during production. Post-Production / Pre-Launch: The RA covers risks that could occur during Launch. Post- Production / Post-Launch: The RA covers risks that could occur in the current and future market. Gather data Obtain a previous RA—a newer report functions better as a template. Identify the RA type. Determine if the risks identified in the template apply to the new product. If no, note “N/A.” Supplement the template with any relevant risks identified in BS EN ISO 14971:2012, ISO 14971:2007, BS EN 62366:2008 and any personal concerns. Input the data into the template format and clearly identify the risks. Risk Assessment Determine type of RA: Using the risk table from R-033 and as seen in figure 8, determine the severity of the risks identified above. Determine the Effect of the risk—the products have never caused death or near of any patients Determine the Exposure of the risk—the products offer either seldom or often based on intended usage. Exposure level affects the final risk least when concerning a product with a minor effect. Determine the Probability of the risk—higher probability could warrant a safer design. Determine the chance of Averting Danger. Ask QA for R-033 for more details Clearly state the Risk level 14 Figure 9 RA Risk Mitigation Compiling the DHF as a Document Writer 15 Describe the Risk in detail. Risk Mitigation Determine if any procedures or materials in place mitigate the risk viz. Instructions for Use (IFU), three levels of packaging ( Carton, Case, Box), QA procedures, precedent set by an earlier product etc. Ask QA if existing protocols affect the product. o Ask specific questions o Use previous RAs as a guide. o Ask for the Procedure. o Write the report number and a summary of the report. Reference any report by number if relevant. Notify the PL or concerned department if a new risk arises. Identify mitigation measures in the process—even if incomplete. Remind those responsible for the new mitigation measures of deadlines. State the mitigation measures in place. Re-evaluate the Risk level with consideration of the mitigation measures. State the new Risk Level. If higher than 7, the product needs severe design changes. Circulate for Review and Signatures The Document Writer needs to procure a minimum of 4 signatures for the RA—one from the PL, one from the SR VP, one from Clinical, one from QA and one from Document Writer. Other departments that sign must also review the document for errors. Ask the PL to review and sign first. He or she can best determine the adequacy of the general document and can direct the document writer to the next signee or substitute signee. Email the PL-approved document to all signees. Print several copies of the document for mark ups. Distribute the document copies to all signees except the SR VP for review. Check with the signee’s progress twice a week or weekly; sending reminder emails if necessary. Make changes if necessary. Obtain signature from PL first Obtain signatures from other signees. Take the signed and revised document to the SR VP. If he or she reviews and signs the RA, the document writer can file it in the DHF. If the SR VP asks for revisions, make the corrections and obtain all the signatures on the revised RA—following the order mentioned above. Compilation The Document Writer usually files the RA in its own section labeled RA, Risk Analysis or Risk Management. The Document writer seldom places the RA divider before the SOP. 16 Compiling the DHF as a Document Writer Figure 10 Design Activities Figure 11 Design Activities 17 Chapter 5: Understanding Product Design Introduction The Document Writer will need strong organizational skills during the Design Phase. He or she will write few if any reports as the other departments must fulfill their obligation to the new product. The Design phase can last months to a year. Design Reviews(R-036-C & R-036-D) The PL or Document Writer can coordinate Design Reviews throughout the Design Process. During the meetings the PL or Document Writer can determine the progress of each department and allow discussion should new developments arise. Design Activities (R-036-B) The Design I / O form describes the Design activities of each department. The department must move towards fulfilling the inputs at this time and yielding the out puts. Design Verification (R-036-E) QA cooperates with CLIN and the PL to determine if the product met the Design Inputs. QA will provide evidence via test results. Design Validation (R-036-F) QA, and the PL cooperate with MFG and ENGR to determine if the machinery and procedures in place will consistently yield the desired product. QA and MFG will perform tests to ensure consistency. RA Review (R-036-D) The Document Writer or PL will hold a meeting to discuss the RA. If the attendees ask for a revision, the Document Writer will create a new RA for the particular phase of development. Design Outputs compliance (R-036-H) The Departments report their solutions to the inputs. If the department fails to match the output with the input, the PL may file a project change request (R-036-H) to accommodate the obtained outputs. 18 Compiling the DHF as a Document Writer Figure 13R-036-D Figure 12R-036-D 19 Chapter 6: Composing the Design Review (R-036-D) Introduction The Document Writer will complete R-036-D (fig 13) following any Design Review (DR). He or she will take notes throughout DR Meeting Email attendees about the Design Review. Prepare attendance sheet. Specify type of Design Review—the PL can help with this. Fill in R-036-D as the meeting progresses. Obtain signatures at the meeting’s conclusion—if unable, make a note and collect signatures later but reference the attendance sheet as proof the meeting attendance. Follow this procedure for every DR review the PL or senior management deems necessary. Compilation Attach the attendance sheet to the meeting notes and place with other meeting notes. Usually the Document Writer places them in an appendix at the DHF’s end. Place the R-036-D in the SOP section and order the R-036-D in some chronological order (if more than one). The Document Writer usually places the R-036-D with R-036-C and behind R-036-B, R-036-H and R-036-A. 20 Compiling the DHF as a Document Writer Figure 14R-036-F (Below) Figure 15 R-036-E (Above) 21 Chapter 7: Recording the Design Verification / Validation (R-036-E & R036-F) Introduction QA will complete both Verification and Validation. The document writer must compile copies of the test report into the DHF and complete R-036-E and F. Completion of R-036-E and F Communicate with QA Obtain copies of the test data as soon as available List the test data numbers in both R-036-E and F (figures 13 & 14) Ensure the test data is accurate o Read the report o Cross reference with current ISO regulations etc. Compilation The Document Writer usually files R-036-E and F behind different tabs (verification and validation). The Document writer then places the copies of the test data behind the corresponding form. 22 Compiling the DHF as a Document Writer Figure 16 R-036-H 23 Chapter 8: Filing the Project Change Request (R-036-H) Introduction The PL can file R-036-H if he deems necessary. If the PL files a R-036-H, the design outputs probably fail to match the design inputs. The PL alone prepares the document, although the Document Writer will obtain the signatures. Signatures Obtain the PL’s signature first. Obtain any signatures other than ENGR / R & D and CFO, President or CEO. Obtain ENGR / R & D signature. Obtain CFO, President or CEO signature. Compilation The Document Writer usually files R-036-H in front of R-036-A.He or she typically places R-036-A in the beginning of the SOP section. 24 Traditional American Breakfast Figure 17Post-Design 25 Chapter 9: Understanding Post-Design Introduction The Document Writer must fully compile the DHF in the Post-Design Phase. QA will complete the DMR and technical file, allowing the document writer to obtain signatures for R-036-B and R-036-G. R-036-B Outputs QA should finish the DMR and Technical File for the product. This allows the Document Writer to circulate the R-036-B for signatures of the Outputs. The document writer should follow the same procedure described for the Design Input signatures (figure 5) in Pre-Design. Refer to the mentioned procedure for more information. Compile the complete DHF The document writer must compile the DHF from all documentation mentioned up to this point. The document writer can arrange the DHF in any logical manner. This manual will describe a typical arrangement. Ship Acceptance (R-036-G) The PL will call a final meeting at which the attendees will sign R-036-G. When they sign, the Document Writer will insert the document into the DHF and complete the DHF. The product can now ship with proper paperwork in line. 26 Figure 18 DHF compiled Traditional American Breakfast 27 Chapter 10: Compile the Complete DHF Introduction The Document writer must compile the DHF in a logical manner. The manual describes a generic manner of organization. Generic DHF Organization The document writer will compile all the relevant files into a DHF. He or she should use a binder with tabs and follow an organization as mention below. The first level bullets represent sections divided with tabs, while the second level bullets represent tabs within sections. Cover page Table of Contents Section 1: Project Plan o Ship Acceptance Form o Project scope and project plan Section 2: SOP o Design Input / Output o Design Review (chronological) o Design Verification & test data o Design Validation & test data Section 3: Risk Analysis o Third Party safety information (i.e. adhesive safety etc.) o Clinical Trials—obtain from Clinical (Not always necessary) Section 4: Appendix o Meeting Notes—Place all the design notes here. o BOM—Obtain from Sales o Miscellaneous—multiple departments will supply information that fail to fit in any section. Place information too little to make another section in the Miscellaneous tab. Ship Acceptance (R-036-G) The PL will arrange a final meeting before the attendees will agree to ship the product. The attendees will only sign with a completed DHF file. The attendees can also signed 28 Figure 19 DHF completed Traditional American Breakfast 29 Chapter 11: Conclusion In his or her job description, the Document Writer must complete more tasks than this manual covers. In an effort to ease the stress, this manual demonstrates the basics requirements for a DHF. In time, the Document Writer will learn far more than the information contained in this manual