Option 3 chapter outline
advertisement

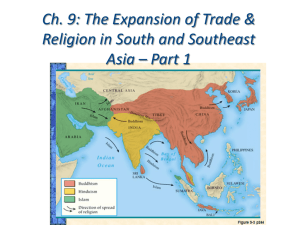
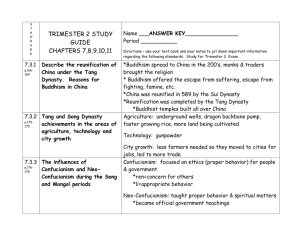
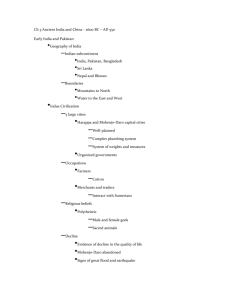
Option # 3 Outline for Chapter 10, 11 or 12 (pick two of the chapters) 1. Complete the chapter outline as you read 2. Make up a vocabulary game using manipulative 3. Submit the outline and the game manipulatives Chapter 10 Life in the Middle Ages: A.D. 1050 to A.D. 1500 Directions: Fill in the outline below. Filling in the blanks will help you as you read and study Chapter 10. I. Section 1: The Church During the Middle Ages (pp. 242–245) A. Monasteries 1. Places where ______________ live and work together B. Convents 1. Places where ______________ live and work together C. Benedictines 1. Followed a rule written by ________________________ 2. Promised never to ______________ , ___________________ , or ___________________ 3. Took care of ________________________ 4. Taught ______________ who lived nearby D. Monasteries and Convents 1. Became centers of ______________ E. Pilgrims 1. Are people who travel to ________________________ 2. Their journeys are called ______________ F. The Crusades 1. Began when ________________________ called for war against the ______________ 2. Fought by ______________ who wanted to win the ______________ from the ______________ 3. Ended when the Muslims conquered ______________ and controlled Palestine 4. Resulted in more power for the ______________ and ________________________ 5. Opened trade between ______________ and ________________________ 6. Caused a split between the ____________________ and the ____________________ II. Section 2: Feudalism (pp. 246–248) A. Feudalism 1. Was a new ______________ and ______________ system 2. Based on the holding of ______________ B. Under the Feudal System 1. ______________ , or lords, owned all the land, and gave it to ______________ 2. The ______________ promised their ______________ to the lords 3. The ______________ , or piece of land, was farmed by the ______________ C. Knights 1. Did most of the ______________ 2. Began training by becoming ______________ 3. Became ______________ at age 15, and ______________ at age 21 4. Promised to defend the __________ , protect the __________ , and be polite to _________ 5. Carried ______________ , ______________ , and ________________________ III. Section 3: The Manor (pp. 249-252) A. The Manor 1. Was the part of the ______________ that ______________ farmed to support a lord’s ______________ 2. Was ________________________ because people who lived there could grow, raise, or make nearly everything they needed B. Serfs 1. Were bound to the ______________ 2. Could not be ______________ or ______________ like slaves 3. Did the ______________ , cut ______________ , and built ______________ C. Farming 1. Improved by the ________________________ ,the ______________ , a better __________ ,the ______________ and the ______________ 2. Changed the population and led to a rebirth of ______________ D. Castles 1. Built by ______________ 2. Were dark, ______________ , and ______________ 3. Nobles held contests called ____________________ in which knights would __________ IV. Section 4: Culture in the Middle Ages (pp. 253–256) A. Learning 1. Took place in schools set up by ______________ in ______________ 2. Students in ______________ studied subjects of higher learning B. Art 1. Was displayed in beautiful ______________ and ______________ 2. Helped people who could not read or write learn about ______________ C. Architecture 1. The ________________________ style is like what the Romans built, with its ______________ and ______________ 2. The ______________ style uses thin walls, many ______________ , and flying ________________________ D. Literature 1. Was written in either ______________ or the language of the ____________________ 2. Aquinas wrote a book called ________________________ 3. Stories like the ________________________ , the _________________________ , and Beowulf tell about the heroic deeds of a ______________ E. Law 1. Henry II introduced the use of a ______________ in ______________ courts 2. A trial is a court case in which a ______________ examines ______________ to decide if someone has done wrong 3. The English council of church leaders and nobles is called ________________________ Chapter 11 Africa and the Americas: A.D. 300 to A.D. 1590 Directions: Fill in the outline below. Filling in the blanks will help you as you read and study Chapter 11. I. Section 1: The Rise of Islam (pp. 264–267) A. Muhammad 1. Born in the Arabian town of _____________________________ 2. Had a _____________________________ of _____________________________ , who told him he was the messenger of _____________________________ 3. Fleed __________________ and went to Medina on a journey called _________________ B. Islam 1. Started by teachings of _____________________________ 2. _____________________________ surrender themselves to Allah 3. Holy book is called _____________________________ 4. Has five _____________________________ , or duties II. Section 2: Islamic Civilization (pp. 268–271) A. Islam Spread 1. Because of holy wars, or _____________________________ 2. Across _____________________________ and into Europe 3. Across the __________________________ and __________________________ Empires to _______________________ , ________________________ , and ______________________ B. Baghdad 1. Capital of the _____________________________ dynasty 2. Center of _____________________________ C. Muslim Contributions 1. Improved ________________________ , resulting in a ________________________ of food 2. Made a science of ___________________ and discovered ____________________ diseases 3. Arab _______________________ figured out the earth is ______________________ 4. Muslim scholar _____________________________made discoveries which led to _____________________________ 5. Islamic art never shows ________________________ or ________________________ 6. Poetry is about the beauty of _____________________ and __________________________ III. Section 3: African Kingdoms (pp. 272–276) A. Ghana 1. Founded about A.D. ________ 2. Called “the land of _____________________________ ” 3. Had a powerful ____________ , but did not conquer its _____________________________ 4. Fell because _____________________________ invaded B. Mali 1. _____________________________ took control of the gold fields 2. __________________________ became a Muslim and ran a _________________________ and _____________________________ empire 3. Fell because ________________________________________________ C. Songhai 1. Became powerful in the _____________________________ by controlling the _____________________________ and _____________________________ trade 2. Divided into provinces by King _____________________________ 3. Fell to Arab army that had _____________________________ IV. Section 4: Early Civilizations in the Americas (pp. 277–282) A. Olmecs 1. Lived in _____________________________ 2. Raised _____________________________ 3. Invented a kind of _____________________________ writing B. Mayas 1. Traded with people in _____________________________ 2. Invented a _____________________________ with no mistakes C. Aztecs 1. Destroyed _____________________________ around 1160 2. Built capital of _____________________________ 3. Worshipped many ___________ and believed in _________________________ sacrifice D. Incas 1. Settled in valley of _____________________________ around 1100 2. _____________________________ to connect their empire 3. Invented the _____________________________ , which is used as a lever Chapter 12 India, China, and Japan: 563 B.C. to A.D. 1620 Directions: Fill in the outline below. Filling in the blanks will help you as you read and study Chapter 12. I. Section 1: Buddhism (pp. 290–292) A. Siddharta Gautama 1. Took the name of ___________________ , which means ___________________ 2. Founder of ___________________ B. Buddhists and Hindus 1. Both believe in ___________________ 2. ___________________ do not believe in the caste system C. Spread of Buddhism 1. Monasteries became important __________________________________ 2. Buddhism spread from ________________ into _______________ , ______________ , _______________ , _________________ , ______________ , and _______________ II. Section 2: India (pp. 293–296) A. The Gupta Dynasty 1. Ruled India during the __________________ , a rich and __________________ time 2. Gupta rulers were ___________________ B. Cultural Advances During the Golden Age 1. Gupta literature is famous for its ___________________ 2. Indian artists decorated ___________________ and temples 3. Scientists discovered the size of the ______________ and understood _______________ 4. Doctors learned to ___________________ people agaisnt disease C. Fall of Gupta Dynasty 1. Caused by attack from the ___________________ of central Asia D. The Moghul Empire 1. Established by ___________________ 2. Akbar appointed _________________ , or nonmilitary, officials to the government III. Section 3: China (pp. 297–300) A. The T’ang Dynasty 1. China became the ___________________ and most ___________________ country in the world 2. Welcomed ___________________ from other lands 3. Educated people wrote ___________________ 4. Artists painted about ___________________ B. The Sung Dynasty 1. The Chinese invented __________________ , causing __________________ to spread 2. The capital, ___________________ , was a ___________________ city 3. Sung inventions include _____________ , the _____________ , and the _____________ 4. Artisans painted ___________________ , or nearly perfect paintings, and made beautiful ___________________ IV. Section 4: The Mongols Conquer China (pp. 301–302) A. Mongol Rulers 1. Greatest ruler was ___________________ 2. ___________________ established the Yuan Dynasty 3. Built great _______________ , and protected ______________ and ______________ B. Ming Rulers 1. Thought foreingers were ___________________ , and began to _____________ China from other countries V. Section 5: Japan (pp. 303–304) A. Japan’s Geography 1. Has protected it from ____________________ 2. Has also brought ideas from ______________ , ______________ , and _______________ B. Religion 1. ____________________ was born in Japan and has no holy books 2. Buddhism came to Japan through ___________________ from Korea VI. Section 6: Japan Develops Its Own Culture (pp. 305–308) A. Feudalism 1. ___________________ were military dictators who controlled officials, ___________________ , and ___________________ 2. Daimyos controlled large pieces of land called ___________________ 3. ___________________were warriors who fought for lords, and followed a code of honor called ___________________ VII.Section 7: The Tokugawa Unify Japan (pp. 309–310) A. Tokugawa Family 1. In 1623, began to ____________________________________ 2. Forced _________________ to leave and said no one could be a __________________ 3. Did not allow the ___________________ to leave Japan B. Rich Culture 1. Included _______________ , the art of flower arranging; ________________ dramas; and ________________ 2. Japanse paintings showed the ___________________ , and gardens copied