Type of storm Definition Where does it typically form, and why? What
advertisement
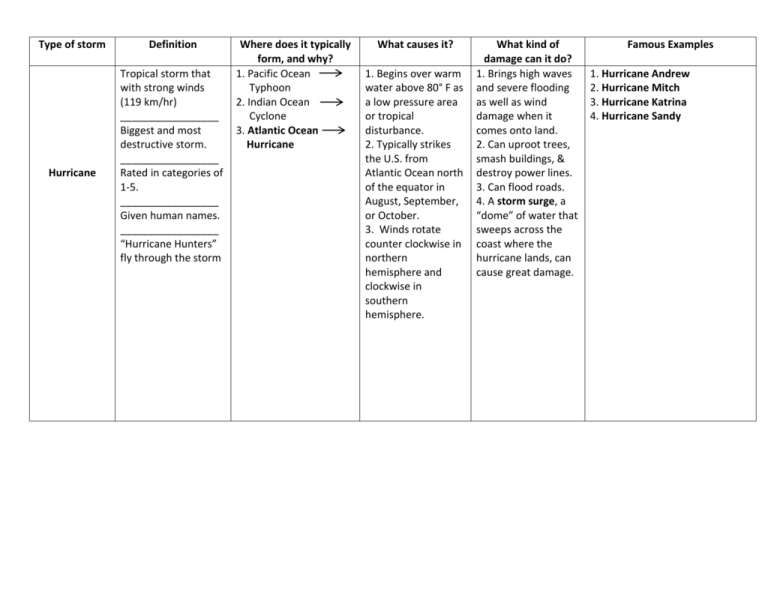
Type of storm Hurricane Definition Tropical storm that with strong winds (119 km/hr) _________________ Biggest and most destructive storm. _________________ Rated in categories of 1-5. _________________ Given human names. _________________ “Hurricane Hunters” fly through the storm Where does it typically form, and why? 1. Pacific Ocean Typhoon 2. Indian Ocean Cyclone 3. Atlantic Ocean Hurricane What causes it? 1. Begins over warm water above 80° F as a low pressure area or tropical disturbance. 2. Typically strikes the U.S. from Atlantic Ocean north of the equator in August, September, or October. 3. Winds rotate counter clockwise in northern hemisphere and clockwise in southern hemisphere. What kind of damage can it do? 1. Brings high waves and severe flooding as well as wind damage when it comes onto land. 2. Can uproot trees, smash buildings, & destroy power lines. 3. Can flood roads. 4. A storm surge, a “dome” of water that sweeps across the coast where the hurricane lands, can cause great damage. Famous Examples 1. Hurricane Andrew 2. Hurricane Mitch 3. Hurricane Katrina 4. Hurricane Sandy Tornado Rapidly whirling funnel shaped cloud that reaches down from a storm cloud to touch Earth’s surface. _________________ Rated on the Fujita Scale from (F)0-(F)5 If it forms over a lake or ocean it is called a waterspout. __________________ Develop in low heavy cumulonimbus clouds (clouds that bring thunderstorms). __________________ Often occur in spring & early summer. __________________ “Tornado Alley” 1. When a warm, humid air mass moves north and meets a cold dry air mass. The cold air moves under the warm air, which rises. 1. Causes very precise/specific damage (can level houses on one street & leave neighboring houses standing). 2. Damage comes from strong winds & flying debris. 3. Can move large objects for many miles. 1. More tornadoes happen in the US than anywhere else-“Tornado Alley”-north-central Texas across central Oklahoma, Kansas, and Nebraska. __________________________ Tri- State Tornado of 1925. Super Outbreak of 148 tornados in 1974 Oklahoma City in 1999 Greenburg, Kansas in 2007 Type of storm Thunderstorm Drought Definition Where does it typically form, and why? 1. Form within large cumulonimbus clouds or thunderheads. 1. Heavy rain storms accompanied by thunder & lightning. - Lightning: sudden spark of energy between clouds, within clouds, or cloud to ground. - Thunder: when lightning heats the air it expands suddenly & explosively. 1. Long periods of low 1. Can occur almost precipitation. anywhere on Earth. What causes it? 1. Warm air is forced upward at a cold front. 1. Jet stream pattern changes and causes unusual weather of less (or more) precipitation. What kind of damage can it do? 1. Lightning can shatter tree tops & start forest fires. 2. Can cause serious burns, heart failure, & unconsciousness in people. 1. Can cause entire crops to fail. 2. In less developed counties it can cause widespread hunger or famine. Famous Examples etc. We do not know famous examples of thunderstorms because they are so common, however, they can often produce more severe storms such as tornadoes. __________________________ Thunderstorms can develop into Super cells, which are a storm that produces severe weather, sometimes tornadoes. 1. Scientists try to produce rain during droughts w/ cloud seeding—tiny drops of carbon dioxide & silver nitrate. __________________________ 1987-1989 Drought that covered 36% of US. __________________________ The Dust Bowl Drought 19331940