Cell Cycle
advertisement

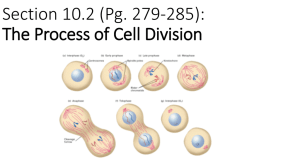
Topic 2: Cells Learning Opportunity 5.08 Cell Cycle Outline the stages in the cell cycle including interphase (G1, S, G2), mitosis and cytokinesis (2.5.1) The life cycle of a cell is known as the __________________________ and consists of several different stages. The cell will spend a certain amount of time each in each stage depending on what type of cell it is. For cells that are actively growing and dividing (like skin cells), the entire cell cycle can be completed in about 24 hours. Other cells, such as certain types of nerve cell, will never fully complete the cell cycle as they do not divide. The Cell Cycle The first phase in the cell cycle is known as ___________________________. During interphase, the cell is ___________ _______________________________________________________. Cells spend about 90% of their lives in interphase, which can can be broken down into 3 stages: G1 phase During this time there is (or gap 1) Interphase S (synthesis) phase The cell prepares for division; G2 phase there is _________________ (or gap 2) ____________________________and an _____________________________ _________________________________ http://schoolworkhelper.net/2010/11/cell-cycles-interphasemitosis-cytokinesis/ Nuclear Division _______________ Mitosis _________________________________ ________________ this ensure that there are the same number of chromosomes Division Cell from cell to cell Cytokinesis _________________________________ ________________ and the rest of the cell Mitosis - Key Terms Before we go into any more detail on the process of mitosis, it is important to review a few key terms: Chromatin As you know, inside the nucleus of every cell is DNA. When the cell is in interphase of the cell cycle, that DNA is in a form known as ________________________. Chromatin refers to ___________________________________________________ in the nucleus during _________________________. Remember learning that prokaryotic cells have "naked DNA"? That's because their DNA is not wrapped around proteins to make it compact like the DNA of eukaryotic cells. Think of chromatin like spaghetti and meatballs - the that is an active period in proteins are the meat balls you can wrap the spaghetti long State strands of interphase DNA are the spaghetti and the the life of a cell when many metabolic around! reactions occur, including protein synthesis, DNASee replication, andbelow: an increase in the the image number of mitochondria and/or chloroplasts (2.5.3) Topic 2: Cells 5.08 Chromosomes When the cell is about to start mitosis, the now replicated DNA will ___________________________________itself into structures called ____________________________. This will keep things nice and _______________________ in the nucleus. If chromatin is like spaghetti and meatballs, Learning Opportunity think of chromosomes like fusili pasta. When the cell enters mitosis, each chromosome is made up of two partners - the original DNA and its duplicate. Chromatids The _____________________________refer to the _______ _________________________________________________. They are completely identical. One chromatid is the original DNA and one is the duplicate. Centromere This is ______________________________________________________. PROPHASE The first phase of mitosis is known as ____________________. During this phase, the following events occur: - chromatin fibres ______________________ (become more tightly coiled to become ___________________________ - _______________________________ to opposite poles - _________________________________ (made of microtubules) and attach to chromosome’s centromeres - nuclear membrane starts to _________________ METAPHASE - chromosomes _________________________ ______________________________________ - centromeres of each chromosome lie on the plate - nuclear membrane completely dissolves Topic 2: Cells Learning Opportunity 5.08 ANAPHASE - centromeres divide and __________________ ________________________________ - chromosomes ____________________________ as microtubules shorten - centromeres move towards poles first because they are attached to the microtubules - identical set of chromosomes moves to each pole to each pole TELOPHASE - chromosomes _____________________________ - spindle fibres dissolve - _________________________________________ Can you identify cells in the different stages of mitosis? Try this: http://www.biology.arizona.edu/Cell_BIO/activities/cell_cycle/0 1.html After mitosis After the nucleus has divided, now the rest of the cell will too in a process known as cytokinesis. In animal cells the cytoplasm divides, pinching inwards to form cleavage furrow. In plants a new cell wall forms and separates the two cells. Animations: http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__mitosis_and_cytokinesis.html http://www.bcscience.com/bc9/pgs/v_animate_001_mitosis.html Explain how mitosis produces two genetically identical nuclei (2.5.5) One of the purposes of mitosis is two create genetically IDENTICAL nuclei. This is able to be accomplished because during the S-phase, ________________________________________________________________. Therefore just prior to the beginning of mitosis there is actually ________________________________________________________________in a cell. Each chromosome in this state is represented by a pair of sister chromatids. These sister chromatids are then separated in anaphase as the spindle microtubules attaches to centromere and pulls the sister chromatids to opposite poles. As the sister chromatids separate they are called chromosomes. This means that ____________________________________ ____________________________.same genetic material). State that growth, embryonic development, tissue repair and asesxual reproduction involve mitosis (2.5.6) The following processes would not be possible without mitosis: ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ State that tumours (cancers) are the result of uncontrolled cell division and that these can occur in any organ or tissue (2.5.2) As we have previously discussed, cancer is a group of diseases associated with ____________________________________ ___________________________________________.