CarboxlicAcidsFunc G..
advertisement
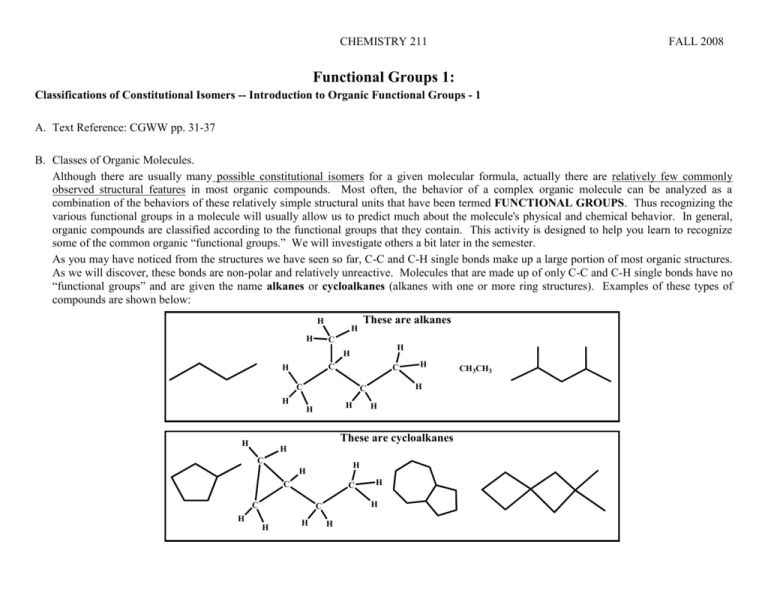
CHEMISTRY 211 FALL 2008 Functional Groups 1: Classifications of Constitutional Isomers -- Introduction to Organic Functional Groups - 1 A. Text Reference: CGWW pp. 31-37 B. Classes of Organic Molecules. Although there are usually many possible constitutional isomers for a given molecular formula, actually there are relatively few commonly observed structural features in most organic compounds. Most often, the behavior of a complex organic molecule can be analyzed as a combination of the behaviors of these relatively simple structural units that have been termed FUNCTIONAL GROUPS. Thus recognizing the various functional groups in a molecule will usually allow us to predict much about the molecule's physical and chemical behavior. In general, organic compounds are classified according to the functional groups that they contain. This activity is designed to help you learn to recognize some of the common organic “functional groups.” We will investigate others a bit later in the semester. As you may have noticed from the structures we have seen so far, C-C and C-H single bonds make up a large portion of most organic structures. As we will discover, these bonds are non-polar and relatively unreactive. Molecules that are made up of only C-C and C-H single bonds have no “functional groups” and are given the name alkanes or cycloalkanes (alkanes with one or more ring structures). Examples of these types of compounds are shown below: H H H These are alkanes C H H C H C C H H H H H C C C H H H C H H These are cycloalkanes H C H H C H H H CH3CH3 2 Func. Groups-1 Because alkanes contain only carbon and hydrogen they are know as hydrocarbons and they often form the framework that holds the other specific structural groupings of atoms that we call functional groups. Func. Groups-1 3 C. Exploration of Specific Organic Functional Groups: Each of the following sections gives examples of molecules with the particular bonding sequence of the identified functional group paired with a second set of molecules that do not contain that specific bonding sequence. For each functional group, use the differences between the two sets of structures to: Define the specific sequence of bonding that characterizes the functional group. Draw two new structures of molecules with the specific functional group and no other. 1. Alkenes These are alkenes H H H C H H C C H These are not alkenes H H H C C H H CH3CHCHCH2CH3 H C N H C H CH3CH2CCCH2CH3 C H H O H Specific Bonding Sequence for an Alkene Circle the sequence in each structure above and define it in words below: H H C C H H H C Draw Two New Alkene Structures below An alkene contains a carbon double bond. 2. Alkynes These are alkynes These are not alkynes H H H C C C H H CH3CCCH2C(CH3)3 C H H N H Specific Bonding Sequence for an Alkyne Circle the sequence in each structure above and define it in words below: An alkyne has a carbon triple bond. H H H C C H C C H CH3CH2CHCHCH2CH3 C H H H Draw Two New Alkyne Structures below N 4 3. Func. Groups-1 Alcohols These are alcohols O H H H C O O H H H C C H O C H These are not alcohols H H H C Specific Bonding Sequence for an Alcohol Circle the sequence in each structure above and define it in words below: An alcohol contains a hydroxyl group attached to a single carbon. O C H H O H C H H C H CH3CH2OH H H C H H H H N O O O H Draw Two New Alcohol Structures below 4. Ethers These are not ethers These are ethers H H O H C CH3CH2OC(CH3)2CH2CH3 H H H H C C H O O N H C H C C H O C H H Specific Bonding Sequence for an Ether Circle the sequence in each structure above and define it in words below: From what is shown on the paper, ethers contains one oxygen atom bonded to Two carbons. All single bonds. Molecule contains C, H, O. No other elements. O H H H H C H CH3CH2COOCH3 H O O Draw Two New Ether Structures below 5. Amines These are amines H H H N C H C C H H H N H H N H H C H These are not amines H CH3CH2NH2 H H O H H C H O H H C C H C O N CH3CH2COOCH2CH3 H N H Func. Groups-1 5 Specific Bonding Sequence for an amine Circle the sequence in each structure above and define it in words below: All single bonds. One N atom in molecule. Molecule has only C, H, N. The N Can have one or more carbons bonded to it. Draw Two New Amine Structures below D. Application: Recognition of Specific Organic Functional Groups: 1. Monofunctional compounds: a. Each of the following molecules has only one functional group. Classify each according to the functional group it contains: a. c. b. O CH3CH2CH2CH2NHCH3 d. e. f. CH3CH2CH2C(OH)(CH3)2 O H 2. Write a complete structural formula, other than those given elsewhere in this activity, for: a. an alcohol b. an alkene c. an ether d. an amine e. an alkyne 3. Polyfunctional compounds: Molecules can contain more than one functional group. Those shown below are examples of “poly functional” molecules. Identify all functional groups in the following molecules. a. H b. N O H 6 c. N H Func. Groups-1 d. CH3 O N H H CH3 H H O H O H