Study Guide for Meiosis and Mendelian Genetics Test Your test will
advertisement

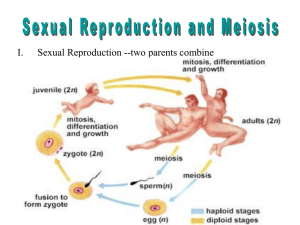
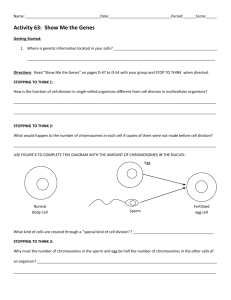
Study Guide for Meiosis and Mendelian Genetics Test Your test will be on Tuesday, February 18th Standard 2a: Students know meiosis is an early step in sexual reproduction in which the pairs of chromosomes separate and segregate randomly during cell division to produce gametes containing one chromosome of each type -Be able to tell the number of chromosomes in a haploid gamete when you are given the number of chromosomes in a diploid somatic cell -Be able to tell the number of chromosomes in a diploid somatic cell when given the number of chromosomes n a haploid gamete -Know what happens during crossing over -Know the meiosis diagrams below and know when the cells are diploid, when they are haploid, and what the chromosomes look like at each stage Standard 2b: Students know only certain cells in a multicellular organism undergo meiosis. -Know what kinds of cells are produced during meiosis in general, and specifically in oogenesis and spermatogenesis -Know the major differences in structure and function of somatic cells vs. germline cells Standard 2c: Students know how random chromosome segregation explains the probability that a particular allele will be in a gamete. -Be able to state the probability that a zygote will receive any allele and why that is the probability Standard 2d: Students know new combinations of alleles may be generated in a zygote through the fusion of male and female gametes (fertilization) -Know what two cells combine to make a zygote, and what a zygote becomes when it grows up -Know the definitions of diploid and haploid -Be able to explain why gametes have different combinations of alleles (different from each other and different from the person who made them) Standard 2f: Students know the role of chromosomes in determining an individual’s sex. -Know which two sex chromosomes females have and which two sex chromosomes males have. -Seriously, this is a really easy standard. I expect every single one of you to get a 4 on this. Standard 2g: Students know how to predict possible combinations of alleles in a zygote from the genetic makeup of the parents -Be able to complete a Punnett square AND tell me what alleles the offspring will have Standard 3a: Students know how to predict the probable outcome of phenotypes in a genetic cross from the genotypes of the parents and mode of inheritance (autosomal or Xlinked, dominant or recessive). -Be able to complete a Punnett square for simple dominant/recessive inheritance. If I give you the descriptions of the genotypes and the letters to use for the alleles, you need to be able to tell me the expected ratios and/or percentages of phenotypes of the offspring -Same as above, but for X-linked traits -Know the difference between codominance and incomplete dominance Standard 3b: Students know the genetic basis for Mendel’s laws of segregation and independent assortment. -Know Mendel’s laws of segregation and independent assortment – be able to explain what they have to do with chromosomes (as in what does it mean when chromosomes segregate, and what does it mean when chromosomes assort independently) -Be able to predict what happens when something goes wrong during meiosis – including what might happen if chromosomes did not segregate properly AND what might happen if chromosomes did not assort independently (think about how many chromosomes you might find in a gamete, and which parent the alleles might come from)