Large-Signal Characterization of Power Inductors in EV Bidirectional
advertisement

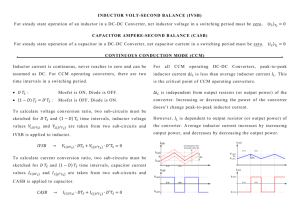
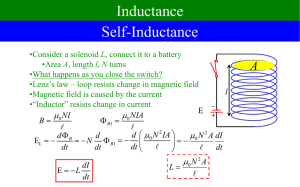
Large-Signal Characterization of Power Inductors in EV Bidirectional DC–DC Converters Focused on Core Size Optimization ABSTRACT This project is focused on core size optimization of power inductors in bidirectional dc–dc converters. It presents an experimental large-signal characterization procedure for power inductors in electric vehicle applications and a method to obtain an inductance reference value for the power inductor in dc–dc converters’ simulation studies. It discusses the importance of the inductor design project by describing important constraints such as core size and saturation. CIRCUIT DIAGRAM EXISTING SYSTEM The power inductor plays an essential role in the overall performance of the system. Critical aspects are related to core material limitations, i.e., saturation and core losses, both of which depend on the changing flux. Other aspects are related to the transient performance of the converter. A recurrent topic is the magnetics performance and optimization, and one of the main challenges is how to improve the components’ choice and sizing. The filter inductor is typically sized based on its current rating and maximum permissible ripple. However, due to the highcurrent response of such energy storage elements, the converter may operate for short periods with much higher currents than the rated values. In such conditions, the power inductor core may reach important levels of flux density that can be close to material saturation. PROPOSED SYSTEM The main objective of this project is to present an adequate design of the power inductor without using interleaving techniques by proposing two approaches, i.e., initially, by an appropriate selection of core material. It is a common practice to build inductors with gapped cores to prevent saturation. Powder alloy or powder iron cores are manufactured from highly compressed powdered ferrous alloy or iron. Small air gaps are evenly distributed throughout the core material, and this acts in a similar way to gapping a ferrite core. TOOLS AND SOFTWARE USED: MP LAB ORCAD/PSPICE MATLAB/SIMULINK OUTPUT: HARDWARE SIMULATION REFERENCE: Marina S. Perdigão, Member, IEEE, João Pedro F. Trovão, Member, IEEE, J. M. Alonso, Senior Member, IEEE, and E. S. Saraiva, Life Member, IEEE, “LargeSignal Characterization of Power Inductors in EV Bidirectional DC–DC Converters Focused on Core Size Optimization”, IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INDUSTRIAL ELECTRONICS, VOL. 62, NO. 5, MAY 2015






![• [A] WO 9853550 A1 19981126 - MUNK NIELSEN STIG [DK] • [ID](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008241369_1-754aeea07c3d8e9488bccb33bdba5023-300x300.png)
