Are You Ready to Rock? Unit/Lesson Plan Title: Are You Ready to
advertisement

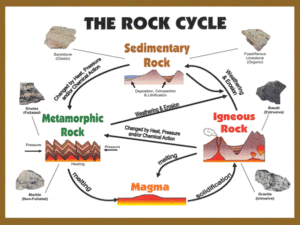
Are You Ready to Rock? Unit/Lesson Plan Title: Are You Ready to Rock??? Subject: Science with intergration of Language Arts and Math Grade Level: 4 Length of Lesson: 2 weeks Unit/Lesson Summary: This is an intergrated unit that will be on the topic of the three types of rocks. The lessons will have hands on experiments that will help with the gathering of information for the content specific writing task. Key Vocabulary: rock, igneous rock, sedimentary rock, metamorphic, erosion, weathering, sediments, mineral, intrusive, extrusive, fossils, pressure, Essential Question(s): How would you compare and contrast the different types of rocks? NCSCOS Essential Standards Addressed in Unit/Lesson: Objective 2.03: Explain how rocks are composed of minerals. Objective 2.04: Show that different rocks have different properties. Objective 2.06: Classify rocks and rock-forming minerals using student-made rules. Materials/ Resources (also list web resources, technology tools and safety requirements): Sylvester and the Magic Pebble by William Steig Chocolate chips graham crackers candle cake icing brown construction paper mini marshmellow glue bottles Frosted Flakes baggies sprinkles Starburst wax paper electric griddle or frying pan pancake mix (just-add-water type) water for the mix oil for the griddle plates and napkins, spatula assorted foods, some that melt and some that don't: raisins, coconut, marshmallows, nuts, chocolate chips, berries, etc. Procedure: Introduction Day: *To introduce the concept of rocks, have the students create a KWL chart on rocks using the Promethean board. *Then read the book Sylvester and the Magic Pebble as a whole group. * After reading, discuss the content specific writing activity students will do at the end of the unit. Students will be asked to choose 2 different types of rocks and write a paper comparing and contrasting them. Following Day (can be independently or work collaborative with a team) Igneous Rocks: Day 1: Use the following Promethean planet flip charts to introduce the rock: Rock_Soils.flp Rock_types_vote.flp Take notes on rocks. Use various websites to locate pictures of this type of rock. Day 2: Review vocabulary and information on igneous rocks. Have 3 centers set up for students to experiment: * Center 1: Teacher stationed with chocolate chips and chocolate melter. Teacher will melt the chips and pore the mix on wax paper to cool to demonstrate how igneous rocks form. *Center 2: Assistant teacher will light candle and let some of the wax melt. Let the liquid wax drip onto a piece of foil and harden. * Center 3: Wrap a piece brown construction paper around a bottle of glue. Squeeze the glue and let it drip down the side of construction paper and harden. Sedimentary Rock: Day 1: Use the following Promethean planet flip charts to introduce the rock: Rock_Soils.flp Rock_types_vote.flp Take notes on rocks. Use various websites to locate pictures of this type of rock. Students will use graham crackers and icing to show layers of sedimentary rocks. Day 2: Review vocabulary and information on sedimentary rock. Have mini marshmallow, chocolate chips, frosted flakes and sprinkles in a bag. Students will have wax paper on their desk. Have students take items from the baggie to and smash them together (using pressure) by sticking and squeezing them together. Metamorphic Rock: Day 1: Use the following Promethean planet flip charts to introduce the rock: Rock_Soils.flp Rock_types_vote.flp Take notes on rocks. Use various websites to locate pictures of this type of rock. Give the students two different colored StarBurst candies. Students will take each flavor and apply heat and pressure to them by squishing them together in their hands, then combining them together. Day 2: Review vocabulary and information on metamorphic rock. 1. Allow students to observe each of the ingredients (including the pancake mix) before you combine them. You may wish to have them record these observations in their science journal. Tell students that these ingredients represent the minerals of the rock. 2. Ask students what two factors are needed to form metamorphic rock (heat and pressure). 3. Combine the ingredients to make rock batter. 4. Place the completed rock batter onto the griddle and flatten with the spatula. The griddle represents heat and the flattening with the spatula represents pressure. 5. When finished cooking, place the metamorphic rock cakes on plates and allow students to observe them after they have cooled. Students can then record their answers to the questions listed below. 6. After observing the rock cakes, eat and enjoy! *After hands on experiment, refresh students on the content specific writing task. To Wrap Up Unit: *Do the writing content specific task. Students will be allowed to use the internet and notes to write this task. Unit/Lesson Accommodations for Differentiated Instruction Enrichment: Online Scavenger Hunt- studetns will go onto webpages to find pictures and information on the types of rocks. Remediation: Edible Rocks activity- students will be given ziploc baggies with core samples made from different types of candy bars. Students will be in groups to decode slides with clues to figure out which core sample matches what clue. Cross Curricular Extension: ART: create their own rock MUSIC: create their own Rock Rap using Garage Band Assessments: 1. Participation grades 2. Content Specific task 3. Rock test Created by: Tonya Kepley, Lisa Pinion, Angela Mullinax, Amber Nichols Email: nicholam@rss.k12.nc.us mailto:nicholam@rss.k12.nc.usmailto:nicholam@rss.k12.nc.us Metamorphic Rock Sedimentary Rock Igneous Rock Metamorphic means ____________________ ___. Metamorphic rock may start as ____________________ ___, ____________________ ___, or even another ____________________ __ rock, but then, somewhere deep underground, gets changed by ____________________ ___ and ____________________. The heat and pressure that metamorphose rock is not enough to _______________ it, but still enough to cause changes. Most metamorphic rocks form in places where ____________________ ___ are being made. Metamorphic rocks that form at ______________ temperatures and pressures have ________________ grains. Metamorphic rocks that form at _______________ temperatures and pressures have _______________ grains. Sedimentary rocks are formed by ____________________ _ being ___________________ and ________________ together over a long time. weathering erosion The material that is dropped in the bottoms of stream, river, or lakes from erosion is called ____________________ ___. * Sedimentary rocks cover about ________ of the land on earth and most of the land on the bottom of the ocean. * Most __________________ are found in sedimentary rock. Some examples of Sedimentary Rocks include: Minerals in the earth are in liquid form and are called __________________. Magma is squeezed around inside the earth and as it pushes towards the surface of the earth, it starts to ___________________. As it cools, it turns to ____________________ ____________________ ______. Liquid rock that reaches the earth’s surface is called _________________. ____________________ __ igneous rocks form INSIDE the earth’s crust. These rocks cool more slowly, allowing time for larger _________________ to form. ____________________ __ igneous rocks form OUTSIDE the earth’s crust. ____________________ __ is the most common type of igneous rock. Rock Test Use the following words to complete the sentences below. granite sediments change igneous rock fossils sedimentary rock pressure lava weathering erosion metamorphic rock squeezed magma stuck cool solid igneous rock heat crystals intrusive extrusive 1. Metamorphic means _______________________. 2. - 6. Metamorphic rock may start as ____________________________________ , ____________________________________ , or even another __________________ , but then, somewhere deep underground, gets changed by _______________________ and ____________________________. 7. - 9. Sedimentary rocks are formed by ____________________________________ being ____________________ and ________________ together over a long time. 10. ________________________ is the process by which wind and moving water carry away bits of rock. 11. ________________________ is the process by which rocks are broken down into smaller pieces. 12. Most _____________________________ are found in sedimentary rocks. 13. Minerals in the earth are in liquid form and are called __________________. 14. Magma is squeezed around inside the earth and as it pushes towards the surface of the earth, it starts to ___________________. 15. As it cools, it turns to ______________________________________________. 16. Liquid rock that reaches the earth’s surface is called _________________. 17. ______________________ igneous rocks form INSIDE the earth’s crust. 18. These rocks cool more slowly, allowing time for larger _________________ to form. 19. ______________________ igneous rocks form OUTSIDE the earth’s crust. 20. ______________________ is the most common t ype of igneous rock.