Freshwater Prezi Transcript
advertisement

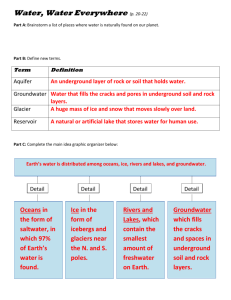
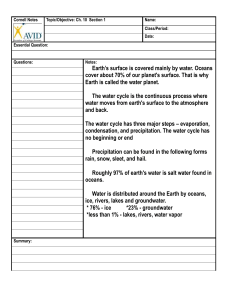
FRESHWATER EARTH'S WATER 97% Saltwater---3% Freshwater Oceans Contain Salt Water Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic Ice Sheets of freshwater Cover Antarctica, Greenland They break and melt as they reach warmer water Most of the freshwater is found here Rivers & Lakes Sources of freshwater for humans Contain very little of the earth's freshwater Groundwater Fills cracks and sapces in soil More freshwater here than in rivers and lakes Water Cycle Continuous process where water moves from the earth's surface to the atmosphereand back 3 Continuous Steps Evaporation Liquid water heats up and changes to gas (Water Vapor) Plants release water into the air through their leaves (Transpiration) Condensation Warm air carries the water vapor up where it cools Drops of water clump together to form clouds Precipitation Water droplets grow larger Cloud can't hold large drops so it falls to the ground Surface Water Rivers Snow Melts in the mountains, water drains off....rivers form Tributaries: Smaller rrs and streams that feed the main river Remember---a river system is the river and it's tributaries Watersheds Areas that providewater for the river... also known as Drainage Basins Divides Ridges of land that separate watersheds Continental Divide: The longest in N. America--Follows the Rocky Mountains Ponds Small, Shallow areas of standing Water... Form when water collects in depressions or low areas LAKES Deeper/Bigger than ponds---Sunlight doesn't reach the bottom Reservoirs--Lakes that hold human water supplies Wetlands Areas that stay wet most of the year 3 types 1. Marshes: Grassy, covered by shallow water 2. Swamps: Flooded Forest with trees & Shrubs, mostly in warm, humid climates 3. Bogs: Cooler areas left from melting ice sheets....lots of moss here Water Underground Comes from Precipitation---soaks into the ground with gravity---fills up spaces between particles & cracks. Permeable vs. Impermeable Permeable---large pores allow water to pass through Impemeable: Don't allow water through How does this relate to groundwater??? Saturated vs. Unsaturated Saturated Zone: Totally filled (saturated) with water... Top: Water Table Unsaturated zone: Area above the water table where more water can be absorbed Groundwater to Surface Springs: groundwater flows from bubbles and cracks deep in the land Aquifers: Underground layers of rock that hold water Wells: Areas where aquifer has been drilled to bring water to the surface. Pumps Used to bring groundwater up---easier than a crank and bucket Pumping water too fast can cause the well to dry up... If pump goes out, you have to use other means to get the water to the surface Wells Artesian Wells: Pressure in the aquifer causes water to rise on it's own with no pump Regular Wells: Require outside force to bring up water... Springs & Geysers Springs flow easily from cracks in the surface Geysers: Hot sprinere water "erupts" from the surface from the pressure in the hot water... Ice