6th Grade SpringBoard Curriculum - Wylie Independent School District
advertisement
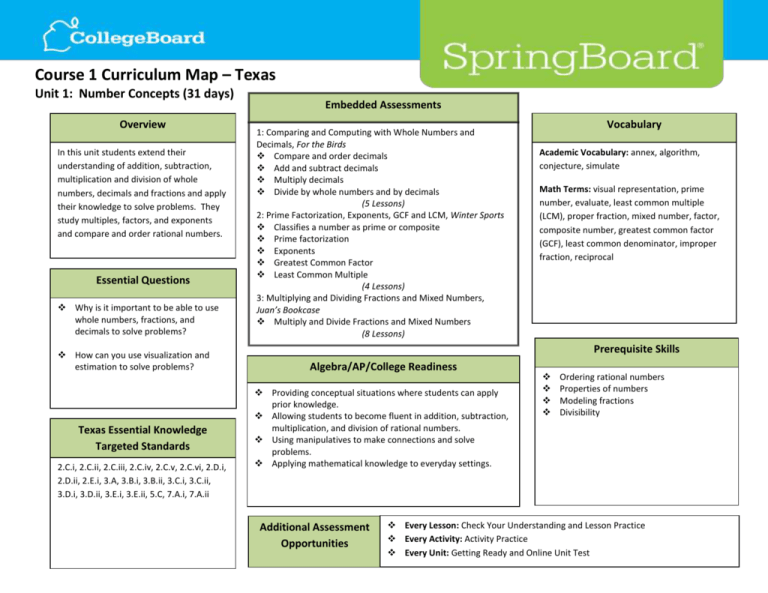
Course 1 Curriculum Map – Texas Unit 1: Number Concepts (31 days) Overview In this unit students extend their understanding of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of whole numbers, decimals and fractions and apply their knowledge to solve problems. They study multiples, factors, and exponents and compare and order rational numbers. Essential Questions Why is it important to be able to use whole numbers, fractions, and decimals to solve problems? How can you use visualization and estimation to solve problems? Texas Essential Knowledge Targeted Standards 2.C.i, 2.C.ii, 2.C.iii, 2.C.iv, 2.C.v, 2.C.vi, 2.D.i, 2.D.ii, 2.E.i, 3.A, 3.B.i, 3.B.ii, 3.C.i, 3.C.ii, 3.D.i, 3.D.ii, 3.E.i, 3.E.ii, 5.C, 7.A.i, 7.A.ii Embedded Assessments 1: Comparing and Computing with Whole Numbers and Decimals, For the Birds Compare and order decimals Add and subtract decimals Multiply decimals Divide by whole numbers and by decimals (5 Lessons) 2: Prime Factorization, Exponents, GCF and LCM, Winter Sports Classifies a number as prime or composite Prime factorization Exponents Greatest Common Factor Least Common Multiple (4 Lessons) 3: Multiplying and Dividing Fractions and Mixed Numbers, Juan’s Bookcase Multiply and Divide Fractions and Mixed Numbers (8 Lessons) Vocabulary Academic Vocabulary: annex, algorithm, conjecture, simulate Math Terms: visual representation, prime number, evaluate, least common multiple (LCM), proper fraction, mixed number, factor, composite number, greatest common factor (GCF), least common denominator, improper fraction, reciprocal Prerequisite Skills Algebra/AP/College Readiness Providing conceptual situations where students can apply prior knowledge. Allowing students to become fluent in addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of rational numbers. Using manipulatives to make connections and solve problems. Applying mathematical knowledge to everyday settings. Additional Assessment Opportunities Ordering rational numbers Properties of numbers Modeling fractions Divisibility Every Lesson: Check Your Understanding and Lesson Practice Every Activity: Activity Practice Every Unit: Getting Ready and Online Unit Test Course 1 Curriculum Map – Texas Unit 2: Integers (16 days) Overview In prior units students have studied whole numbers, fractions and decimals, and operations with these numbers. In this unit students extend the study of number systems to the integers. The study includes numerical operations, ordering numbers, absolute value and the coordinate plane. Students use integers to solve real-world problems using the coordinate plane and numerical operations. Embedded Assessments 1: Number Line and Adding and Subtracting Integers, Hot and Cold Use the number line Add integers Subtract integers (5 Lessons) 2: Coordinate Plane and Multiplying and Dividing Integers, Scavenger Hunt Use the coordinate plane Multiply integers Divide integers (4 Lessons) Vocabulary Academic Vocabulary: elevation Math Terms: absolute value, integer, opposite, additive inverse, coordinate plane, origin, quadrants, ordered pair, reflection . Essential Questions How can integers be represented visually and how can operations with integers be represented with models? How are positive and negative numbers used in real-world situations? Texas Essential Knowledge Targeted Standards 2.A.i, 2.A.ii, 2.A.iii, 2.B.ii, 2.C.i, 2.C.ii, 2.C.iii, 2.C.iv, 2.C.v, 2.C.vi, 2.D.i, 2.D.ii, 3.C.i, 3.C.ii, 3.D.i, 3.D.ii, 3.D.iii, 3.D.iv, 11.A Prerequisite Skills Algebra/AP/College Readiness Providing opportunities to connect operations on real numbers to real-world contexts. Encouraging students to learn and use mathematics language and to communicate mathematics precisely Perform computations with numbers Create visual representations and models Order whole numbers Locate numbers and ordered pairs on number lines and the coordinate plane by justifying their solutions both verbally and in written form. Modeling problem solving in collaborative groups. Additional Assessment Opportunities Divisibility Every Lesson: Check Your Understanding and Lesson Practice Every Activity: Activity Practice Every Unit: Getting Ready and Online Unit Test Course 1 Curriculum Map – Texas Unit 3: Expressions and Equations (29 days) Overview The focus of this unit is expressions and equations. Students write, interpret and use expressions and equations. They understand the use of variables in expressions, equations, and inequalities and they solve one-step equations and inequalities using addition, subtraction, multiplication and division and graph solutions on number lines. Essential Questions Why are tables, graphs, and equations Embedded Assessments 1: Order of Operations and Expressions, The Cost of After-School Activities Read, write, and evaluate expressions Apply the order of operations Apply properties to generate equivalent expressions Use variables to represent numbers Solve real-world and mathematical problems by writing and solving equations (6 Lessons) 2: Expressions and Equations, The School Book Fair Solve real-world and mathematical problems by writing and solving equations and inequalities Graph an inequality Analyze the relationship between the dependent and independent variables (11 Lessons) Vocabulary Academic Vocabulary: compare, contrast Math Terms: numerical expression, variable, coefficient, algebraic expression, term, unit rate, equation, solution, inverse operations, inequality, rate of change, ordered pair, independent variable, dependent variable Prerequisite Skills useful for representing relationships? How can you use equations to solve real- Algebra/AP/College Readiness world problems? Encouraging students to model situations with algebraic expressions and equations. Texas Essential Knowledge Targeted Standards 4.A.i, 4.A.ii, 4.A.iii, 4.A.iv, 4.B.i, 4.B.ii, 4.B.iii, 4.B.iv, 4.B.v, 4.B.vi, 4.B.vii, 4.B.viii, 7.C.i, 7.C.ii, 7.C.iii, 7.D.i, 7.D.ii, 7.D.iii, 7.D.iv, 7.D.v, 7.B.i, 7.B.ii, 7.B.iii, 9.A.i, 9.A.ii, 10.B, 4.G, 7.A, 10.A.i, 10.A.ii, 10.A.iii, 10.A.iv, 9.C, 9.B.i, 9.B.ii, 6.A.i 6.A.ii, 6.A.iii, 6.A.iv, 6.B, 6.C.i, 6.C.ii, 6.C.iii, 6.C.iv Complete tables of values Solve equations Plot points on a coordinate plane Evaluate expressions Opposites and reciprocals Providing opportunities to write, solve, and graph linear equations and inequalities. Encouraging students to reason quantitatively and abstractly as they move from concrete examples to abstract ideas. Expecting students to discuss and justify interpretations and conclusions. Additional Assessment Opportunities Every Lesson: Check Your Understanding and Lesson Practice Every Activity: Activity Practice Every Unit: Getting Ready and Online Unit Test Course 1 Curriculum Map – Texas Unit 4: Ratios (22 days) Embedded Assessments Overview In this unit students study ratios and percents. They use manipulatives and tables to compare ratios and use ratios and unit rates to solve real-world problems. Students use models to understand percent, convert between fractions, decimals and percents, and apply their understanding to solve problems. Essential Questions Vocabulary 1: Ratios and Rates, A Summer Job Solve problems involving ratios and proportional relationships Write equivalent ratios (7 Lessons) 2: Understanding and Applying Percents, An Ice Cream Treat Find the percent of a quantity as a rate per 100 Represent ratios and percents with fractions and decimals Use equivalent percents, fractions, and decimals to show parts of the same whole Represent percents with concrete models, fractions, and decimals (6 Lessons) Academic Vocabulary: benchmark Math Terms: ratio, equivalent ratios, rate, dimensional analysis, conversion factor, unit rate, proportion, percent, average Why is it important to understand calculations with ratios, rates, and percents? Why are proportional relationships important in mathematics? Prerequisite Skills Algebra/AP/College Readiness Providing opportunities for conceptual situations where Texas Essential Knowledge Targeted Standards 4.B.i, 4.B.ii, 4.B.iii, 4.B.iv, 4.B.v, 4.B.vi, 4.B.vii, 4.B.viii, 4.C, 4.D, 4.E.i, 4.E.ii, 4.E.iii, 4.E.iv, 4.E.v, 4.E.vi, 4.F.i, 4.F.ii, 4.F.iii, 4.F.iv, 4.F.v, 4.F.vi, 4.F.vii, 4.F.viii, 4.G, 4.H, 5.A.i, 5.A.ii, 5.A.iii, 5.A.iv, 5.A.v, 5.A.vi, 5.A.vii, 5.A.viii, 5.A.ix, 5.A.x, 5.A.xi, 5.A.xii, 5.A.xiii, 5.A.xiv, 5.A.xv, 5.A.xvi, 5.B.i, 5.B.ii, 5.B.iii, 5.B.iv, 5.B.v, 5.B.vi, 5.C, 6.A.i, 6.A.ii, 6.A.iii, 6.A.iv, 6.B, 6.C.i, 6.C.ii, 6.C.iii, 6.C.iv students can apply prior knowledge. Encouraging students to use a variety of representations to Number lines Fractions and Decimals Convert Unit Measures Number Systems Solve Equations discover mathematical ideas and make connections. Asking students to write about mathematics using precise language when explaining their solutions. Presenting opportunities for students to look for repetition in calculations, generalize procedures, and discover shortcuts. Additional Assessment Opportunities Every Lesson: Check Your Understanding and Lesson Practice Every Activity: Activity Practice Every Unit: Getting Ready and Online Unit Test







