here - Ms. Anderson`s Room 280
advertisement
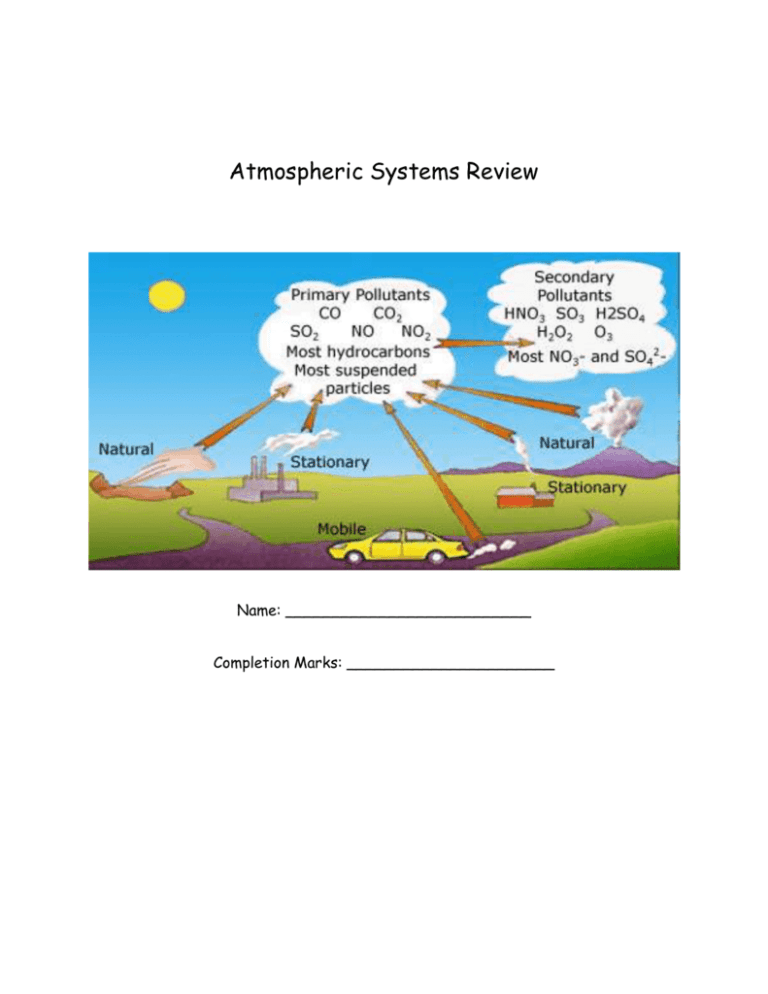
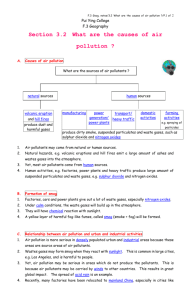
Atmospheric Systems Review Name: __________________________ Completion Marks: ______________________ Glossary: Contaminant Pollutant Sick Building Syndrome Anthropogenic Primary Air Pollutants Secondary Air Pollutants Air Quality Health Index 1. Complete the table below of the different primary air pollutants: Air Pollutant Description Sources Carbon monoxide - colourless and odourless gas formed when wood, gasoline, and other fuels are burned - burning fossil fuels for transportation and generating electricity - burning wood for heat and clearing land Nitrogen oxides - reddish/brown gas that readily reacts with other compounds - responsible for photochemical smog - solid particles or liquid droplets (collectively called aerosols) suspended in air - range in size from what can be seen with the eye to those requiring powerful microscopes - motor vehicle exhaust - burning fossil fuels and biomass - forest fires - colourless gas with a sharp odour - reacts with water vapour in the atmosphere to form sulfur-containing acids - wide range of very reactive, toxic compounds that vaporize readily and exist as gases in air - many undergo reactions in the presence of sunlight to form ground level ozone - burning sulfur-rich coal in power plants - burning biomass - industrial gases - volcanic activity - burning fossil fuels and wood - refineries and other industrial plants - burning tobacco - paints, glues, fabrics, building materials, copy machines/printers, personal care products Particulate matter Sulfur dioxide VOCs - burning plant material - agriculture - travel on roads - industrial processes - construction - mining - volcanoes - sea spray Effects of Human Health - reduces amount of oxygen that blood can carry to cells - high levels in urban areas can cause headaches, fatigue, and blurred vision - prolonged and/or high exposures is deadly - irritates eyes and lungs - increases chance of respiratory infections - causes chronic bronchitis - small particles can enter the nose and mouth and damage tissue of lungs and tubes leading to them - worsens asthma, bronchitis, and other respiratory conditions - some increase change of cancer - sulfur-containing acids can burn lung tissue if inhaled - inhalation symptoms include chest pain, sore throat, headache, nausea - irritate eyes, nose, and throat - can cause headaches, nausea, dizziness - higher concentrations can damage internal organs such as the lungs, liver, and brain - some increase chance of cancer 2. Explain why all pollutants are contaminants, but not all contaminants are pollutants. Because a contaminant is a substance in an environment that occurs in concentrations that are higher than what would be expected. And a pollutant, is a substance in an environment that is harmful or could become harmful to people or other living things. Example: you can have more compost in your soil, it would be considered a contaminant because of the increased amount, but NOT a pollutant because it is not harmful. 3. What is photochemical smog? Why is it called a secondary air pollutant? It forms when pollutants from the exhaust pipes of cars and trucks and the smokestacks of industrial plants react chemically in the presence of sunlight. Secondary air pollutants are the result of interactions between primary air pollutants and other primary air pollutants and other gases and particles that are naturally present in the atmosphere. 4. What is the Air Quality Health Index? Why is reporting it for a given region important for the people who live there? To help people understand and make decisions related to the health effects of air quality, Environment Canada, with the provinces and territories, has devised the Air Quality Health Index (AQHI). The AQHI is based on the health risks linked to common air pollutants, including ozone and particulate matter. The AQHI uses the scale below to indicate the air quality and its associated high risks. 5. Describe the roles that provincial and federal governments play in managing air quality. Federal: There is a federal environmental law (the Canadian Environmental Protection Act) that addresses national environmental standards. It commits governments to meet defined pollution reduction targets. Provincial: The Clean Air Act - Protects Saskatchewan's air quality by regulating emissions that originate in the province. 6. Describe how a catalytic converter helps to reduce emissions of air pollutants from motor vehicles. Catalytic converters help reduce emissions. These devices use materials called catalysts that convert potential pollutants into harmless substances before they enter the air. 7. Name and describe two devices that industry uses to help reduce the amount of particulate matter that is released into the air. The first is: industrial filters, which trap fine particles. The filters act like the bags found in vacuum cleaners, allowing air to pass but stopping particles. 2. The second is: electrostatic precipitators, which are more expensive, but are extremely effective! Particulates pick up an electrostatic charge as they rise in a smokestack. The charged particulates are attracted to a plate that carries an opposite charge. 8. How would an urban forest contribute to improving air quality? Plants help to improve air quality by removing dust and air pollution such as carbon dioxide from the air. They also reduce energy consumption, which can release air pollutants, by providing natural shade and windbreaks. 9. Complete the table below on indoor air pollutants. Indoor Air Pollutant Description of Pollutant Effects on Human Health Second-Hand Smoke Cigarettes VOCs Radon Synthetic household items, such as furniture, carpets, adhesive and cleaning products, etc. Uranium in the ground Asbestos Mineral used in insulation Lung cancer Moulds Damp, dark areas in buildings Found everywhere Allergic reactions, and respiratory damage Fever, cough, chills, etc. Bacteria Cause cancer, headaches, sore throat, nausea Headaches, dizziness, and eye and respiratory irritation. Lung cancer 10. It is recommended that people have carbon monoxide detectors, such as the one below, in their homes. Why do you think they are important to have? Carbon monoxide detectors are important to have because carbon monoxide is a clear, odourless, colourless gas that is very toxic to people. While it is undetectable by human senses, it can be deadly if inhaled in high amounts 11. The Blue Ridge Mountains in Georgia get their name from the blue-coloured gases given off by plants that grow there. In the Northwest Territories, the Smoking Hills are rich in rock made up of carbon and sulfur compounds that can spontaneously ignite, releasing the smoke that gives their name. a) What other natural sources of air pollution are there? Answers may include one of the following: volcanoes give off particulate matter and gases; lightning causes forest fires that produce particulate matter and gases; wind storms stir up dust and dirt into the air; plants can release large amounts of pollen into the air. b) Sound people be concerned about these natural sources as they are about anthropogenic sources? Give reasons to justify your opinion. Answers should clearly state an opinion about natural sources of air pollution that is supported by at least one statement. Sample answer: No, people should not be as concerned about natural sources of air pollution, because they are at much lower concentrations and are released less frequently than the products or processes that produce anthropogenic (humanmade) sources. or Yes, if people are highly sensitive to the type of pollution in the area, they should take precautions or move out of the area. 12. List three ways YOU can improve air quality.