Unit 3.2 (solution)
advertisement
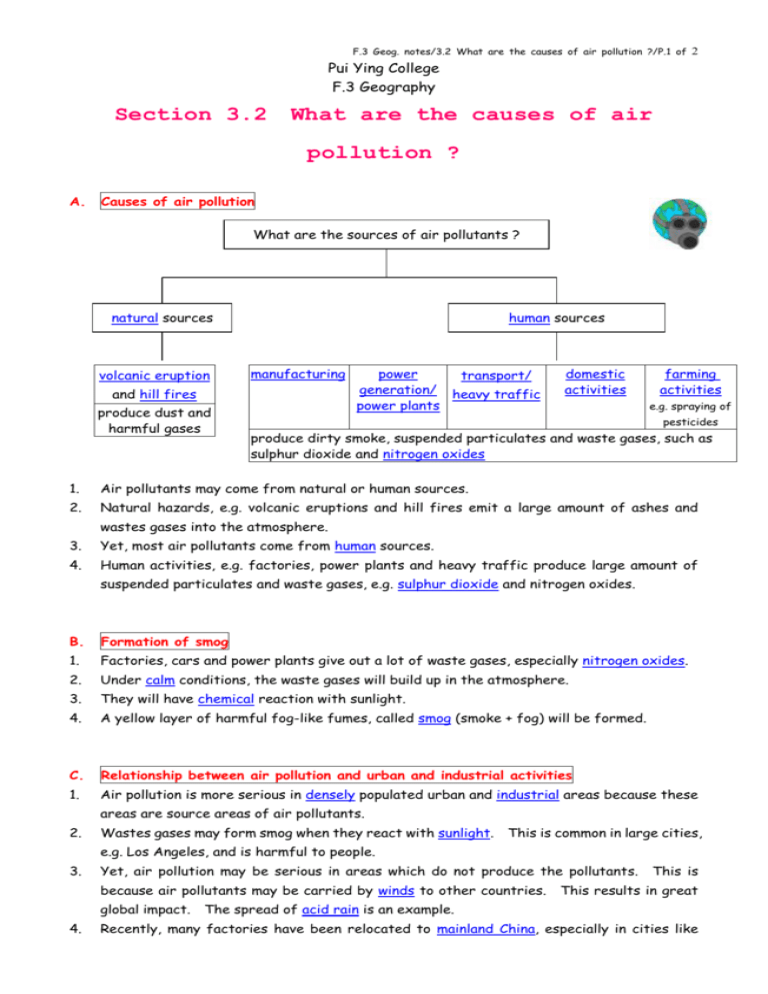
F.3 Geog. notes/3.2 What are the causes of air pollution ?/P.1 of 2 Pui Ying College F.3 Geography Section 3.2 What are the causes of air pollution ? A. Causes of air pollution What are the sources of air pollutants ? natural sources volcanic eruption human sources manufacturing and hill fires produce dust and harmful gases power transport/ generation/ heavy traffic power plants domestic activities farming activities e.g. spraying of pesticides produce dirty smoke, suspended particulates and waste gases, such as sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides 1. Air pollutants may come from natural or human sources. 2. Natural hazards, e.g. volcanic eruptions and hill fires emit a large amount of ashes and wastes gases into the atmosphere. 3. Yet, most air pollutants come from human sources. 4. Human activities, e.g. factories, power plants and heavy traffic produce large amount of suspended particulates and waste gases, e.g. sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides. B. Formation of smog 1. Factories, cars and power plants give out a lot of waste gases, especially nitrogen oxides. 2. Under calm conditions, the waste gases will build up in the atmosphere. 3. They will have chemical reaction with sunlight. 4. A yellow layer of harmful fog-like fumes, called smog (smoke + fog) will be formed. C. Relationship between air pollution and urban and industrial activities 1. Air pollution is more serious in densely populated urban and industrial areas because these areas are source areas of air pollutants. 2. Wastes gases may form smog when they react with sunlight. This is common in large cities, e.g. Los Angeles, and is harmful to people. 3. Yet, air pollution may be serious in areas which do not produce the pollutants. This is because air pollutants may be carried by winds to other countries. This results in great global impact. The spread of acid rain is an example. 4. Recently, many factories have been relocated to mainland China, especially in cities like F.3 Geog. notes/3.2 What are the causes of air pollution ?/P.2 of 2 Shenzhen and Guangzhou. Pollutants from these regions are blown to Hong Kong and cause smog on windless days. D. Comparison of air quality in inner city and new towns 1. In inner city areas, streets are narrow and buildings are tall. So, pollutants cannot be easily blown away by wind. 2. In new towns in the suburbs, land uses are well-planned. Factories are often carefully sited. They may be separated from residential land uses by green belts or open space. Besides, streets are wider and population density is lower. So, pollutants can be blown away more easily. Vocabulary 1. natural sources 6. transport 11. sulphur dioxide 2. volcanic eruption 7. domestic activities 12. nitrogen oxides 3. human sources 8. farming activities 13. calm 4. manufacturing 9. spraying of pesticides 14. chemical reaction with sunlight 5. power generation 10. suspended particulates 15. densely populated urban areas











