Final Exam Review 2b Acids Bases Thermo Spring 2012
advertisement

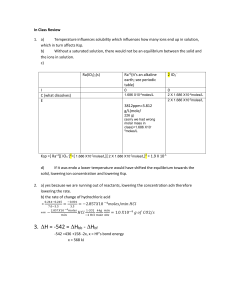
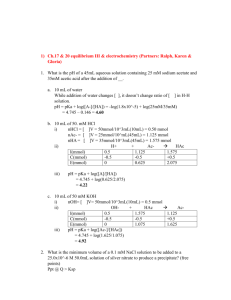
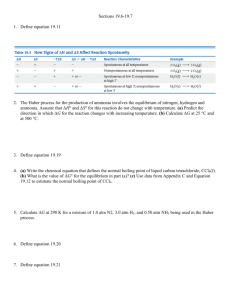
Dr. Steward’s CHM152 Exam Review 2b 1. Determine the pH and pOH of the following 4 solutions: a) A 4.5 x 10-3 M HBr solution. b) A 3.67 x 10-5 M KOH solution. c) A solution made by diluting 25 mL of 6.0 M HCl until the final volume of the solution is 1.75 L. d) 5.0 L of an aqueous solution that contains 1.0 grams of HBr and 1.0 grams of nitric acid. 2. Identify the following as strong or weak acids, strong or weak bases, neutral salts, basic salts or acidic salts. LiCl ________________, NH3__________________, NH4ClO4_____________________, HClO4______________, Ba(OH)2 _____________, Ba(CH3COO)2_________________, HF_________________, NaF_________________, KOH________________________, AlBr3_______________, K2CO3________________, Ca(NO3)2_____________________. 3. Write a balanced chemical equation to show that sodium cyanide (NaCN) is basic in water solution. 4. What is the Kb expression and value for the equilibrium above? 5. Which one of the following salts, when dissolved in water, produces the solution with the highest pH? a. KI b. KBr c. KF d. KCl 6. If an equal number of moles of HCN and KOH are added to water, what is the resulting solution: acidic, basic, or neutral? Explain. 7. Calculate the pH of a 0.100 M NaCH3COO solution. Ka for acetic acid is 1.8 x 10-5. 8. Calculate the pH of a 0.100 M CH3NH3Cl solution. Kb for methylamine, CH3NH2, is 3.7 x 10-4. 9. A 50.0 mL sample of 0.500 M HC2H3O2 acid is titrated with 0.150 M NaOH. Ka = 1.8x10-5 for HC2H3O2. Calculate the pH of the solution after the following volumes of NaOH have been added: a) 0 mL; b) 166.7 mL; c) 180.0 mL. 10. What is the concentration of a saturated silver (I) acetate solution? Ksp(AgC2H3O2) = 1.94 x 10-3. 11. What is the concentration of a saturated lead chloride solution? Ksp(PbCl2) = 1.17 x 10-5. 12. Silver phosphate, Ag3PO4, is an insoluble salt that has a Ksp = 1.3 x 10-20. a) Calculate the molar solubility of Ag3PO4 in pure water. b) Calculate the molar solubility of Ag3PO4 in a solution containing 0.020 M Na3PO4 (a soluble salt). 17. a .Calculate the standard free energy change, ΔG, for the following at 25 C: MgO(s) + C(graphite) Mg(s) + CO(g) ΔH = 491.18 kJ ΔS = 197.67 J/K b. Is this reaction spontaneous at 25 C? If not, at what temperature can we make this reaction spontaneous? 18. a) Calculate G for the following reaction. b) What is the value of the equilibrium constant at 298 K? c) Is this reaction spontaneous at 298 K? 3C2H2(g) C6H6(g) G f (C 2 H 2 ) = 209.2 kJ kJ ; G f (C6 H 6 ) = 129.7 mol mol 19. For the unbalanced reaction SO2(g) + O2(g) → SO3(g) calculate ΔG at 25.0ºC when the reactants and product are at the following partial pressures: 10.0 atm SO2 , 10.0 atm O2 , and 1.00 atm SO3. 20. In each of the following equations, indicate the element that has been oxidized and the one that has been reduced. You should also label the oxidation state of each before and after the process: 1. 2 Na + FeCl2 2 NaCl + Fe 2. 2 C2H2 + 5 O2 4 CO2 + 2 H2O 3. 2 PbS + 3 O2 2 SO2 + 2 PbO 21. a) Write the overall balanced equation for the cell and calculate the cell emf under standard conditions. 3(Zn2+ + 2e- Zn) E red = -0.76 V 2(Al Al3+ + 3e-) E ox = +1.66 V b) Calculate G° at 298 K. c) What is the value of the equilibrium constant, K, for this reaction at 298 K? 22. Which combination below will undergo a spontaneous reaction? Half Reaction Table Br2(l) + 2e- 2Br–(aq) Cu2+(aq) + 2e- Cu(s) Ni2+(aq) + 2e- Ni(s) Al3+(aq) + 3e- Al(s) a. b. c. d. e. E red +1.06 V +0.34 V −0.28 V −1.66 V Ni 2+(aq) with Br–(aq) Cu(s) with Al3+(aq) Ni (s) with Br–(aq) Br–(aq) with Cu2+(aq) Br2(l) with Ni(s) 23. A voltaic cell is constructed that used the following reaction and operates at 298 K: 2Al(s) + 3Mn2+(aq) 2Al3+(aq) + 3Mn(s) a. What is the EMF of this cell under standard conditions? (Use Appendix D for Eored values.) b. What is the EMF of this cell when [Mn2+] = 0.10 M and [Al3+] = 1.5 M?