Properties of Common Substances Lab new version
advertisement
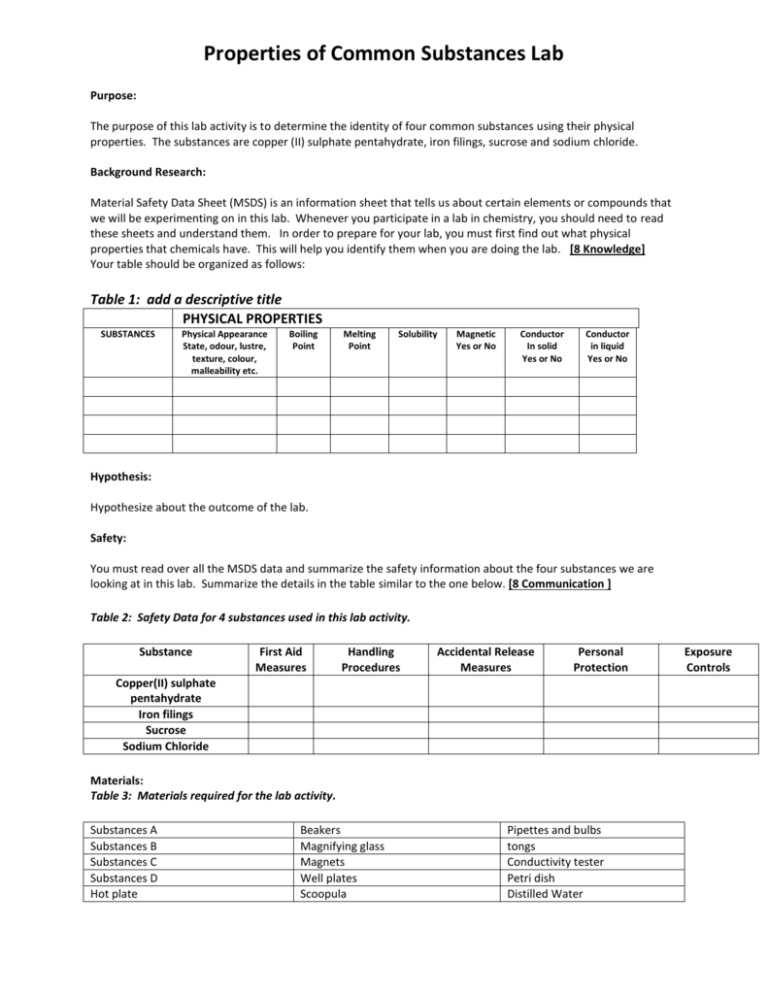
Properties of Common Substances Lab Purpose: The purpose of this lab activity is to determine the identity of four common substances using their physical properties. The substances are copper (II) sulphate pentahydrate, iron filings, sucrose and sodium chloride. Background Research: Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) is an information sheet that tells us about certain elements or compounds that we will be experimenting on in this lab. Whenever you participate in a lab in chemistry, you should need to read these sheets and understand them. In order to prepare for your lab, you must first find out what physical properties that chemicals have. This will help you identify them when you are doing the lab. [8 Knowledge] Your table should be organized as follows: Table 1: add a descriptive title PHYSICAL PROPERTIES SUBSTANCES Physical Appearance State, odour, lustre, texture, colour, malleability etc. Boiling Point Melting Point Solubility Magnetic Yes or No Conductor In solid Yes or No Conductor in liquid Yes or No Hypothesis: Hypothesize about the outcome of the lab. Safety: You must read over all the MSDS data and summarize the safety information about the four substances we are looking at in this lab. Summarize the details in the table similar to the one below. [8 Communication ] Table 2: Safety Data for 4 substances used in this lab activity. Substance First Aid Measures Handling Procedures Accidental Release Measures Personal Protection Copper(II) sulphate pentahydrate Iron filings Sucrose Sodium Chloride Materials: Table 3: Materials required for the lab activity. Substances A Substances B Substances C Substances D Hot plate Beakers Magnifying glass Magnets Well plates Scoopula Pipettes and bulbs tongs Conductivity tester Petri dish Distilled Water Exposure Controls Procedure: 1. 2. Collect a small scoop of the sample of each of the chemicals (A,B,C and D) used for this experiment. Be sure to keep them separate and labelled so that you know which substance is which. Using the observation table as a guide, take relevant observations and complete the observation table. a. Physical Appearance: Look at the sample and record what you see. b. Magnetic: Place a magnet beneath sample. If sample moves then it is magnetic. c. Melting Point: Place sample on hot plate. You will not have an exact temperature for comparison but the relative temperature should help you determine the identity. d. Conductor. Use conducting device. A red light indicates a positive result. e. Soluble. Place small amount of sample into water. Gently agitate (stir). If sample dissolves it is soluble. f. Conductor (pt. 2). If sample was not a conductor as a solid and gave a positive soluble test, retest conductor as a solution. Observations: Create an observation table (titled Table 4: ____ **hint: it should look like table 1) in the observations section of your lab report. Use the procedure to decide what headings should be used. [8 Thinking/Inquiry] Analysis: Complete the following questions in your lab report. 1. Determine the identity of each of the substances A – D and provide an explanation for each. Hint: you should discuss the physical properties that led you to determine the identity. To confirm an identity at least 2 physical properties should be used. [12 Thinking/Inquiry] 2. Why is it not safe to smell the solids? [2 Application] 3. If you were colour blind how could you determine the difference between copper (II) sulfate pentahydrate and sucrose? [2 Application] 4. Why is it important to read over MSDS before starting a lab? [2 Application] Conclusion: Evaluate your tests to determine whether they were useful for distinguishing all the substances from each other, according to their properties. What improvements could you make? Restate your hypothesis and summarize your findings in a couple of sentences. [2 Knowledge] EVALUATION Communication (8 marks for safety and 7 marks for overall organization) /15 Application Knowledge /6 Thinking/Inquiry /10 /20






