Unit 7 HW Packet - Garnet Valley School District
advertisement

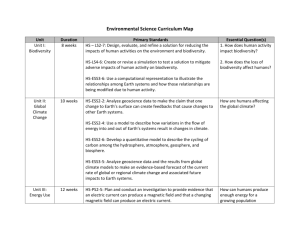
Name: ______________________ Pd. ___ Unit 7 Biodiversity HWP Chapter 16, part 1 (pgs 325-337) 1. Define biological diversity. 2. Distinguish between species richness, genetic diversity and ecosystem diversity. 3. How does biodiversity provide ecosystem services to us? 4. Why is a broad genetic base necessary for a species’ health? 5. What does biodiversity have to do w/ medicines? 6. What does biodiversity have to do w/ ethics? 7. What’s the difference btwn background extinction and mass extinction? 8. What is the difference btwn an endangered species and a threatened species? 9. List 4 characteristics common to many endangered species: a. b. c. d. 10. What is an endemic species? 11. Why is habitat fragmentation a problem for some species? 12. What is a biodiversity hotspot? 13. List 4 main causes of loss of biodiversity: a. b. c. d. 14. How do invasive species endanger native species? 1 Name: ______________________ Pd. ___ Chapter 16, part 2 (pgs 337-345) 1. What is conservation biology? 2. What is the difference between in situ conservation and ex situ conservation? 3. How do habitat corridors protect biodiversity? 4. What is restoration ecology? 5. What role does a zoo have in biodiversity preservation? 6. What are the issues w/ captive-breeding programs? 7. What is a seed bank? 8. Briefly describe the Endangered Species Act. 9. How do Habitat Conservation Plans (HCPs) work? 10. Explain the controversy of CITES. 11. What is wildlife management? 12. Distinguish between wildlife management and conservation biology. 13. Describe common ways to manage aquatic species such as: a. Trout? b. Whales? 2 Name: ______________________ Pd. ___ Chapter 22, part 1 (pgs 462-470) 1. What is a pest? 2. Distinguish btwn narrow-spectrum pesticides and broad-spectrum pesticides. 3. Define botanicals. 4. Distinguish btwn first-generation pesticides and second-generation pesticides. 5. List the 3 major classes of insecticides: a. b. c. 6. What is a broad-leaf herbicide? 7. How can pesticides help with disease control? 8. How can pesticides help with crop protection? 9. Why are monocultures more susceptible to pest problems? 10. What is genetic resistance? 11. What is the pesticide treadmill? 12. How does resistance management work? 13. How can a pesticide create a new pest? 14. What are some of the long-term effects of pesticides on human health? 15. Why are endocrine –disrupting pesticides of particular concern? 3 Name: ______________________ Pd. ___ Chapter 22, part 2 (pgs 470-478) 1. How does intercrop mixtures and strip cutting help control pests? 2. What is meant by biological controls? 3. How can pheromones control pests? 4. What is the sterile male technique? 5. Describe how genetic controls can be used in IPM. 6. What is Integrated Pest Management (IPM)? 7. Why is IPM considered to be a systems approach? 8. List the 2 fundamentals of IPM: a. b. 9. What is the goal of the Food, Drug and Cosmetics Act (FDCA)? 10. What did the Delany clause state? 11. What are the 2 inconsistencies in the Delany Clause? 12. What is the goal of the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA)? 13. What is the goal of the Food Quality Protection Act? 14. What is a persistent organic pollutant? 15. Describe the purpose of the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pesticides. 4