File - Mr. LaFranca`s Earth Science Class
advertisement

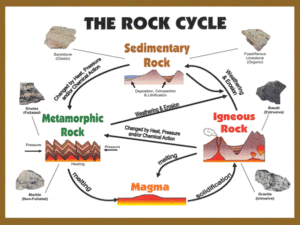
HW #8 Name: ___________________________________________________ Period: ________ COOL ES FACTS OF THE WEEK! 1. The first geologist on the moon was Harrison Schmitt who was part of the Apollo 17 mission? From the rock samples he collected, scientists have been able to learn many things about the moon. 2. Geodes are dull balls of igneous or sedimentary rock on the outside, but contain beautiful crystals on the inside. 3. The Taj Mahal built between 1632 and 1654 in India is made entirely out of marble. IMPORTANT REMINDERS: / TOPICS FOR THE WEEK: Time Zones THEUse Rthe OCK CYCLE, ROCK NAMES words in the box to fill in the blanks. underground rocks Cemented weathering texture crystals Magma solidify extrusive foliation heat pressure Sedimentary lava Metamorphic compacted deposited vesicular Igneous erosion _________(1) come in three major types: Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic. Rock can also be found in some “in between” states . _________ (2) is rock that is melted into liquid form due to high temperatures. When it comes out of a volcano it is called ________(4). _____________ (4) rocks are always formed from sediments. ____________ (1) is a process in which rocks are broken into sediments. _________ (5) is a process in which these sediments are transported by water, wind or gravity to a new location. As sediments become ____________ (5) or dropped off in the ocean, they can become buried and __________ (4) together due to pressure. Over time they become ___________ (1) together like cement on a sidewalk to become a solid rock. There are two types of sedimentary rocks. ____________ (1) rocks contain sediment and chemical are formed from evaporated sea water. __________ (4) rocks are always formed by heat and__________ (3). As we go down into the Earth’s surface, _________ (3) and pressure increases. This pressure and heat can cause a rock to change into a new form called a metamorphic rock. These rocks are usually found deep____________ (1). Some metamorphic rocks have mineral alignment or ________ (3). ___________ (5) are always formed from magma or lava after it cools down. When rock becomes is exposed to a very high temperature it will melt into magma. When magma cools down it will ________ (3) into an igneous rock. Intrusive igneous rock have intergrown __________ (2) that formed by slow cooling underground. ____________ (3) igneous rocks are volcanic and are usually glassy or fine grained because they cooled quickly. Some volcanic rock may be ____________ (4), having tiny air bubbles. The _____________ (2) or the way the crystals or grains look, can help us identify a rock. Practice Questions 1. Igneous Rocks Name the two processes that form an Igneous Rock. Identify two locations that Igneous Rocks form How does cooling rate affect mineral crystal size? Which two textures are intrusive? Extrusive? Which composition describes rocks light in color and low density? Which composition describes rocks dark in color and high density? Describe 2 key identifying features of Igneous rocks Which Igneous Rock? o Slow cooling, coarse texture, contains quartz __________________________ o Fast cooling, glassy texture, vesicular, contains pyroxene ____________________ o Intrusive, very coarse, light color _____________________________ o Mono-minerallic, Mafic _______________________________ o Volcanic, Fine, non-vesicular ________________________ 2. Sedimentary Rocks Define Clastic sedimentary rocks Name the two processes that form clastic sedimentary rocks. In what type of environment are sedimentary rocks formed? Identify 3 features of Sedimentary rocks. Describe the process that forms a crystalline sedimentary rock. List two organically formed sedimentary rocks. Grain size Which Sedimentary Rock? o 0.1 cm _______________________ o 0.0009 cm _________________________ o 0.0001 cm _________________________ 3. Metamorphic Rocks How are metamorphic rocks formed? What is the difference between Regional and Contact Metamorphism? Name two identifying features of Metamorphic rocks Name two key identifying minerals in Metamorphic rocks Name the Metamorphic Rock from the Parent Rock it formed from: PARENT ROCK METAMORPHIC ROCK o Shale ___________________________ o Quartz Sandstone ___________________________ o Bituminous Coal ___________________________ o Limestone ___________________________ o Conglomerate ___________________________ Regents Questions