Grade 3 Benchmark Levels
advertisement

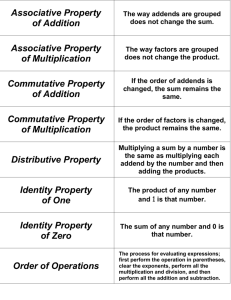
3rd Grade Benchmark Levels Operations and Algebraic Thinking November January March June ℗ 3.OA.3 ℗ 3.OA.3 ℗ 3.OA.3 ℗ 3.OA.3 Standard 3.OA.3 4: Using a Level 3 Method, accurately solves word problems using multiplication and division within 100 using a symbol or letter for the unknown in all positions of the equation 3: Using a Level 1 Method, solves word problems using multiplication and division within 100 and writes a matching equation with minimal errors. 4: Using a Level 3 Method, accurately solves word problems using multiplication and division within 100 using a symbol or letter for the unknown in all positions of the equation 3: Using Level 2 and minimal Level 1 Methods, solves word problems using multiplication and division within 100 and writes a matching equation with minimal errors and can identify the unknown in at least half of the 3rd grade problem types. 4: Using a Level 3 Method, accurately solves word problems using multiplication and division within 100 using a symbol or letter for the unknown in all positions of the equation 3: Using Level 2 Methods, solves word problems using multiplication and division within 100 using a symbol for the unknown in most positions of the equation with minimal errors. 4: Using a Level 3 Method, accurately solves word problems using multiplication and division within 100 using a symbol or letter for the unknown in all positions of the equation 3: Using Level 3 and minimal Level 2 Methods, solves word problems using multiplication and division within 100 using a symbol for the unknown in all positions of the equation with minimal errors. 2: Using Level 2 and minimal Level 1 Methods, solves word problems using multiplication and division within 100 and writes a matching equation with minimal errors and can identify the unknown in some positions of the equation with errors. 2: Using Level 3 and Level 2 Methods, solves word problems using multiplication and division within 100 using a symbol for the unknown in some positions of the equation with minimal errors. 1: Cannot do above 1: Cannot do above Use multiplication and division within 100 to solve word problems in situations involving equal groups, arrays, and measurement quantities, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem. *refer to 3.OA.7 for computation benchmarks 2: Using Level 1 Methods, solves word problems using multiplication and division within 100 and writes a matching equation with support. 2: Using Level 2 and Level 1 Methods, solves word problems using multiplication and division within 100 and writes a matching equation with support. 1: Cannot do above 1: Cannot do above FWPS Draft Benchmark Levels by FWPS is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. 3rd Grade Benchmark Levels Operations and Algebraic Thinking November January March June ℗ 3.OA.5 ℗ 3.OA.5 ℗ 3.OA.5 ℗ 3.OA.5 Standard: 3.OA.5 4: Uses relevant properties (commutative, associative and distributive) to solve problems involving multiplication and division. 4: Uses relevant properties (commutative, associative and distributive) to solve problems involving multiplication and division. 4: Uses relevant properties (commutative, associative and distributive) to solve problems involving multiplication and division. 4: Uses relevant properties (commutative, associative and distributive) to solve problems involving multiplication and division. 3: Uses commutative property with multiplication and begins to use the distributive property with multiplication. 3: Uses commutative and distributive property with multiplication and division and begins to use the associative property with multiplication. 3: Uses properties (commutative, associative and distributive) to solve problems involving multiplication and division with minimal errors. 2: Uses commutative property with multiplication and begins to use the distributive property of multiplication with support. 2: Uses commutative and distributive property with multiplication and division and begins to use the associative property of multiplication with support. Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide.2 Examples: If 6 × 4 = 24 is known, then 4 × 6 = 24 is also known. (Commutative property of multiplication.) 3 × 5 × 2 can be found by 3 × 5 = 15, then 15 × 2 = 30, or by 5 × 2 = 10, then 3 × 10 = 30. (Associative property of multiplication.) Knowing that 8 × 5 = 40 and 8 × 2 = 16, one can find 8 × 7 as 8 × (5 + 2) = (8 × 5) + (8 × 2) = 40 + 16 = 56. (Distributive property.) 3: Uses commutative property with addition and subtraction and begins to relate it to multiplication. 2: Uses commutative property with addition and subtraction and begins to relate it to multiplication with support. 2: Uses at least two properties (commutative, associative and distributive) to solve problems involving multiplication and division or uses all with significant errors. 1: Cannot do above 1: Cannot do above 1: Cannot do above 1: Cannot do above FWPS Draft Benchmark Levels by FWPS is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. 3rd Grade Benchmark Levels Operations and Algebraic Thinking November January March June ℗3.OA.7 ℗3.OA.7 ℗3.OA.7 ℗3.OA.7 Standard 3.OA.7 4: a) Recall multiplication facts 0-10 within 5 seconds and b) Recall corresponding division facts within 5 seconds. 4: a) Recall multiplication facts 0-10 within 5 seconds and b) Recall corresponding division facts within 5 seconds. 4: a) Recall multiplication facts 0-10 within 5 seconds and b) Recall corresponding division facts within 5 seconds. 3: a) Use a relevant (Level 3) method to recall most multiplication facts (2,5,10) within 5 seconds and b) Use a relevant (Level 3) method to recall most corresponding division facts within 5 seconds. 3: a) Use a relevant (Level 3) method to recall most multiplication facts (0-5 &10) within 5 seconds and b) Use a relevant (Level 3) method to recall most corresponding division facts within 5 seconds. 3: a) Use a relevant (Level 3) method to recall most multiplication facts (0-6 & 9,10) within 5 seconds and b) Use a relevant (Level 3) method to recall most corresponding division facts within 5 seconds. Fluently multiply and divide within 100, using strategies such as the relationship between multiplication and division 2: a) Use a relevant (Level 2 or 3) method to recall some multiplication facts (2,10) within 5 seconds and b) Use a relevant (Level 2 or 3) method to recall some corresponding division facts within 5 seconds 2: a) Use a relevant (Level 2 or 3) method to recall some multiplication facts (2,3,4,5,10) within 5 seconds and b) Use a relevant (Level 2 or 3) method to recall some corresponding division facts within 5 seconds 4: a) Recall multiplication facts 0-10 within 5 seconds and b) Recall corresponding division facts within 5 seconds. 3: a) Use a relevant (Level 3) method to recall most multiplication facts 0-10 within 5 seconds and b) Use a relevant (Level 3) method to recall most corresponding division facts within 5 seconds. 2: a) Use a relevant (Level 2 or 2: a) Use a relevant (Level 2 3) method to recall some or 3) method to recall some multiplication facts 0-10 within multiplication facts (0-5 & 10) 5 seconds and within 5 seconds and b) Use a relevant (Level 2 or 3) b) Use a relevant (Level 2 or method to recall some 3) method to recall some corresponding division facts corresponding division facts within 5 seconds. within 5 seconds 1: Cannot do above 1: Cannot do above 1: Cannot do above 1: Cannot do above FWPS Draft Benchmark Levels by FWPS is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. 3rd Grade Benchmark Levels Operations and Algebraic Thinking November January March June ℗3.OA.8 ℗3.OA.8 ℗3.OA.8 ℗3.OA.8 Standard 3.OA.8 4: a) Accurately solves two step word problems using any of the four operations. b) Writes an accurate equation using letters to represent the unknown. c)Provides an accurate explanation using drawings, numbers and words. 3: a) Solves two step word problems using addition and subtraction (with minimal computation errors) b) Writes an accurate equation using a symbol to represent the unknown. c) Provides an accurate explanation using drawings. 4: a) Accurately solves two step word problems using any of the four operations. b) Writes an accurate equation using letters to represent the unknown. c)Provides an accurate explanation using drawings, numbers and words. 3: a) Solves two step word problems using addition, subtraction and multiplication (with minimal computation errors) b) Writes an accurate equation using a symbol to represent the unknown. c)Provides an accurate explanation using drawings. Solve two-step word problems using the four operations. Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies including rounding 2: a) Attempts two step word problems using addition and subtraction (with minimal computation errors or 2: a) Attempts two step word problems using addition, subtraction and multiplication (with minimal computation errors or skipping one of 4: a) Accurately solves two step word problems using any of the four operations. b) Writes an accurate equation using letters to represent the unknown. c)Provides an accurate explanation using drawings, numbers and words. 4: a) Accurately solves two step word problems using any of the four operations. b) Writes an accurate equation using letters to represent the unknown. c)Provides an accurate explanation using drawings, numbers and words. 3: a) Solves two step word problems using addition, subtraction and multiplication (with minimal computation errors) b) Writes an accurate equation using a letter to represent the unknown. c) Provides an accurate explanation using drawings and words. 3: a) Solves two step word problems using any of the four operations. (with minimal computation errors) b) Writes an accurate equation using letters to represent the unknown. c)Provides an accurate explanation using drawings, numbers or words. 2: a) Attempts two step word problems using addition, subtraction and multiplication (with minimal computation errors or skipping one of the steps) b) Attempts an accurate 2: a) Attempts two step word problems using any of the four operations (with minimal computation errors or skipping one of the steps) b) Attempts an accurate equation but may not use a letter to represent the FWPS Draft Benchmark Levels by FWPS is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. skipping one of the steps) b) Attempts an accurate equation but may not use a symbol to represent the unknown. c)Attempts an accurate explanation using drawings (may be confusing) the steps) b) Attempts an accurate equation but may not use a symbol to represent the unknown. c)Attempts an accurate explanation using drawings (may be confusing) equation but may not use a letter to represent the unknown. c)Attempts an accurate explanation using drawings and words. (may be confusing) unknown. c)Attempts an accurate explanation using drawings, numbers or words. (may be confusing) 1: Cannot do above. 1: Cannot do above 1: Cannot do above Operations and Algebraic Thinking Standard: 3.OA.5 Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide.2 Examples: If 6 × 4 = 24 is known, then 4 × 6 = 24 is also known. (Commutative property of multiplication.) 3 × 5 × 2 can be found by 3 × 5 = 15, then 15 × 2 = 30, or by 5 × 2 = 10, then 3 × 10 = 30. (Associative property of multiplication.) Knowing that 8 × 5 = 40 and 8 × 2 = 16, one can find 8 × 7 as 8 × (5 + 2) = (8 × 5) + (8 × 2) = 40 + 16 = 56. (Distributive property.) 1: Cannot do above ℗ 3.OA.5 4: Uses relevant properties (commutative, associative and distributive) to solve problems involving multiplication and division. 3: Uses commutative property with addition and subtraction and begins to relate it to multiplication. 2: Uses commutative property with addition and subtraction and begins to relate it to multiplication with support. ℗ 3.OA.5 ℗ 3.OA.5 ℗ 3.OA.5 4: Uses relevant properties (commutative, associative and distributive) to solve problems involving multiplication and division. 4: Uses relevant properties (commutative, associative and distributive) to solve problems involving multiplication and division. 4: Uses relevant properties (commutative, associative and distributive) to solve problems involving multiplication and division. 3: Uses commutative property with multiplication and begins to use the distributive property with multiplication. 3: Uses commutative and distributive property with multiplication and division and begins to use the associative property with multiplication. 3: Uses properties (commutative, associative and distributive) to solve problems involving multiplication and division with minimal errors. 2: Uses commutative property with multiplication and begins to use the distributive property of multiplication with support. 2: Uses commutative and distributive property with multiplication and division and begins to use the associative property of multiplication with support. 1: Cannot do above 1: Cannot do above 2: Uses at least two properties (commutative, associative and distributive) to solve problems involving multiplication and division or uses all with significant errors. 1: Cannot do above 1: Cannot do above FWPS Draft Benchmark Levels by FWPS is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. 3rd Grade Benchmark Levels Operations and Algebraic Thinking November January March June ℗ 3.OA.9 ℗ 3.OA.9 ℗ 3.OA.9 ℗ 3.OA.9 Standard 3.OA.9 4: Explains patterns when multiplying and dividing using facts 0-10 and references the properties. 4: Explains patterns when multiplying and dividing using facts 0-10 and references the properties. 4: Explains patterns when multiplying and dividing using facts 0-10 and references the properties. 3: Explains patterns when multiplying and dividing using facts of 2, 5 and 10. 3: Explains patterns when multiplying and dividing using facts of 0-5 and 10. 3: Explains patterns when 3: Explains patterns when multiplying and dividing using multiplying and dividing using facts of 0-6 and 9 and 10. facts 0-10. 2: Explains patterns when multiplying and dividing using facts of 2 and 10 with prompting. 2: Explains patterns when multiplying and dividing using facts of 2, 5 and 10 with prompting. 2: Explains patterns when multiplying and dividing using facts of 0-5 and 10 with prompting. 2: Explains patterns when multiplying and dividing using facts of 0-6 and 9 and 10 with prompting. 1: Cannot do above 3.NBT.2 1: Cannot do above 3.NBT.2 1: Cannot do above 3.NBT.2 1: Cannot do above 3.NBT.2 4: Uses multiple Level 3 strategies efficiently and flexibly to add and subtract within 1,000 3: Uses Level 3 strategies efficiently to add within 1,000 with minimal errors 2: Uses Level 1 or 2 strategies to add within 1,000 with errors 4: Uses multiple Level 3 strategies efficiently and flexibly to add and subtract within 1,000 3: Uses Level 3 strategies efficiently to add and subtract within 1,000 only regrouping once with minimal errors 2: Uses Level 2 strategies to 4: Uses multiple Level 3 strategies efficiently and flexibly to add and subtract within 1,000 3: Uses Level 3 strategies efficiently to add and subtract within 1,000 with minimal errors 2: Uses some Level 3 and some Level 2 strategies efficiently to Identify arithmetic patterns (including patterns in the addition table or multiplication table), and explain them using properties of operations. For example, observe that 4 times a number is always even, and explain why 4 times a number can be decomposed into two equal addends. Operations and Algebraic Thinking 4: Uses Level 3 Methods efficiently and flexibly to Fluently add and subtract add and subtract within within 1000 using strategies 1,000. and algorithms based on 3: Uses Level 2 strategies place value, properties of efficiently to add and operations, and/or the relationship between addition subtract within 1,000 with and subtraction. minimal errors 2: Uses Level 1 strategies to add and subtract within Standard 3.NBT.2 4: Explains patterns when multiplying and dividing using facts 0-10 and references the properties. FWPS Draft Benchmark Levels by FWPS is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. 1,000 with errors 1: Cannot do above 1: Cannot do above add and subtract within 1,000 only grouping once with errors 1: Cannot do above add and subtract within 1,000 with errors 1: Cannot do above FWPS Draft Benchmark Levels by FWPS is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.