1ST 9 WEEKS TEST 2013-2014 Multiple Choice Identify the choice
advertisement

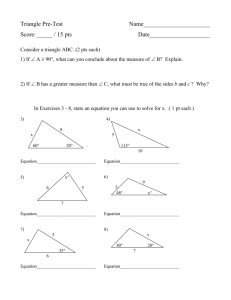
1ST 9 WEEKS TEST 2013-2014 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Observations that are descriptions or statements of information are called: a. numerical data c. qualitative data b. quantitative data d. descriptive data 2. What does infer mean? a. make observations without looking b. to test a prediction in an experiment c. draw a conclusion from previous or unspoken evidence d. make an educated guess 3. Which of the following is not an example of a scientific hypothesis? a. Earthquakes happen because of stresses along continental plates. b. Some animals can detect ultrasound frequencies caused by earthquakes. c. Paintings are prettier than sculptures. d. Lava takes different forms depending on how it cools. 4. Which of the following increases the reliability of a scientific explanation? a. vague statements c. repeatable data b. notes taken after the investigation. d. several likely explanations. 5. Observations that involve measurements and numbers are called: a. numerical data c. qualitative data b. quantitative data d. descriptive data 6. Trina wanted to find out which of her bouncy balls can bounce the highest. She dropped the first ball onto the cement sidewalk. She the dropped the second ball from the same height onto the grass. She recorded how high each ball bounded. How could her experiment be improved? a. Measure the time it takes for each ball to reach its maximum height. b. Bounce both balls on the same surface. c. Drop the second ball from a higher height. d. Bounce the ball on the grass two times. 7. Which of the following statements is a quantitative observation? a. There’s an empty aquarium tank in the classroom b. The tank used to contain live fish c. The tank is 50 cm long, 30 cm wide, and 18 cm deep d. The tank is waterproof 8. Suppose you are planning an experiment to determine which disinfectant is best for killing bacteria often found in kitchens. Which of the following would be the most logical responding variable for your experiment? a. Amount of detergent c. Type of detergent b. Number of bacteria that survive after d. Source of bacteria using the detergent. 9. When scientists study how well new medicines work, one group of patients receive the medicine, while a second group does not. Why? a. By not giving the medicine to one group of patients, scientists can see the effects of that medicine on the other group b. The scientists did the experiment wrong because both groups should have received the medicine for the investigation to be accurate c. The group that didn’t receive the medicine couldn’t afford to buy the medicine d. None of the above. 10. Which of the following statements is a quantitative observation you can make about the animals shown in the diagram? a. Both animals are invertebrates that live c. Animal B has a body with three main on land sections, two antennae on its head, and three pairs of legs b. Animal A has a narrow body with a d. Both animals have similar appearance, pattern on its back and extremely long but animal A seems to be bigger than legs. animal B. 11. A lab group is choosing a scientific question to research on the internet. The group chooses to research the question: “What kinds of sounds make the best music?” Which of the following statements most correctly describes the group’s question? a. The question is scientific because the study of sound is a scientific topic b. The question is scientific because it can be answered by gathering evidence about the natural world c. The question is not scientific because it is too broad d. The question is not scientific because it involves personal opinions. 12. The diagram shows a sketch of fossils, or preserved remains, found at different rock layers at a particular location. Which of the following statements is a qualitative observation based on this diagram? a. The five types of fossils are classified as different kinds of animals. b. The fossils in layer A are ancestors of the fossils in other layers. c. The bottom fossil in layer E has a body that is made up of segments. d. Scientists can use this diagram to help learn how old each fossil is 13. The diagram above shows one way to measure the volume of an irregular object. Which of the following measurements gives the correct volume of the rock? a. 20 mL c. 6 mL b. 3 mL d. 23 mL 14. Viruses are particles smaller than bacteria. Viruses can cause disease when they invade specific types of living things. Which of the following is a scientific question about viruses? a. Is it right to destroy disease-causing viruses? b. Why do some viruses infect only plants, while other viruses infect only animals? c. How much money should be spent trying to eliminate diseases caused by viruses? d. Should government make rules for the way diseases caused by viruses are treated? 15. How many centimeters longer is Leaf A than Leaf B? a. 5.8 cm c. 2.7 cm b. 4.3 cm d. 1.5 cm 16. A lab group is investigating this question: “When wind-driven sand particles strike rock, does sand particle size affect how fast rock is broken down?” Which of the following would be the group’s manipulated variable? a. Time it takes to break down a given c. The size of the sand particles amount of rock b. Mass of sand used d. The process used to create artificial wind 17. Which statement below accurately describes the mass of the solid in the diagram? a. 226.5 g b. 220.65 g c. 76.5 g d. There is no way to find the mass of the solid using this information 18. Every element has its own atomic number. The atomic number is the number of ____ in the nucleus of an atom of the element. a. electrons c. positrons b. neutrons d. protons 19. An atom has a neutral charge because a. the atom has twice as many neutrons as protons b. the atom has the same number of protons and neutrons c. the atoms has the same number of protons and electrons d. the atom the same number of electrons and neutrons 20. How do two isotopes of an element differ from one another? a. They have different numbers of c. They have different numbers of protons electrons b. They have different numbers of d. There is no difference neutrons Use the periodic table to answer the following questions: 21. Which line on the periodic table separates the metals from the non-metals and metalloids? a. I c. III b. II d. IV 22. Which two elements have properties similar to those of Chlorine (Cl) a. Fluorine (F) and Bromine (Br) c. Phosphorus (P) and Silicon (Si) b. Nitrogen (N) and Carbon (C) d. Xenon (Xe) and Argon (Ar) 23. Which two elements in group 14 are most likely to be malleable and good conductors of electricity? a. Germanium (Ge) and Silicon (Si) b. Tin (Sn) and Lead (Pb) c. Carbon (C) and Silicon (Si) d. none 24. How many electrons can the elements in the carbon group gain, loose, or share? a. 1 c. 4 b. 5 d. 6 25. How many electrons can the elements in the nitrogen group gain, or share? a. 2 c. 7 b. 5 d. 3 26. Out of these three elements, which two are most likely to combine as a result of a chemical reaction? Magnesium Mg, Neon Ne, Chlorine Cl a. Ne & Cl c. Mg & Ne b. Mg & Cl d. none will react 27. Bob has a chunk of pure substance that is dull and crumbles when dropped. If he attaches it to an electrical source, what will happen? a. it will conduct electricity because it is a non-metal b. nothing because it is a non-metal and doesn’t conduct electricity c. nothing because it is a metal and metals don’t conduct electricity d. it will conduct electricity because it is a metal Use the table below to answer the following questions 8 9 10 O F Ne oxygen Fluorine Neon 15.999 18.998 20.179 16 17 18 S Cl Ar Sulfur 32.06 Chlorine Argon 35.453 39.948 28. Which combination of elements represents part of a group, or family of elements, of the periodic table? a. oxygen, fluorine, and neon c. fluorine and chlorine b. sulfur, chlorine, and argon d. oxygen and chlorine 29. Which element has properties most similar to oxygen? a. fluorine because it is in the same c. neon because it is a gas period b. sulfur because it is in the same group d. none of these share properties with oxygen 30. All of the following are ways in which atoms can form bonds with other atoms EXCEPT a. losing electrons c. sharing neutrons b. gaining electrons d. sharing electrons 31. The only balanced equation shown is ____ a. H2 + O2 H2O c. Ag + H2S Ag2S + H2 b. AgNO3 + NaI AgI + NaNO3 d. Na + Cl2 NaCl 32. Describe how a battery causes electrons to move in a circuit. a. A battery has a positive terminal that attracts electrons and a negative terminal that repels electrons b. A battery has a positive terminal that repels electrons and a negative terminal that attracts protons c. A battery has a positive terminal that attracts protons and a negative terminal that repels electrons d. A battery has a positive terminal that attracts electrons and a negative terminal that repels protons 33. Describe how the electric resistance of a wire changes as the wire becomes longer. How does the resistance change as the wire becomes thicker? a. A longer wire has more resistance. A wire has less resistance as it becomes wider. b. A longer wire has less resistance. A wire has less resistance as it becomes wider. c. A longer wire has less resistance. A wire has more resistance as it becomes wider. d. A longer wire has more resistance. A wire has more resistance as it becomes wider. 34. Explain why the electric wires in houses are usually made of copper. a. Copper is inexpensive and can wire a whole house relatively cheaply b. Copper is a poor conductor of electricity and has a low resistance so more heat is produced when current flows in copper wires c. Copper is a good conductor of electricity and has a low resistance so less heat is produced when current flows in copper wires d. Copper is expensive and so must be high quality material 35. Explain why buildings are wired using parallel circuits rather than series circuits. a. so current will stop flowing in c. To save on money and energy bills by appliances after another appliance or turning off several appliances at once device is turned off or disconnected b. so current will continue to flow in d. buildings are not wired in parallel appliances after another appliance or circuits, they are wired in series device is turned off or disconnected circuits 36. A metal wire is made thinner. How would you change the length of the wire to keep the electric resistance of the wire from changing? a. double the length c. shorten the wire length b. triple the length d. keep the length the same Carefully review the table and answer the following questions Approximate Cost of Electricity For Some Appliances Appliance Wattage Average Daily Use Approximate Cost per (Hours) month Air Cleaner 35 24 $2.00 Box Fan 100 24 $5.75 Clothes Dryer 5,000 1/2 $6.00 Color TV (19 inch) 70 6 $1.05 Personal Computer 150 8 $2.90 Laser Printer 70 2 $0.30 37. Which of the listed appliances costs the most to operate each month? a. Box Fan c. Clothes Dryer b. Personal Computer d. Color TV 38. According to the table, if two appliances are used for the same number of hours, the one with higher watttage will cost ____. a. more to operate c. the same to operate b. less to operate d. can’t answer from table. 39. The color TV costs more to operate than the laser printer because ___. a. The wattage of the color tv is higher. b. the color TV is on longer. c. the color TV is bigger. d. the power company charges more for TVs 40. Describe how you can tell if whether the type of charge on two different objects is the same or different. a. Bring the two objects together. If they move toward each other they are of opposite charge. b. Bring the two objects together. If they move toward each other they have the same charge. c. Bring the two objects together. If they move away from each other they are of opposite charge. d. There is not enough information given here to determine the charges. 41. Charges are not able to flow easily through a. conductors c. insulators b. superconductors d. solenoids Use this table to complete the following questions Power ratings of some appliances Appliance Power (W) Computer 350 Color TV 200 Stereo 250 Toaster 1,100 Microwave 900 Hair Dryer 1,000 42. Which appliance will use the most energy if it is run for 15 minutes? a. microwave c. stereo b. computer d. colot TV 43. Suppose using 100 W for 1 hour costs $0.10. How much would it cost to run the color TV for 8 hours? a. $1.00 c. $1.60 b. $10.00 d. $0.16 44. Power grids use alternating current (AC) in transmission and distrubution systems. Which statement explains why AC is used instead of direct current (DC)? a. Transmission wires cannot carry c. Electrical energy must be transmitted enough direct current to supply the as alternating curent because that is needs of the power grid how it is produced at power plants b. The voltage can be changed in an d. Direct current would not be useful to alternating current system to transfer electric company customers because energy more efficiently appliances operate on alternating current 45. Which list shows the path of electricity from a local power substation to a lamp in a home? a. Substation transformer junction box outlet electric ciucuit of lamp b. Substation outlet junction box transformer electric circuit of lamp c. Substation junction box transformer outlet transformer electric curcuit of lamp d. Substation transformer junction box outlet transformer electric curcuit of lamp 46. Which of the following is required for an electric curent to flow? a. insulators c. an electric device b. positive charges d. an unbroken circuit 47. Which equation expresses Newton’s second law of motion? a. F = ma c. F = m - a b. F = m/a d. F = m + a 48. A probe traveling through outer space is moving at a constant velocity. Which statement applies to the motion of this probe? a. An unbalanced force is acting on the probe, causing it to accelerate. b. The probe will undergo constant acceleration until a force acts on it. c. The probe will continue on its current path until an unbalanced force acts on it. d. The force that makes the probe move through space is equal to its mass divided by its velocity. 49. The following diagram shows the direction of motion of two objects of equal mass just before they collide. According to Newton’s Third Law, which diagram shows the motion of the two objects after they have collided? a. c. b. d. The following diagram shows an experiment in which data were collected about falling objects. Study the diagram above and then answer the following questions about the experiment. 50. Which of these is the most likely hypothesis for the experiment depicted on the left above? a. The more mass an object has, the c. Objects with less mass fall faster then faster it will fall. objects with more mass. b. The less mass an object has, the faster d. Objects of different masses can still it will fall. fall at the same speed. 51. The feather is falling at a different speed than the balls because the feather _____. a. has more gravity acting upon it c. has more friction acting upon it b. has less gravity acting upon it d. has less friction acting upon it 52. You do not know an object’s velocity until you know its a. speed c. speed and direction b. reference point d. acceleration 53. An object used as a reference point to determine motion should be a. accelerating c. decelerating b. stationary d. changing direction 54. If you are sitting in a train, looking out the window and you see another train pass, what is your frame of reference to tell which train is moving? a. your body c. the passing train b. your train d. the landscape 55. Two students on opposite sides of a box apply forces to the box. What must be true if the box does not accelerate? a. The forces are balanced. b. The forces are unbalanced and in the same direction. c. The forces are unbalanced and opposite, with the greater force to the left. d. The forces are unbalanced and opposite, with the greater force to the right. 56. An object weighs 300 newtons on Earth. The same object weighs only 50 newtons on the moon. Why does an object weight less on the moon than on Earth? a. because objects have less mass on the moon b. because there is weightlessness in space c. because the moon’s mass is far more than that of the Earth d. because the moon has less gravitational pull than the Earth 57. Two boys wearing in-line skates are standing on a smooth surface with the palms of their hands touching and their arms bent, as shown above. If boy X pushes by straightening his arms out and boy Y holds his original position, what is the motion of both boys? a. Boy X does not move and Boy Y moves backward b. Boy Y does not move and Boy X moves backward c. Both Boy X and Boy Y move backward d. The motion depends on how hard Boy X pushes 58. The above diagram in an example of which law? a. Newton’s 1st c. Newton’s 3rd b. Newton’s 2nd d. Law of Conservation of Momentum 59. A car accelerates from rest to speed of 24 m/s in 8 seconds. What is the car’s average acceleration? a. 16 m/s2 c. 3 m/s2 2 b. 24 m/s d. 192 m/s2 60. A force that causes an object to move in a circle is called a(n) ___ a. balanced force c. gravitational force b. unbalanced force d. centripetal force 61. The distance-versus- time graph above shows the motion of a jogger. The line is divided into segments. The middle segment is horizontal. What does that tell you about the jogger’s progress between minute 6 and minute 8? a. The jogger ran at a constant speed c. The jogger decreased speed between between minute 6 and minute 8 minute 6 and minute 8. b. The jogger increased speed between d. The jogger was stationary between minute 6 and minute 8. minute 6 and minute 8. 62. Fossil fuels are considered nonrenewable resources because they a. burn so quickly. b. are in such high demand. c. take hundreds of millions of years to form. d. pollute the air. 63. The most plentiful fossil fuel in the United States is a. coal. c. natural gas. b. oil. d. wood. 64. What is the result of using fossil fuels more rapidly than they are formed? a. The reserves will eventually be used c. The reserves will not be affected. up. b. The reserves will be refilled more d. The price of fossil fuels will fall. quickly. 65. The intense heat from Earth’s interior that warms the magma beneath Earth’s surface is called a. hydrogen power. c. geothermal energy. b. tidal energy. d. solar energy. 66. The three major fossil fuels are coal, oil, and a. wood. c. uranium. b. natural gas. d. electricity. 67. Fossil fuels are considered nonrenewable resources because they a. burn so quickly. c. are in such high demand. b. take hundreds of millions of years to d. pollute the air. form. 68. Which of the following is an advantage of solar energy? a. It will not run out for billions of years. c. It must be collected from a huge area. b. It is not available at night. d. No backup energy sources are needed. 69. In a nuclear power plant, what is used to change water into steam? a. the burning of natural gas c. captured solar energy b. geothermal energy d. heat released from nuclear fission reactions 70. Energy conservation means a. slowing down a chemical change. b. using fossil fuels to produce electricity. c. burning a fuel to release energy. d. reducing energy use. 71. Which of the following is an example of energy conservation? a. leaving your home uninsulated c. recycling aluminum soda cans b. leaving lights on whenever you leave a d. driving a car alone into the city at rush room hour 72. Solar cells are sometimes used to power all of the following EXCEPT a. calculators. c. telephones. b. lights. d. passenger trains. 73. Nuclear reactions result in tremendous amounts of a. uranium. c. fission. b. energy. d. mass. 74. The ozone layer protects people from which of the following? a. too much ultraviolet radiation c. the effects of radon b. carbon monoxide poisoning d. allergies 75. One group of gases that is responsible for destroying ozone in the ozone layer is a. car exhaust fumes. c. nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides. b. Chloroflurocarbons (CFCs) d. carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide. 1ST 9 WEEKS TEST 2013-2014 Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: C C C C B B C B A C D C B B D C C D C B C A B C D B B C B C B A A C B C C A PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. 66. 67. 68. 69. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: OBJ: TOP: ANS: OBJ: TOP: ANS: OBJ: TOP: ANS: OBJ: TOP: ANS: OBJ: ANS: OBJ: BLM: ANS: OBJ: ANS: OBJ: B PTS: 1 A PTS: 1 C PTS: 1 A PTS: 1 C PTS: 1 B PTS: 1 A PTS: 1 B PTS: 1 A PTS: 1 C PTS: 1 A PTS: 1 D PTS: 1 B PTS: 1 C PTS: 1 B PTS: 1 D PTS: 1 A PTS: 1 D PTS: 1 C PTS: 1 C PTS: 1 C PTS: 1 D PTS: 1 D PTS: 1 C PTS: 1 DIF: L1 06.05.01.02: Explain why fossil fuels are considered nonrenewable resources. source_sx09_e_environmental_science_ch05_005 BLM: knowledge A PTS: 1 DIF: L1 06.05.01.01: Name the three major fossil fuels. source_sx09_e_environmental_science_ch05_020 BLM: knowledge A PTS: 1 DIF: L1 06.05.01.02: Explain why fossil fuels are considered nonrenewable resources. source_sx09_e_environmental_science_ch05_006 BLM: knowledge C PTS: 1 DIF: L1 06.05.02.01: Identify and describe various renewable sources of energy. source_sx09_e_environmental_science_ch05_027 BLM: knowledge B PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. E-160 E.5.1.2 Name the three major fossil fuels. BLM: knowledge B PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. E-164 E.5.1.3 Explain why fossil fuels are considered nonrenewable resources. knowledge A PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. E-166 E.5.2.1 Explain the forms of energy provided by the sun. BLM: comprehension D PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. E-176 E.5.3.2 Explain how a nuclear power plant produces electricity. 70. 71. 72. 73. 74. 75. BLM: ANS: OBJ: ANS: OBJ: ANS: OBJ: ANS: OBJ: BLM: ANS: OBJ: BLM: ANS: OBJ: BLM: knowledge D PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. E-182 E.5.4.2 Identify ways individuals can conserve energy. BLM: knowledge C PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. E-182 E.5.4.2 Identify ways individuals can conserve energy. BLM: application D PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. E-166 E.5.2.1 Explain the forms of energy provided by the sun. BLM: application B PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. E-174 E.5.3.1 Describe what happens during a nuclear fission reaction. comprehension A PTS: 1 DIF: L2 REF: p. E-147 E.4.5.1 Describe how human activities have damaged the ozone layer. comprehension B PTS: 1 DIF: L1 REF: p. E-148 E.4.5.1 Describe how human activities have damaged the ozone layer. knowledge