3. Verbs
advertisement

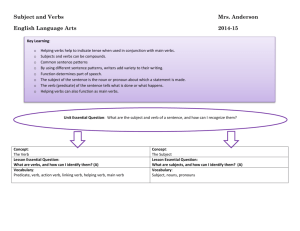
Verbs Doing words. They can express actions and states. Stative Verbs - express states of being or processes in which there is no obvious action. (to know, to believe, to remember) Dynamic Verbs - actions which may be physical, mental or perceptual . (to jump, to think, to see) Transitive Verbs - they must be followed by an object to complete their meaning. (I carried the baby, they found the lost ring, we can make a Christmas cake) Intransitive Verbs - don’t need to be followed by an object, often describes motion or position. (It happened, the children laughed) Many verbs can be transitive or intransitive (I was eating/I was eating cake) Auxiliary Verbs - construct different timescales, questions and negatives, add emphasis or give information about the mood or attitude of speaker / writer. (I have gone, Do you want to go out, I did not watch tele, The baby does want food) Modal Verbs - convey a range of attitudes and moods about the likelihood of an event taking place. (can/could, may/might, must/shall/should, will/would) Regular Verbs (4 forms) Base Form Infinitive walk to walk 3rd Person Singular Present Tense walks Past Tense and Past Participle walked Present Participle walking Irregular Verbs (5 forms) Base Form Infinitive write to write 3rd Person Singular Present Tense writes Past Tense wrote Past Participle have written Present Participle writing Voice - The action and person responsible for it can be conveyed using the active and passive voice. Active Voice - expresses the action of the verb, directly linking it to the thing carrying out the action. (The car stopped suddenly. The girl picked up a book) Passive Voice - reorders the elements of the sentence. The subject is moved to the end of the sentence and the object is moved to the start. The active verb is replaced by a passive verb. Active: The police hit the rioter. Passive: The rioter was hit (by the police). Active: The young child threw the ball and broke the window. Passive: The ball was thrown and the window was broken (by the child). Aspect - describes the timescale. Is the action/state of the verb complete or in progress? Perfect Aspect - have+pp. Present Perfect - has(or have)+pp. Used for an action continuing in the present. (We have eaten in this restaurant for years) Past Perfect - had+pp. Describes a previous time in the past. (The building had decayed years ago) Progressive Aspect - be+pp OR have+be+pp. Implies an activity is on-going & probably not complete. Present Progressive The boys are playing football Past Progressive The boys were playing football Present Perfect Progressive - The boys have been playing football all day Past Perfect The boys had been playing throughout the summer Finite and Non-Finite Verbs Finite Verbs - change their form to show contrast of number, tense and person. Non-Finite Verbs - never change their form. Activity Underline the verbs. Lexical or auxiliary verbs? a) She had gone to town. b) They had a picnic in the country. c) I can do the work. d) Did you like the concert? Underline the verbs. Describe their forms? a) The eagles flapped their wings. b) She laughs at herself. c) You have gone mad. d) I carried the child away. e) The frog was croaking loudly. f) We chased the intruder. g) You have been silly. h) What has been happening? Rewrite these active sentences in the passive (inc passive agent). a) The strong waves lifted the boat above the dangerous sandbank. b) The monks rang the bells to warn the surrounding villagers of the impending danger. c) After the disturbance, the police shut the pub. Rewrite these active sentences in the passive (NOT inc passive agent). a) The guards beat the prisoners. b) The bully left the child face down the in playground. c) The scientists discovered the way to split the atom and created the first atom bomb. Wednesday 26th December Boxing Day I was woken at dawn by the sound of Grandad Sugden’s rusty Ford Escort refusing to start. I know I should have gone down into the street and helped to push it but Grandma Sugden seemed to be doing all right on her own. It must be all those years of flinging sacks of potatoes about. My parents were wisely pretending to be asleep… Went back to sleep but the dog licked me awake at 9:30, so I took it for a walk past Pandora’s house. Her dad’s Volvo wasn’t in the drive so they must still be staying with their relations. On the way I passed Barry Kent, who was kicking a football up against the wall of the old people’s home. He seemed full of seasonal goodwill for once and I stopped to talk with him. He asked what I’d had for Christmas… Underline all the verbs Find: 2 lexical verbs 2 primary auxiliary verbs 2 stative verbs 2 model auxiliary verbs 2 dynamic verbs Rewrite a passive sentence in an active voice. Find 1 example of the progressive aspect, and 1 of the perfective aspect. Find 1 example of present tense, and 1 of past tense. Find 2 examples of a finite verb and 2 examples of a non-finite verb.