5. Basic Beliefs of Buddhism (2)
advertisement

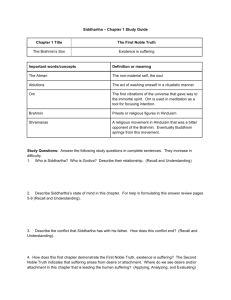
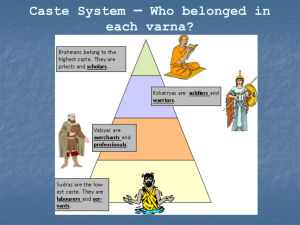
BASIC BELIEFS OF BUDDHISM The basic beliefs of Buddhism can be demonstrated in the following concepts and doctrines: THE FOUR NOBLE TRUTHS The First Noble Truth is the existence of suffering. Birth is painful and death is painful; disease and old age are painful. Not having what we desire is painful and having what we do not desire is also painful. The Second Noble Truth is the cause of suffering. It is the craving desire for the pleasures of the senses, which seeks satisfaction now here, now there; the craving for happiness and prosperity in this life and in future lives. The Third Noble Truth is the ending of suffering. To be free of suffering one must give up, get rid of, extinguish this very craving, so that no passion and no desire remain. The Fourth Noble Truth leads to the ending of all pain by way of the Eightfold Path. THE EIGHTFOLD PATH The first step on that path is Right Views: You must accept the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path. The second is Right Resolve: You must renounce the pleasures of the senses; you must harbor no ill will toward anyone and harm no living creature. The third is Right Speech: Do not lie; do not slander or abuse anyone. Do not indulge in idle talk. The fourth is Right Behavior: Do not destroy any living creature; take only what is given to you; do not commit any unlawful sexual act. The fifth is Right Occupation: You must earn your livelihood in a way that will harm no one. The sixth is Right Effort: You must resolve and strive heroically to prevent any evil qualities from arising in you and to abandon any evil qualities that you may possess. Strive to acquire good qualities and encourage those you do possess to grow, increase, and be perfected. The seventh is Right Contemplation: Be observant, strenuous, alert, contemplative, and free of desire and of sorrow. The eighth is Right Meditation: When you have abandoned all sensuous pleasures, all evil qualities, both joy and sorrow, you must then enter the four degrees of meditation, which are produced by concentration. BUDDHIST PRECEPTS There are five precepts taught by Buddhism that all Buddhists should follow: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Kill no living thing. Do not steal. Do not commit adultery. Tell no lies. Do not drink intoxicants or take drugs. Other precepts apply only to monks and nuns: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Eat moderately and only at the appointed time. Avoid that which excites the senses. Do not wear adornments. Do not sleep in luxurious beds. Accept no silver or gold. SACRED SCRIPTURES In Theravada (Southeast Asian) Buddhism, there are three groups of writings considered to be holy scripture, known as the "Three Baskets" (Tripitaka). The Vinaya Pitaka (discipline basket) contains rules for the higher class of Buddhists; the Sutta Pitaka (teaching basket) contains the discourses of Buddha; and the Abidhamma Pitaka (metaphysical basket) contains Buddhist theology. Mahayana (Chinese, Japanese, Vietnamese, etc.) Buddhism contains an incredibly large amount of holy writings, over five thousand volumes. The oldest scriptures are based on Sanskrit, while others have been written in Nepalese, Tibetan, and Chinese. There are no clear limits as to what should be admitted as scripture, so thousands of writings on the topic have been admitted. BASIC BUDDHIST BELIEFS THE MIDDLE PATH – The Opposite Of All Extremes, sitar string and perfect harmony 3 MARKS OF EXISTENCE 1. 2. 3. Anatta – no self Anicca - impermanence Dukkha - suffering Discussion Questions: 1. Who are you? Answer in 3 sentences or less. 2. Is there anything in your closet, that at one point, you had to wear/have, but now, you wouldn’t be caught dead in it? - How do you explain this? - Are you the same self that you were then? 3. Is there anyone for whom, once upon a time, you were over-the-moon, but now, you don’t even know what you were thinking? - How do you explain this? - Are you the same self that you were then? 4. Are you the same self you were 10 years ago? At birth? Will you be the same self in 20 years? 5. Is your arm you? Is your finger you? What is you? What is self? 6. Is anything in life permanent? 7. Does Buddhism’s perspective on suffering, craving and desire make sense to you? Explain your thoughts. THE NOBLE EIGHTFOLD PATH RIGHT UNDERSTANDING See clearly what you want to do with your life. RIGHT WORK Try not to take jobs that will harm others. RIGHT THOUGHT Do not waste time daydreaming. RIGHT EFFORT Try your best at all times. RIGHT SPEECH Say only good things RIGHT MINDFULNESS Pay full attention to what you are doing. RIGHT ACTION Good deeds are unselfish deeds. RIGHT CONCENTRATION Try to concentrate on what you have to do. The Four Noble Truths Reflection First Noble Truth: Our existence is permeated with suffering. a) What stops a person from being truly happy? b) What are the sources of sorrow in your life? Second Noble Truth: Suffering is caused by our attached desires. a) What is the difference between hope and expectation? b) Name three sorrows that you have. Is there is a desire that is the source of pain? Third Noble Truth: To remove suffering, one must remove attached desiring. Why is it difficult to stop desiring in our society? Fourth Noble Truth: To remove attached desiring, one must follow the Noble Eightfold Path. What do you have to learn to do in order to remove attached desiring?