Homework #4 Factor Proportions (20pts) On the box diagram below

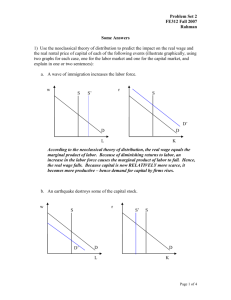
Homework #4 Factor Proportions (20pts)
1.
On the box diagram below place an endowment point so that foreign is abundant in labor.
0-home
Labor
0-foreign Capital
2.
On the box diagram above connect the origin (0 – home) with the endowment point with the help of two vectors one of which represents the K/L ratio of a labor intensive industry ( textiles ), and the other one represents the K/L ratio of the capital intensive industry ( cars )
3.
On the box diagram above illustrate relocation of labor to foreign by shifting the endowment point vertically (so that the amount of capital stays the same). a.
Connect the origin with the new point using vectors with the same K/L as in the previous question ( dashed lines ) b.
Noting the length of vectors is proportional to the output of each industry show what happens to the output of shoes and computers in foreign.
The red dashed line represents output of labor intensive textiles and it shrinks. The output of capital intensive cars increases as can be seen because the dashed green line that represents output used to produce is longer than the solid green line which represents output of cars before the movement of labor.
4.
Following the textbook example, during the class discussion we considered a case when price of computers increases at home. This could be a result of a trade liberalization that allows home to freely export the good where it has comparative advantage. Consider an increase in the price of shoes (produced using labor intensively) in the foreign country that is labor abundant. This could be the result of the same trade liberalization. Following the logic of the Stolper-Samuelson theorem, describe the effect of the change in price on the real returns to capital and labor in the foreign country.
a.
Using a PPF, show the effect of change in price on the outputs of computers and shoes
Q
S
Q
C
Foreign b.
What is the effect of the change in the outputs on the Wage/Rental ratio? Explain using drawings if necessary.
As production of computers deceases more capital is vacated than can be employed by the shoe industry using existing K/L ratios. There is a surplus of capital, capital is less scarce than labor, and the price of capital drops. Both industries increase use of capital until the shortage is dissipated completely. c.
What is the effect of the change in Wage/Rental ratio on K/L in each industry? Explain using drawings if necessary.
Increase in the price of labor relative to capital lowers L/K in each industry because the producers substitute away from labor to capital. This is due to concave isoquants or decreasing MPL/MPK as more labor is use. d.
What is the resulting effect of the increase in the price of shoes on the real returns to capital and wage? Explain, show calculations or formulas where necessary
Since R=MPK
C
*P
C
, and R=MPK
S
*P
S
, the marginal product of capital in both industries can be thought of as the real return to capital (real rental) in terms of respectively computers and shoes: MPK
C
=R/P
C
, and
MPK
S
=R/P
S
. Similarly MPL in both industries can be thought of as real wage in terms of respectively computers and shoes: MPK
L
=W/P
C
, and MPL
S
=W/P
S
. Since K/L in both industries increases in response to the increase in W/R, the marginal product of capital drops (because there is less labor per unit of capital) and the marginal product of labor increases (because there is more capital per unit of labor).
Using the expressions for real wages and rentals we conclude
5.
Please, solve the following problems at the end of chapter 4: 1 and 6
6.
Please, solve the following problems at the end of chapter 5: 1, 3, 11