Physical Science Curriculum Map 2014
advertisement

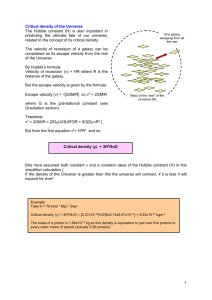
Physical Science Curriculum Map 2014-2015 L Sheets All Science Courses X1 Identify questions and concepts that guide scientific investigations; X2 Design and conduct scientific investigations; X3 Use technology and mathematics to improve investigations and communications; X4 Formulate and revise explanations and models using logic and evidence (critical thinking); X5 Recognize and analyze explanations and models; and X6 Communicate and support a scientific argument. Please note that the order here may not be the order in which ideas are taught. 1) Safety Review 2) Scientific Method Review A) Study of Matter 1) Classification of matter a) Mixture vs Pure Substance (1) Start Matter Concept Map and Vocabulary pages b) Heterogeneous vs. homogeneous, composition (element, compound) (1) Amount of solid able to dissolve in solution increases with temperature (usually) (a) Kinetic - Molecular Theory of Matter (2) Water dissolves many things and is a solvent (also need solute) c) Properties of matter / Physical changes (1) Physical (a) color, solubility, odor, hardness, density, melting point and boiling point, viscosity, and malleability are mentioned specifically (b) Phase changes, phase change diagrams and analysis of them - must include investigation of this (2) Chemical (reactivity) Properties / changes d) States of matter and its changes (1) Loss/Gain of Energy and relation to phase changes (a) Expansion of substance due to movement of molecules (i) Density changes that accompany this (ii) Density calculated from slope of mass vs. volume graph (similar to distance / time graph for speed) 1. Densities of pennies (Pre-'82 and Post-'83) a. Skills: Massing and volume by water displacement (2) Use graphs of different substances to determine differences in densities (a) Density of solid vs. liquid water 2) Atoms a) Models of the atom (components) (1) Atom composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons (a) Mass, charge of particles (2) Rutherford and gold foil (http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/electromag/java/rutherford/) (a) atom mostly empty space (b) central nucleus (c) electron cloud b) Ions (cations and anions) (1) Atoms gain / lose electrons to become cations or anions (a) Ion cards c) Isotopes (1) atomic number and mass number (a) Number of particles in atoms (2) Atomic spectra (a) Flame test demo 3) Periodic trends of the elements a) Position of metals / non-metals taught previously in middle school (1) Refresher of above: (a) Properties of metals vs non-metals (b) Metalloids (c) Representative groups / Transition Elements b) Periodic law (1) Similar properties repeat by columns / groups (a) For this age includes columns 1, 2, and 17 (i) Names and properties of each group (ii) Valence numbers (the only periodic trend needed except for properties) 4) Bonding and compounds a) Bonding (ionic and covalent) (Note: Nothing is said in the Model Curriculum about the reason atoms bond - I think this is important.) (1) Atoms gain, lose or share electrons to: (a) become stable with 8 electrons in the outer shell, lower potential energy, and form molecules or 3D lattices (i) Metal (cation) + non-metal (anion) get opposite charges and attract 1. attract other ions to form crystal lattices (ii) Two non-metals may share electrons to form bonds 1. May result in molecules or crystal lattices (diamond, sugar) (iii) Most bonds fall on a continuum between purely ionic and purely covalent (2) Must be able to determine formulas for columns 1, 2, and 17 (3) Prefixes from 1 - 10 only b) Nomenclature (1) Ionic Compounds (a) Using regular nomenclature students will be able to name or write the formula if given a correct name and vice versa. (2) Covalent Compounds (a) Using Greek prefixes students will be able to name or write the formula if given a correct name. 5) Reactions of matter a) Chemical reactions (1) Endothermic vs exothermic (2) Reaction in a bag (a) Also may be used as a review for physical changes b) Nuclear reactions (1) Involve changes in the nucleus (a) Releases larger amounts of energy than chemical changes (b) Strong nuclear force not balanced (i) Why needed, why out of balance (ii) Particles and rays are emitted in an effort to make nucleus stable (iii) Results in changes in nucleus (2) Half-life (a) Half-life definition (b) Unique for any isotope (c) Used in radioactive dating (3) Fission and fusion (a) Definitions and properties (4) Other Uses of radioactivity (Tracers) (a) Cancer treatment (b) Flow of biological materials Physical Science Curriculum Map 2014-2015 L Sheets B) Energy and Waves 1) Quantifying energy a) Quantifying kinetic energy KE = 0.5*m*v2 b) Quantifying gravitational potential energy GPE = mgh 2) Conservation of energy a) GPE is relative to reference point (1) KE and GPE transfer back and forth (a) Pendulum (2) Heat is graveyard of energy (3) PhET lab - Forces in 1-D shows this or Energy Skate Park 3) Transfer and transformation of energy (including work) a) W = F*d (Force in same direction as movement) (1) PhET Lab to show this? 4) Waves a) Transmit energy b) Properties of waves (1) Refraction, reflection, diffraction, absorption, superposition / interference (a) Absorption: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DThUKDM_Wtk (2) Doppler (below) (a) Explanation and result (b) Used in Formation of Universe section (3) Relationship of frequency and wavelength (4) Relationship of energy with frequency and amplitude c) Radiant energy and the electromagnetic spectrum (1) Radiates in all directions (2) Bands on EM spectrum (a) Relative energy and wavelength (b) Relative positions of bands and visible spectrum d) Opaque, translucent, transparent as they relate to transmission of light and images (1) Diffuse reflections e) Doppler shift 5) Thermal energy (Should already know: conduction, radiation, convection) a) Transfer rate depends on conductivity, color, and size (1) Conductivity (a) Thermal conductors = high rate of heat transfer (b) Thermal insulators = Low rate of thermal transfer (2) Smooth light absorb least, Rough dark absorb most b) Objects continually absorb / transfer thermal energy 6) Electricity a) Movement of electrons caused by power source doing work b) Conductors and Insulators c) Current flow of electrons (or positive charges depending on who you are) d) Electric potential (voltage) - supplies energy to electrons e) Resistors and transfer of energy (1) Oppose the rate of charge flow (2) Do work (light up, toast bread etc.) f) Construction of circuits (virtual or "live") must include measuring effects of resistances and power supplies. (1) Series (a) Effect on resistances (2) Parallel (a) Effect on resistances g) Labs to Use: In Dropbox folder - may need to be modified/explained. Both have good points. (1) Basic Circuit Lab in Map Folder is workable. (2) Series and Parallel Circuits (uses the meters to measure) C) Forces and Motion 1) Motion a) Introduction to one-dimensional vectors b) Displacement, velocity (constant, average and instantaneous) and acceleration c) Interpreting position vs. time and velocity vs. time graphs 2) Forces a) Force diagrams b) Types of forces (gravity, friction, normal, tension) c) Field model for forces at a distance 3) Dynamics (how forces affect motion) a) Objects at rest b) Objects moving with constant velocity c) Accelerating objects D) The Universe 1) History of the universe a) Big Bang Model (1) 12-14 billion yrs ago universe exploded from a few mm to all the stuff today (a) Still expanding (i) Proof: Hubble's Law, Red Shift 1. Farther away a galaxy the greater the red shift 2. Red shift = Doppler effect: "Stuff" moving away, farther away = moving faster (ii) Cosmic background radiation (b) Cooled enough for atoms to form (i) Atoms gathered due to gravity and became Gas clouds (ii) Gas Clouds became stars / galaxies 1. Stars gathered by gravitation a. Gravity caused them to heat and fusion took place b. Fusion formed all the other elements 2. Galaxies are classified by size and shape 3. We live in the Milky Way Galaxy - a spiral galaxy (c) Technology provides new discoveries (i) Space probes (ii) Telescopes (iii) Computers to manage data (2) Websites for kids: (a) http://www.esa.int/esaKIDSen/SEMSZ5WJD1E_OurUniverse_0.html (b) http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/ocr_gateway/energy_resources/big_bangrev1.s html (Second "Page" of this shows the red shift. Other things in science may be found here like bio and chem. Interactive sites and tests.)) (c) http://science.nationalgeographic.com/science/space/universe/origins-universe-article/ (d) http://www.space.com/13320-big-bang-universe-10-steps-explainer.html b) Websites: (1) Ask and astrophysicist < http://imagine.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/ask_astro/answers/971108a.html > religion and why/how it happened vs. science did it happen? (2) Scholarly article < http://wmap.gsfc.nasa.gov/universe/bb_concepts.html > (3) Article plus video < http://science.nasa.gov/astrophysics/focus-areas/what-powered-the-big-bang/ > (4) Test of Big Bang Cosmology < http://wmap.gsfc.nasa.gov/universe/bb_tests.html > (5) One of many religious sites (this one is Christian but there are also Muslim sites) < http://www.ichthus.info/BigBang/intro.html > (6) Advances in technology and understanding about universe < http://mos.seti.org/pages/science.html > 2) Galaxy formation Physical Science Curriculum Map 2014-2015 L Sheets a) Galaxy = groups of stars, star systems, star clusters, dust and gas bound by gravity b) Classified by size and shape (1) Our solar system is part of the Milky Way Galaxy (spiral) (2) Doppler shift / red shift (also in waves section) 3) Stars a) Formation; stages of evolution b) Fusion in stars (1) Stars formed from clouds of H and He (a) Gravitational attraction heated them and fusion started (b) All elements heavier than H and He formed in the fusion reactions c) Stars classified by color, size, luminosity and mass (1) Use Hertzprung-Russell diagram to estimate sizes and predict evolution of stars (a) (<http://www.atnf.csiro.au/outreach/education/senior/astrophysics/stellarevolution_hrintro.ht ml> more scholarly (b) < http://aspire.cosmic-ray.org/Labs/StarLife/hr_diagram.html> Power point - looks easy to understand (2) Patterns of evolution based on mass