Lec. 1 Introduction to Human Biology 1st Grade Students MLT Dept
advertisement

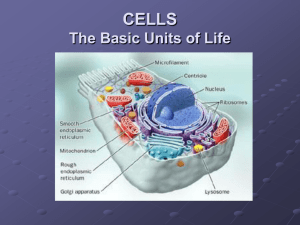
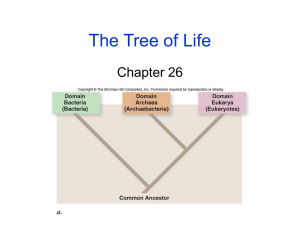
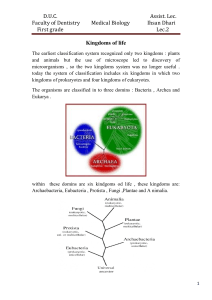
Lec. 1 Introduction to Human Biology 1st Grade Students MLT Dept. What Does Biology mean? Biology: The study of life. Greek origin: Bio: Life Logos: Study of Levels of biological organization: – Atoms – Molecules – Subcellular organelles – Cells – Tissues* – Organs* – Organ systems* – Organism: May consist of a single cell or a complex multicellular organism. * Level of organization not found in all organisms Levels of organization beyond organism: • Population: Group of organisms of the same species that interact with one another. • Community: Several different populations living together in same area (e.g.: lake, forest, jungle). • Ecosystem: Interactions of community with non-living environment (air, water, soil). • Ecosphere: All ecosystems on planet earth. Includes: – Biosphere: All biological communities on earth. – Atmosphere (air) – Hydrosphere (water) 1 Lec. 1 Introduction to Human Biology 1st Grade Students MLT Dept. – Lithosphere (crust) Common features of all organisms: 1. Cells: Basic structural and functional unit of life. Genetic information contained in DNA. 2. Growth and Development: • Growth: Occurs by an increase in cell size, cell number, or both. • Development: Changes that take place during an organism’s life. 3. Energy use and metabolism: • All organisms must take in and transform energy to do work, to live. • Metabolism: All chemical reactions and energy transformations essential for growth, maintenance, and reproduction. . Regulation • External environment may change, but internal environment remains fairly constant. 5. Movement: • Internal movement: Characteristic of all life. • Locomotion: Self-propelled movement from point A to point B. Not observed in all life forms. 6. Respond to environmental stimuli: Organisms respond to internal and external changes (visual stimuli, temperature, light, sound, pressure, etc.). 7. Reproduction: Organisms come from other organisms. Reproduction may be sexual or asexual. 8. Evolutionary adaptation: Populations, not individuals, “evolve” or change over many generations so they can survive in a changing world. 2 Lec. 1 Introduction to Human Biology 1st Grade Students MLT Dept. Kingdom Prokaryotae: Include Bacteria and Cyanobacteria Which they lack nucleus and membrane bound organelles and the nuclear material are spreaded inside the cytoplasm Five Kingdoms of Living World: 2. Kingdom Protista: • Eucaryotes (True nucleus): – Have nuclear membrane around DNA. – Have membrane bound organelles (mitochondria, chloroplast, golgi, endoplasmic reticulum). • Unicellular or simple multicellular. • Most are larger and more complex than bacteria. • Some have cell walls, others don’t. • Some make their own food (phothosynthetic), others must eat other organisms. • Include: Protozoa, algae, slime molds. Kingdom Protista: Eucaryotic Unicellular or Simple Multicellular Organisms 3 Lec. 1 Introduction to Human Biology 1st Grade Students MLT Dept. Five Kingdoms (Continued): 3. Kingdom Fungi: The digestion is external (Outside the body) • Most are multicellular. • Eucaryotes: – Have nuclear membrane around DNA. – Have membrane bound organelles (mitochondria, chloroplast, golgi, endoplasmic reticulum). • Include: Mushrooms, yeasts, and molds. Five Kingdoms (Continued): 4. Kingdom Plantae: • Complex multicellular organisms. • Cellulose cell walls. • Eucaryotes: Have nuclear membrane around DNA and membrane bound organelles. • Autotrophs: Convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into food through photosynthesis. • Include: Trees, flowering plants, and mosses. Five Kingdoms (Continued): 5. Kingdom Animalia: 4 Lec. 1 Introduction to Human Biology 1st Grade Students MLT Dept. • Complex multicellular organisms. • Lack cell walls. • Eucaryotes: Have nuclear membrane around DNA and membrane bound organelles. • Heterotrophs: Obtain chemical energy from living sources. Eat other organisms for nourishment. • Include: Sponges, worms, insects, and vertebrates. Classification of Biological Groups in life cycle 1. Producers or Autotrophs: • Self-nourishing organisms (plants, algae, etc.). • Produce food from simple raw materials. • Most carry out photosynthesis: CO2 + H2O + Sunlight -----> Food + Oxygen • Depend on nonproducers for carbon dioxide 2. Consumers • Mainly animals. • Heterotrophs that obtain food directly or indirectly from producers. • Carry out cellular respiration: Food + Oxygen -----> CO2 + H2O + ENERGY Gas exchange between producers and consumers helps maintain balance of life-sustaining gases in atmosphere. 3. Decomposers: • Some bacteria, fungi, and animals. • Recycle nutrients by breaking down products and bodies of dead organisms. 5 Lec. 1 Introduction to Human Biology 1st Grade Students MLT Dept. • Process is vital because makes nutrients available for use by other organisms. • All organisms interact with each other and the environment they live in. • Interactions between producers, consumers, and decomposers are essential to maintain proper conditions for life on earth. 6