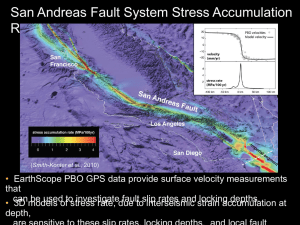
Quiz A Name Period ______ Earthquakes Vocabulary Quiz_____ 1
advertisement

Quiz A Name ____________________________ Period ____________ Earthquakes Vocabulary Quiz _____ 1. earthquake a. instrument used to record seismic activity _____ 2. fire b. second fastest wave that shakes and can only move through solids _____ 3. seismogram c. a smaller earthquake after a bigger one _____ 4. foot wall d. break or crack in the earth’s crust along which rocks shift their position _____ 5. transform (strike-slip) fault e. force that resists the movement of one surface past another surface _____ 6. seismic wave f. occurs because of breaks in gas and electrical lines _____ 7. Mercalli Intensity scale g. scale based on measurements of seismic waves _____ 8. s wave h. fault where the blocks of crust move laterally _____ 9. tsunami i. wave that is the slowest but can cause the most destruction _____ 10. hanging wall j. amount of energy released at an earthquake’s source _____ 11. hypocenter (focus) k. fault along a convergent plate boundary where the hanging wall moves up the foot wall _____ 12. friction _____ 13. landslide _____ 14. Richter scale _____ 15. fault l. a form of energy that travels through the lithosphere and earth’s interior m. a block of crust that is located above a fault plane _____ 16. intensity n. fault along a divergent plate boundary where the hanging wall falls down the foot wall _____ 17. destruction from o. the location where slippage begins seismic vibrations p. sudden return of elastically deformed rock to its undeformed shape _____ 18. epicenter q. the point on Earth’s surface directly above the hypocenter _____ 19. reverse (thrust) fault r. series of large ocean waves _____ 20. p wave s. fastest wave that compresses and can move through liquids _____ 21. normal fault t. destruction from the ground moving up-and-down and side-to-side _____ 22. elastic rebound u. causes damage as land cracks and slumps to more stable ground _____ 23. magnitude v. scale based on observations _____ 24. seismograph w. ground shaking caused by sudden and rapid movement of one block of rock slipping past another along fractures in Earth’s crust _____ 25. surface wave _____ 26. aftershock x. the record of an earthquake; the wiggle y. block of crust that lies underneath a fault plane z. measure of the amount of shaking at a particular location Quiz B Name ____________________________ Period ____________ Earthquakes Vocabulary Quiz _____ 1. earthquake _____ 2. fire _____ 3. seismogram _____ 4. foot wall _____ 5. transform (strike-slip) fault _____ 6. seismic wave _____ 7. Mercalli Intensity scale _____ 8. s wave _____ 9. tsunami _____ 10. hanging wall _____ 11. hypocenter (focus) _____ 12. friction _____ 13. landslide _____ 14. Richter scale a. fault along a divergent plate boundary where the hanging wall falls down the foot wall b. the location where slippage begins c. sudden return of elastically deformed rock to its undeformed shape d. the point on Earth’s surface directly above the hypocenter e. series of large ocean waves f. fastest wave that compresses and can move through liquids g. destruction from the ground moving up-and-down and side-to-side h. causes damage as land cracks and slumps to more stable ground i. scale based on observations j. ground shaking caused by sudden and rapid movement of one block of rock slipping past another along fractures in Earth’s crust k. the record of an earthquake; the wiggle l. block of crust that lies underneath a fault plane _____ 15. fault m. measure of the amount of shaking at a particular location instrument used to record seismic activity _____ 16. intensity n. instrument used to record seismic activity _____ 17. destruction from o. second fastest wave that shakes and can only move through solids seismic vibrations _____ 18. epicenter _____ 19. reverse (thrust) fault _____ 20. p wave _____ 21. normal fault _____ 22. elastic rebound _____ 23. magnitude _____ 24. seismograph _____ 25. surface wave _____ 26. aftershock p. a smaller earthquake after a bigger one q. break or crack in the earth’s crust along which rocks shift their position r. force that resists the movement of one surface past another surface s. occurs because of breaks in gas and electrical lines t. scale based on measurements of seismic waves u. fault where the blocks of crust move laterally v. wave that is the slowest but can cause the most destruction w. amount of energy released at an earthquake’s source x. fault along a convergent plate boundary where the hanging wall moves up the foot wall y. a form of energy that travels through the lithosphere and earth’s interior z. a block of crust that is located above a fault plane Quiz C Name ____________________________ Period ____________ Earthquakes Vocabulary Quiz _____ 1. earthquake a. occurs because of breaks in gas and electrical lines _____ 2. fire b. scale based on measurements of seismic waves _____ 3. seismogram c. fault where the blocks of crust move laterally _____ 4. foot wall d. wave that is the slowest but can cause the most destruction _____ 5. transform (strike-slip) fault e. amount of energy released at an earthquake’s source _____ 6. seismic wave f. fault along a convergent plate boundary where the hanging wall moves up the foot wall _____ 7. Mercalli Intensity scale _____ 8. s wave _____ 9. tsunami _____ 10. hanging wall _____ 11. hypocenter (focus) g. a form of energy that travels through the lithosphere and earth’s interior h. a block of crust that is located above a fault plane i. scale based on observations _____ 12. friction j. ground shaking caused by sudden and rapid movement of one block of rock slipping past another along fractures in Earth’s crust _____ 13. landslide k. the record of an earthquake; the wiggle _____ 14. Richter scale l. block of crust that lies underneath a fault plane _____ 15. fault m. measure of the amount of shaking at a particular location _____ 16. intensity n. series of large ocean waves _____ 17. destruction from o. fastest wave that compresses and can move through liquids seismic vibrations p. destruction from the ground moving up-and-down and side-to-side _____ 18. epicenter q. causes damage as land cracks and slumps to more stable ground _____ 19. reverse (thrust) fault r. second fastest wave that shakes and can only move through solids _____ 20. p wave s. a smaller earthquake after a bigger one _____ 21. normal fault t. break or crack in the earth’s crust along which rocks shift their position _____ 22. elastic rebound u. force that resists the movement of one surface past another surface _____ 23. magnitude v. instrument used to record seismic activity _____ 24. seismograph w. fault along a divergent plate boundary where the hanging wall falls down the foot wall _____ 25. surface wave _____ 26. aftershock x. the location where slippage begins y. sudden return of elastically deformed rock to its undeformed shape z. the point on Earth’s surface directly above the hypocenter Quiz D Name ____________________________ Period ____________ Earthquakes Vocabulary Quiz _____ 1. earthquake a. second fastest wave that shakes and can only move through solids _____ 2. fire b. instrument used to record seismic activity _____ 3. seismogram c. a smaller earthquake after a bigger one _____ 4. foot wall d. force that resists the movement of one surface past another surface _____ 5. transform (strike-slip) fault e. break or crack in the earth’s crust along which rocks shift their position _____ 6. seismic wave f. scale based on measurements of seismic waves _____ 7. Mercalli Intensity scale g. occurs because of breaks in gas and electrical lines _____ 8. s wave h. fault where the blocks of crust move laterally _____ 9. tsunami i. amount of energy released at an earthquake’s source _____ 10. hanging wall j. wave that is the slowest but can cause the most destruction _____ 11. hypocenter (focus) k. fault along a convergent plate boundary where the hanging wall moves up the foot wall _____ 12. friction _____ 13. landslide _____ 14. Richter scale _____ 15. fault _____ 16. intensity _____ 17. destruction from seismic vibrations l. a block of crust that is located above a fault plane m. a form of energy that travels through the lithosphere and earth’s interior n. the location where slippage begins o. fault along a divergent plate boundary where the hanging wall falls down the foot wall p. shape the point on Earth’s surface directly above the hypocenter _____ 18. epicenter q. sudden return of elastically deformed rock to its undeformed _____ 19. reverse (thrust) fault r. fastest wave that compresses and can move through liquids _____ 20. p wave s. series of large ocean waves _____ 21. normal fault t. causes damage as land cracks and slumps to more stable ground _____ 22. elastic rebound u. destruction from the ground moving up-and-down and side-to-side _____ 23. magnitude v. ground shaking caused by sudden and rapid movement of one block of rock slipping past another along fractures in Earth’s crust _____ 24. seismograph _____ 25. surface wave _____ 26. aftershock w. scale based on observations x. measure of the amount of shaking at a particular location y. block of crust that lies underneath a fault plane z. the record of an earthquake; the wiggle Quiz E Name ____________________________ Period ____________ Earthquakes Vocabulary Quiz _____ 1. earthquake a. the record of an earthquake; the wiggle _____ 2. fire b. second fastest wave that shakes and can only move through solids _____ 3. seismogram c. scale based on observations _____ 4. foot wall d. causes damage as land cracks and slumps to more stable ground _____ 5. transform (strike-slip) fault e. force that resists the movement of one surface past another surface _____ 6. seismic wave f. occurs because of breaks in gas and electrical lines _____ 7. Mercalli Intensity scale g. the location where slippage begins _____ 8. s wave h. fault where the blocks of crust move laterally _____ 9. tsunami i. series of large ocean waves _____ 10. hanging wall j. block of crust that lies underneath a fault plane _____ 11. hypocenter (focus) k. ground shaking caused by sudden and rapid movement of one block of rock slipping past another along fractures in Earth’s crust _____ 12. friction _____ 13. landslide l. a form of energy that travels through the lithosphere and earth’s interior m. a block of crust that is located above a fault plane ________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _____ 14. Richter scale _____ 15. fault n. fault along a divergent plate boundary where the hanging wall falls down the foot wall _____ 16. intensity o. scale based on measurements of seismic waves _____ 17. destruction from p. sudden return of elastically deformed rock to its undeformed shape seismic vibrations q. the point on Earth’s surface directly above the hypocenter _____ 18. epicenter r. wave that is the slowest but can cause the most destruction _____ 19. reverse (thrust) fault s. fastest wave that compresses and can move through liquids _____ 20. p wave t. destruction from the ground moving up-and-down and side-to-side _____ 21. normal fault u. break or crack in the earth’s crust along which rocks shift their position _____ 22. elastic rebound v. a smaller earthquake after a bigger one _____ 23. magnitude w. fault along a convergent plate boundary where the hanging wall moves up the foot wall _____ 24. seismograph _____ 25. surface wave _____ 26. aftershock x. instrument used to record seismic activity y. amount of energy released at an earthquake’s source z. measure of the amount of shaking at a particular location