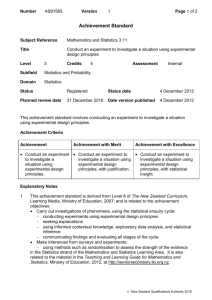
Side-By-Side Kindergarten
advertisement
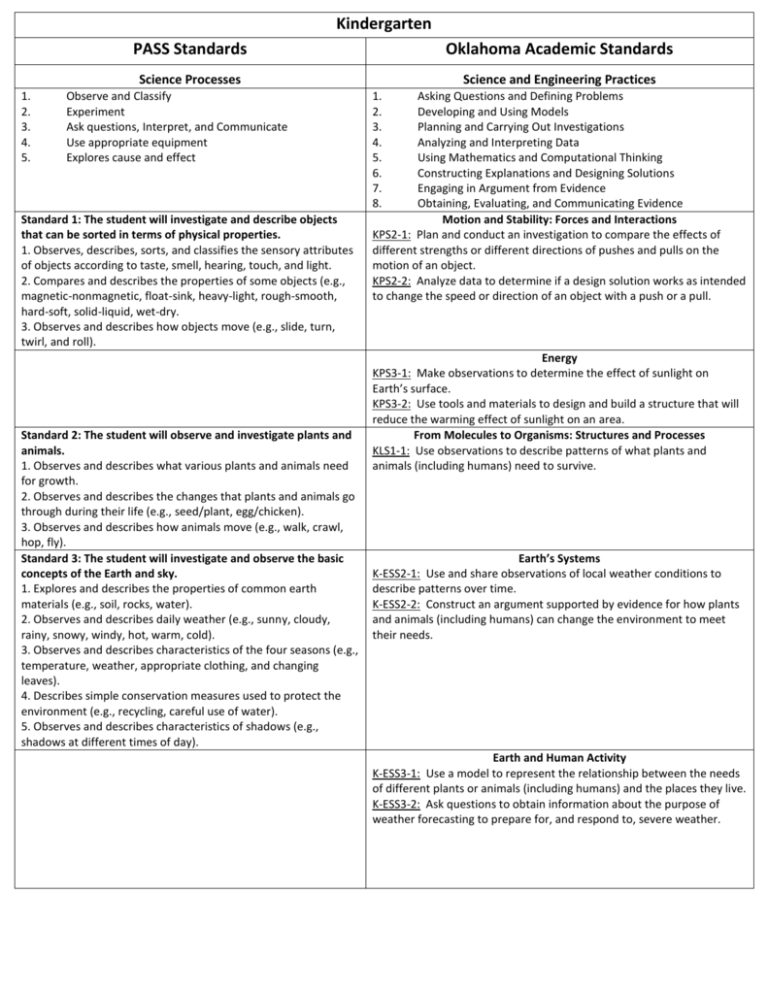
Kindergarten 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. PASS Standards Oklahoma Academic Standards Science Processes Science and Engineering Practices Observe and Classify Experiment Ask questions, Interpret, and Communicate Use appropriate equipment Explores cause and effect Standard 1: The student will investigate and describe objects that can be sorted in terms of physical properties. 1. Observes, describes, sorts, and classifies the sensory attributes of objects according to taste, smell, hearing, touch, and light. 2. Compares and describes the properties of some objects (e.g., magnetic-nonmagnetic, float-sink, heavy-light, rough-smooth, hard-soft, solid-liquid, wet-dry. 3. Observes and describes how objects move (e.g., slide, turn, twirl, and roll). Standard 2: The student will observe and investigate plants and animals. 1. Observes and describes what various plants and animals need for growth. 2. Observes and describes the changes that plants and animals go through during their life (e.g., seed/plant, egg/chicken). 3. Observes and describes how animals move (e.g., walk, crawl, hop, fly). Standard 3: The student will investigate and observe the basic concepts of the Earth and sky. 1. Explores and describes the properties of common earth materials (e.g., soil, rocks, water). 2. Observes and describes daily weather (e.g., sunny, cloudy, rainy, snowy, windy, hot, warm, cold). 3. Observes and describes characteristics of the four seasons (e.g., temperature, weather, appropriate clothing, and changing leaves). 4. Describes simple conservation measures used to protect the environment (e.g., recycling, careful use of water). 5. Observes and describes characteristics of shadows (e.g., shadows at different times of day). 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Asking Questions and Defining Problems Developing and Using Models Planning and Carrying Out Investigations Analyzing and Interpreting Data Using Mathematics and Computational Thinking Constructing Explanations and Designing Solutions Engaging in Argument from Evidence Obtaining, Evaluating, and Communicating Evidence Motion and Stability: Forces and Interactions KPS2-1: Plan and conduct an investigation to compare the effects of different strengths or different directions of pushes and pulls on the motion of an object. KPS2-2: Analyze data to determine if a design solution works as intended to change the speed or direction of an object with a push or a pull. Energy KPS3-1: Make observations to determine the effect of sunlight on Earth’s surface. KPS3-2: Use tools and materials to design and build a structure that will reduce the warming effect of sunlight on an area. From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes KLS1-1: Use observations to describe patterns of what plants and animals (including humans) need to survive. Earth’s Systems K-ESS2-1: Use and share observations of local weather conditions to describe patterns over time. K-ESS2-2: Construct an argument supported by evidence for how plants and animals (including humans) can change the environment to meet their needs. Earth and Human Activity K-ESS3-1: Use a model to represent the relationship between the needs of different plants or animals (including humans) and the places they live. K-ESS3-2: Ask questions to obtain information about the purpose of weather forecasting to prepare for, and respond to, severe weather. Oklahoma Academic Standards Crosscutting Concepts Cause and Effect Simple tests can be designed to gather evidence to support or refute student ideas about causes. (K-PS2-1, K-PS2-2) Events have causes that generate observable patterns. (K-PS3-1, K-PS3-2, K-ESS3-2) Patterns Patterns in the natural and human designated world can be observed and used as evidence. (K-LS1-1, K-ESS2-1) Systems and Systems Models Systems in the natural and designed world have parts that work together. (K-ESS2-2, K-ESS3-1,)