Supplementary information for the manuscript
advertisement

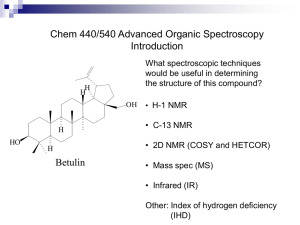
Supplementary information for the manuscript: A Robust Algorithm for Optimizing Protein Structures with NMR Chemical Shifts Mark Berjanskii1, David Arndt1, Yongjie Liang1, and David S. Wishart 1,2,3† 1 Department of Computing Science, University of Alberta; 2Department of Biological Sciences, University of Alberta and 3National Research Council, National Institute for Nanotechnology (NINT), Edmonton, AB, Canada T6G 2E8 † To whom correspondence should be addressed. (Phone: 780-492-0383, email: david.wishart@ualberta.ca) Keywords: protein, structure determination, NMR, chemical shifts 1 Supplementary Figure Legends. Supplementary Figure 1. CONTRA MD biasing in CS-GAMDy. Each biased MD iteration consists of 50 independent MD runs with different starting velocities and several other starting MD parameters. At the end of each biased MD step, final models from these 50 runs are assessed and ranked by the GeNMR knowledge-based function or the RCI-ASA score. The best-scoring model becomes the starting model for the next round of MD biasing. Supplementary Figure 2. CS-GAMDy operation modes. (A) Default full mode: includes both the genetic algorithm and biased molecular dynamics (MD). (B) Only the genetic algorithm for MD without biasing. (C) Only biased MD (D) Only MD without biasing or the genetic algorithm. Supplementary Figure 3. CS-GAMDy stop criteria. (A) Changes in the GeNMR score during CS-GAMDy refinement of a misfolded ubiquitin model. The end of the GeNMR score decay (step 220) is labeled with a blue arrow. The termination point (220 X 5 = step 1100) is shown with a red arrow. (B) C RMSD to the reference model (1UBQ) during the same CS-GAMDy refinement. The RMSD shows no significant changes between the end of the GeNMR score decay (step 220) and the CS-GAMDy termination point (step 1100). Supplementary Figure 4. CS-GAMDy success criteria. (A) GeNMR score vs C RMSD to the best-scoring model. The score drop criterion, the RMSD criterion, and correlation 2 coefficient criterion are indicated with green, black, and red lines, respectively. See the text for explanations of these simulation success criteria. (B) GeNMR score vs C RMSD to the reference model (PDB ID: 1UBQ). The plot demonstrates a good correlation between the GeNMR score and the model accuracy. Supplementary Figure 5. Performance of CS-GAMDy for misfolded models of several proteins from the CS-GAMDy testing set. Model accuracy (backbone RMSD of non-coil regions with respect to the reference structure) is plotted on the X axis (before refinement) and Y axis (after refinement), respectively. 3 Supplementary Figure 1. 4 Supplementary Figure 2. 5 Supplementary Figure 3 6 Supplementary Figure 4 7 Supplementary Figure 5. 8 Supplementary Table 1. Scores and energy terms that are used in CS-GAMDy. Scores or energies ANGLes BONDs IMPRoper DIHEdral VDW ELEC RAMA HBDB RGYR GBIN, GBSE CDIH NOE goap RW Hcount HBener Rama Chi1 Omega Bump Rad Thread SecStr N CA CO CB HA HN RCI-ASA Optimization target Program Role in CS-GAMDy Bond angles Bond length Planarity or chirality Torsion angles van der Waals interactions Electrostatic interactions Torsion angle normality Hydrogen bonding Radius of gyration XPLOR XPLOR XPLOR XPLOR XPLOR XPLOR XPLOR XPLOR XPLOR Molecular dynamics Molecular dynamics Molecular dynamics Molecular dynamics Molecular dynamics Molecular dynamics Molecular dynamics Molecular dynamics Molecular dynamics Solvent properties XPLOR Molecular dynamics XPLOR Molecular dynamics XPLOR Molecular dynamics GOAP RW GeNMR GeNMR GeNMR GeNMR GeNMR GeNMR GeNMR Genetic algorithm Genetic algorithm (GA) MD biasing, GA MD biasing, GA MD biasing, GA MD biasing, GA MD biasing, GA MD biasing, GA MD biasing, GA MD biasing, GA GeNMR MD biasing, GA GeNMR GeNMR GeNMR GeNMR GeNMR GeNMR MD biasing, GA MD biasing, GA MD biasing, GA MD biasing, GA MD biasing, GA MD biasing, GA CSGAMDy MD biasing, GA Agreement with torsion angle restraints Agreement with distance restraints Pairwise atomic interactions Intra-protein distances Hydrogen bonding Hydrogen bonding Phi and Psi torsion angles Side-chain torsion angles Omega torsion angles van der Waals interactions Radius of gyration Intramolecular interactions Agreement with secondary structure from chemical shifts Agreement with 15N shifts Agreement with 13C shifts Agreement with 13CO shifts Agreement with 13Cβ shifts Agreement with 1H shifts Agreement with 1HN shifts Average of Pearson and Kendall Tau coefficients of correlation between RCIderived ASA and model ASA 9 Supplementary Table 2. Important parameters of molecular dynamics and minimization in CS-GAMDy Parameter Temperature Force-field Coefficient for dihedral angle restraints Time step MD length MD minimization Minimization steps Description MD virtual temperature. Ignored if temperature randomization during GA is activated. MD force-field. Forcefield files are stored in Python dictionary “ff_dict” and include PARALLHDG, OPLS. CHARMM, and Amber Weighting coefficient for dihedral angle restraints. Ignored if its randomization during MD biasing is selected. MD integration time step. Ignored if its randomization during MD biasing is selected Number of MD steps If 1, quench MD with Powell’s minimization. Number of Powell’s minimization steps. XPLOR will stop minimization faster if model changes get too small Parameter flag -temp -ff Default value 40,000K parallhdg_new, which corresponds to force-field file parallhdg_new.pro -cdih_coef 200 -timestep 0.002 ps -md_length 10 -post_min 1 -post_min_steps 1000 10 Supplementary Table 3. Important parameters of MD biasing (BMD) in CS-GAMDy Parameter Temperature randomization in MD biasing Description If 1, use temperature that is randomly selected between 10K and the maximal temperature defined either with “-temp” (vide supra) or “-ga_temp_random” (vide infra) flags. Random radius If 1, randomly select weight for of gyration the radius of gyration term from weight the range between 1 and 500. Random weight If 1, randomly select weight for of van der Waals the van der Waals interactions interactions term from between 0 and 1 Random weight If 1, randomly select weight for of the the electrostatic interactions term electrostatic term from between 0 and 1 Random weight Key in Python dictionary of the torsion “cdih_coef_range” that stores angle restraints weights for torsion angle restraints. Default key 9 corresponds to the set: 0, 2000 If 0, no randomization is done Time step If 1, use time step randomly randomization in selected between 0.00001ps and MD biasing the maximal time step. Maximal time Maximal time step in time step step randomization MD length If 1, use MD length that is randomization in randomly selected between 1 and MD biasing the maximal MD length. Maximal MD Maximal length in MD length length randomization Number of Number of independent MD independent MD trajectories starting from the same trajectories model. BMD length Number of BMD iterations BMD ASA score This parameter enables optional model ranking by an accessible surface area (ASA) score. Available scores are pearson, kendall, and pearken (mean of pearson and kendall correlation coefficients ) Parameter flag Default value -bmd_temp_random 1 -rgyr_random 1 -vdw_random 1 -elec_random 1 -cdih_random 9 -bmd_ts_random 1 -max_timestep -bmd_mdl_random 0.01 ps 1 -max_mdl 100 -ns 50 -bmd_length 10 -bmd_asa pearken 11 Supplementary Table 4. Important parameters of genetic algorithm in CS-GAMDy Parameter Description Parameter flag Default value Key in Python dictionary “ga_temp_range_dict” that stores sets of randomly Temperature selected temperatures. If 0, randomization no randomization is done -ga_temp_random 9 in genetic Default key 9 corresponds to algorithm the set: 10,000, 20,000, 40,000, 80,000, 160,000, 320,000, 600,000, 1,000,000. Number of MD biasing Population -pop 10 trajectories in GA population Number of MD biasing Number of trajectories with least-fit -nlos 2 losers final models that get replaced with the best-fit model Types of fitness functions that are being randomly used. There are currently two types of functions: “GNMR_combo” and scoring, GA scores “scoring”. Ranking function -ga_score GNMR_combo “scoring” enables selection of GOAP, RW, and ASA scores. “GNMR_combo” function ranks models with GeNMR score This parameter enables GA GOAP optional model ranking by -ga_goap total_goap_score score the GOAP score This parameter enables GA RW score optional model ranking by -ga_rw rw the RW score This parameter enables optional model ranking by an accessible surface area GA ASA (ASA) score. Available -ga_asa pearken score scores are pearson, kendall, and pearken (mean of pearson and kendall correlation coefficients ) 12 Supplementary Table 5. Information on the distorted protein models. Protein name PyJ Ubiquitin GB3 Q5E7H1 RPA3401 RHOS4 26430 Protein LX PefI tRNA hydrolase domain CSPA Calbindin D9K NE1242 PDB ID BMRB ID Length Folding class 1FAF 1UBQ 1P7E 2JVW 2JTV 4403 5387 18531 15491 15419 79 76 56 88 65 /β /β /β 2JVM 15482 80 β 2JXT 2JT1 15573 15386 86 77 /β /β 2JVA 15471 108 /β 1MJC 4296 69 β 3ICB 19370 75 2JV8 15468 73 /β 13 Supplementary Table 6. Violations of dihedral angle restraints derived from NMR chemical shifts by distorted protein models under different refinement scenarios. Protein name PDB ID PyJ Ubiquitin GB3 Q5E7H1 RPA3401 RHOS4 26430 Protein LX PefI tRNA hydrolase domain CSPA Calbindin D9K NE1242 Average 1FAF 1UBQ 1P7E 2JVW 2JTV Violations of dihedral angle restraints derived from NMR chemical shifts Initial Native Refined Refined Refined by model by by CSXPLOR CSGAMDy with NMR GAMDy with data without NMR NMR data data 111 52 30 44 19 93 0 26 3 15 81 0 27 8 15 101 40 20 33 9 77 33 48 21 3 2JVM 55 29 0 39 15 2JXT 113 46 0 41 21 2JT1 93 37 57 36 0 2JVA 113 50 0 67 15 1MJC 84 17 5 74 3 3ICB 103 37 11 34 16 2JV8 85 92 51 35 15 15 43 40 2 10 14 Supplementary Table 7. Mean Pearson coefficient of correlation between experimental and predicted backbone NMR chemical shifts of distorted protein models under different refinement scenarios. Protein name PDB ID PyJ Ubiquitin GB3 Q5E7H1 RPA3401 RHOS4 26430 Protein LX PefI tRNA hydrolase domain CSPA Calbindin D9K NE1242 Average 1FAF 1UBQ 1P7E 2JVW 2JTV Pearson coefficient of correlation between experimental and predicted backbone NMR chemical shifts Initial Native Refined by Refined by Refined by model XPLOR CSCS-GAMDy with NMR GAMDy with data without NMR NMR data data 0.33 0.68 0.53 0.55 0.70 0.48 0.84 0.74 0.78 0.82 0.33 0.72 0.53 0.66 0.70 0.26 0.66 0.43 0.43 0.58 0.32 0.77 0.62 0.74 0.81 2JVM 0.29 0.64 0.55 0.46 0.59 2JXT 0.34 0.69 0.62 0.64 0.70 2JT1 0.34 0.81 0.62 0.68 0.80 2JVA 0.40 0.72 0.68 0.52 0.74 1MJC 0.36 0.78 0.55 0.38 0.79 3ICB 0.36 0.68 0.59 0.52 0.65 2JV8 0.41 0.35 0.63 0.72 0.68 0.59 0.58 0.58 0.73 0.72 15 Supplementary Table 8. Secondary structure score from NMR chemical shifts of distorted protein models under different refinement scenarios. Note that a low score is good. Protein name PyJ Ubiquitin GB3 Q5E7H1 RPA3401 RHOS4 26430 Protein LX PefI tRNA hydrolase domain CSPA Calbindin D9K NE1242 Average PDB ID GeNMR secondary structure score from NMR chemical shifts Initial model Native Refined by XPLOR with NMR data Refined by CSGAMDy without NMR data 1FAF 1UBQ 1P7E 2JVW 2JTV 184 160 148 196 188 20 28 20 20 32 36 44 104 32 52 44 56 16 40 36 Refined by CSGAMDy with NMR data 36 32 12 28 28 2JVM 96 48 92 64 32 2JXT 212 28 28 32 16 2JT1 180 28 40 52 20 2JVA 204 52 120 100 52 1MJC 116 28 128 92 24 3ICB 200 24 48 40 28 2JV8 164 171 68 33 120 70 72 54 28 28 16 Supplementary Table 9. Mean Pearson coefficient of correlation between model perresidue ASA and per-residue ASA predicted from NMR chemical shifts of distorted protein models. Protein name PDB ID PyJ Ubiquitin GB3 Q5E7H1 RPA3401 RHOS4 26430 Protein LX PefI tRNA hydrolase domain CSPA Calbindin D9K NE1242 Average 1FAF 1UBQ 1P7E 2JVW 2JTV Pearson coefficient of correlation between model’s ASA and ASA predicted from chemical shifts Initial Native Refined by Refined Refined by model XPLOR by CS-GAMDy with NMR CSwith data GAMDy NMR without data NMR data 0.28 0.81 0.31 0.65 0.73 0.50 0.65 0.41 0.63 0.58 0.58 0.55 0.45 0.54 0.61 0.31 0.77 0.12 0.72 0.70 0.51 0.65 0.31 0.63 0.54 2JVM 0.51 0.73 0.01 0.77 0.72 2JXT 0.35 0.49 0.33 0.51 0.49 2JT1 0.31 0.64 0.38 0.62 0.62 2JVA 0.30 0.58 0.21 0.56 0.46 1MJC 0.34 0.71 0.27 0.68 0.68 3ICB 0.56 0.12 0.46 0.10 0.34 2JV8 0.40 0.41 0.58 0.61 0.21 0.29 0.57 0.58 0.54 0.58 17 Supplementary Table 10. Violations of dihedral angle restraints derived from NMR chemical shifts by ubiquitin comparative models under different refinement scenarios. Template PDB ID ID % 1OTR 2GBK 1UD7 2GBJ 2GBM 1WY8 2DZI 2FAZ 1OQY 1WH3 1WX9 1Z2M 1MG8 1UEL 1IYF 1WE7 1TTN Average 96 92 91 90 90 39 39 37 36 36 34 33 32 32 30 28 26 Violations of dihedral angle restraints derived from NMR chemical shifts Initial Refined by Refined by Refined by model XPLOR CS-GAMDy CS-GAMDy with NMR without with NMR data NMR data data 62 1 34 1 25 1 39 0 44 1 36 0 23 0 41 3 27 3 26 2 74 118 55 2 67 1 41 1 38 83 43 7 89 16 47 3 74 0 34 0 78 0 33 5 35 0 33 6 72 2 38 13 63 1 46 2 75 1 46 0 89 2 53 0 89 33 74 0 60.2 15.5 42.3 2.7 18 Supplementary Table 11. Mean Pearson coefficient of correlation between experimental and predicted backbone NMR chemical shifts of ubiquitin comparative models under different refinement scenarios. Template PDB ID ID % 1OTR 2GBK 1UD7 2GBJ 2GBM 1WY8 2DZI 2FAZ 1OQY 1WH3 1WX9 1Z2M 1MG8 1UEL 1IYF 1WE7 1TTN Average 96 92 91 90 90 39 39 37 36 36 34 33 32 32 30 28 26 Pearson coefficient of correlation between experimental and predicted backbone NMR chemical shifts Initial Refined by Refined by Refined by model XPLOR with CS-GAMDy CS-GAMDy NMR data without NMR with NMR data data 0.52 0.75 0.73 0.78 0.72 0.73 0.69 0.80 0.66 0.73 0.72 0.79 0.72 0.71 0.72 0.82 0.79 0.76 0.78 0.81 0.54 0.10 0.62 0.81 0.61 0.73 0.72 0.78 0.70 0.36 0.67 0.79 0.43 0.71 0.66 0.81 0.62 0.77 0.74 0.78 0.59 0.77 0.73 0.80 0.73 0.77 0.74 0.79 0.56 0.76 0.74 0.76 0.62 0.72 0.71 0.78 0.48 0.70 0.71 0.80 0.43 0.72 0.63 0.80 0.48 0.62 0.55 0.78 0.60 0.67 0.70 0.79 19 Supplementary Table 12. Secondary structure score from NMR chemical shifts of ubiquitin comparative models under different refinement scenarios. Note that a low score is good. Template PDB ID ID % 1OTR 2GBK 1UD7 2GBJ 2GBM 1WY8 2DZI 2FAZ 1OQY 1WH3 1WX9 1Z2M 1MG8 1UEL 1IYF 1WE7 1TTN Average 96 92 91 90 90 39 39 37 36 36 34 33 32 32 30 28 26 GeNMR secondary structure score from NMR chemical shifts Initial Refined by Refined by Refined by model XPLOR CS-GAMDy CS-GAMDy with NMR without with NMR data data NMR data 48 72 44 40 72 108 76 28 68 48 56 32 88 72 48 32 48 32 32 24 96 160 72 32 44 88 32 32 104 160 48 28 88 76 40 32 40 44 44 28 52 44 32 32 52 44 40 28 60 44 36 28 24 96 36 28 68 56 36 28 72 72 52 28 60 96 48 28 63.8 77.2 45.4 29.9 20 Supplementary Table 13. Mean Pearson coefficient of correlation between model’s perresidue ASA and per-residue ASA predicted from backbone NMR chemical shifts of ubiquitin comparative models under different refinement scenarios. Template PDB ID ID % 1OTR 2GBK 1UD7 2GBJ 2GBM 1WY8 2DZI 2FAZ 1OQY 1WH3 1WX9 1Z2M 1MG8 1UEL 1IYF 1WE7 1TTN Average 96 92 91 90 90 39 39 37 36 36 34 33 32 32 30 28 26 Pearson coefficient of correlation between model’s ASA and ASA predicted from chemical shifts Initial model Refined by Refined by Refined by XPLOR with CS-GAMDy CS-GAMDy NMR data without with NMR NMR data data 0.58 0.41 0.61 0.57 0.31 0.04 0.39 0.61 0.54 0.54 0.57 0.63 0.42 0.16 0.38 0.57 0.62 0.42 0.63 0.53 0.42 0.08 0.42 0.63 0.48 0.16 0.57 0.59 0.42 0.25 0.53 0.60 0.38 0.25 0.44 0.59 0.57 0.51 0.61 0.61 0.63 0.50 0.60 0.62 0.58 0.50 0.63 0.61 0.62 0.01 0.62 0.66 0.49 0.17 0.62 0.59 0.43 0.15 0.41 0.61 0.57 0.06 0.59 0.63 0.55 0.51 0.55 0.55 0.51 0.28 0.54 0.60 21 Supplementary Table 14. Comparative models with different sizes and types of protein architecture along with the % identity to the comparative model template. Protein name PyJ Elongation Factor 1 GB3 Foxo4 Hamster PrP Vts1 NifU-like protein cg2496 Cadherin Adenylate kinase NFU1 homolog Size Folding class ID % to Template 4403 79 34 1F60 4117 91 /β 55 1P7E 1E17 1ZXH 2C6Y 18531 4675 56 150 /β /β 63 42 1B10 1XYX 4307 142 /β 95 2D3D 2FE9 6922 88 96 2LTL 2FFM 18487 119 /β 19 2KPT 1SUH 2KW7 1EDH 16569 4380 148 146 /β β 24 64 2CDN 1S3G 4840 201 /β 37 2M5O 1TH5 19068 97 /β 20 PDB ID Template PDB ID BMRB ID 1FAF 1GH6 1B64 22 Supplementary Table 15. Violations of dihedral angle restraints derived from NMR chemical shifts that were observed in comparative models with different sizes and types after their refinement under different refinement scenarios. Protein name PDB ID PyJ Elongation Factor 1 GB3 Foxo4 Hamster PrP Vts1 NifU-like protein cg2496 Cadherin Adenylate kinase NFU1 homolog Average 1FAF Violations of dihedral angle restraints derived from NMR chemical shifts Initial Native Refined Refined Refined model by by by XPLOR GAMDy GAMDy with without with NMR NMR NMR data data data 81 52 0 36 21 1B64 31 89 0 37 3 1P7E 1E17 1B10 2D3D 52 52 78 59 0 19 0 0 1 109 3 0 37 41 45 23 4 11 40 5 2LTL 81 61 22 85 10 2KPT 1SUH 78 49 120 69 39 1 64 52 1 15 2CDN 113 181 147 76 12 2M5O 79 37 8 69 5 68.5 58.2 30.0 51.4 11.5 23 Supplementary Table 16. Mean Pearson coefficient of correlation between experimental and predicted backbone NMR chemical shifts of comparative models with different sizes and types of protein architecture under different refinement scenarios. Protein name PDB ID PyJ Elongation Factor 1 GB3 Foxo4 Hamster PrP Vts1 NifU-like protein cg2496 Cadherin Adenylate kinase NFU1 homolog Average 1FAF Pearson coefficient of correlation between experimental and predicted backbone NMR chemical shifts Initial Native Refined Refined Refined model by by by XPLOR GAMDy GAMDy with NMR without with data NMR data NMR data 0.50 0.68 0.59 0.54 0.69 1B64 0.79 0.67 0.74 0.75 0.78 1P7E 1E17 0.43 0.58 0.72 0.71 0.55 0.28 0.54 0.61 0.67 0.70 1B10 0.38 0.50 0.46 0.43 0.42 2D3D 0.60 0.77 0.61 0.70 0.67 2LTL 0.43 0.65 0.55 0.41 0.64 2KPT 1SUH 0.55 0.76 0.79 0.62 0.61 0.66 0.61 0.68 0.74 0.71 2CDN 0.56 0.66 0.37 0.61 0.63 2M5O 0.52 0.81 0.66 0.56 0.81 0.55 0.69 0.55 0.58 0.68 24 Supplementary Table 17. GeNMR secondary structure score from NMR chemical shifts of comparative models with different sizes and types of protein architecture under different refinement scenarios. Note that a low score is good. Protein name PDB ID PyJ Elongation Factor 1 GB3 Foxo4 Hamster PrP Vts1 NifU-like protein cg2496 Cadherin Adenylate kinase NFU1 homolog Average 1FAF GeNMR secondary structure score from NMR chemical shifts Initial Native Refined Refined Refined model by by by XPLOR GAMDy GAMDy with without with NMR NMR NMR data data data 48 20 28 60 24 1B64 44 60 44 64 36 1P7E 1E17 60 64 20 40 56 156 36 56 20 56 1B10 40 28 44 56 24 2D3D 36 52 20 48 24 2LTL 124 48 92 132 52 2KPT 1SUH 144 100 60 92 128 92 156 84 80 88 2CDN 124 104 252 116 116 2M5O 100 32 76 100 68 80.4 52.0 89.8 82.5 53.5 25 Supplementary Table 18. Mean Pearson coefficient of correlation between model’s perresidue ASA and per-residue ASA predicted from backbone NMR chemical shifts of comparative models with different sizes and types of protein architecture under different refinement scenarios. Protein name PDB ID PyJ Elongation Factor 1 GB3 Foxo4 Hamster PrP Vts1 NifU-like protein cg2496 Cadherin Adenylate kinase NFU1 homolog Average 1FAF Pearson coefficient of correlation between model’s ASA and ASA predicted from chemical shifts Initial Native Refined Refined Refined model by by by XPLOR GAMDy GAMDy with NMR without with data NMR data NMR data 0.70 0.81 0.58 0.59 0.57 1B64 0.64 0.64 0.54 0.58 0.55 1P7E 1E17 0.45 0.61 0.55 0.72 0.48 0.20 0.50 0.48 0.51 0.54 1B10 0.63 0.73 0.53 0.59 0.63 2D3D 0.55 0.59 0.46 0.50 0.50 2LTL 0.43 0.55 0.21 0.36 0.45 2KPT 1SUH 0.48 0.60 0.75 0.58 0.27 0.54 0.48 0.60 0.56 0.58 2CDN 0.56 0.62 0.22 0.50 0.54 2M5O 0.57 0.64 0.27 0.49 0.66 0.57 0.65 0.39 0.52 0.55 26