Plant Propagation and Reproductive Mechanisms Summary
advertisement

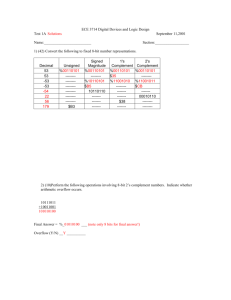
SBI3U Plants-Anatomy, Growth and Function By: Laura Pepper & Suzette McLean-Fletcher Teaching the Concept of Plant Reproductive Mechanisms and Propagation: A Summary Background Information: In higher plants there are mainly two methods of reproduction-sexual reproduction that involves the formation of gametes where seeds are used for propagation and asexual reproduction, in which there the vegetative parts are used for propagation. Sexual reproduction in plants involves male and female plant organs. The female structures involved in sexual reproduction are the stigma, the style and the ovary. The stigma is the sticky portion of the pistil that captures pollen. The style is long and slender and supports the stigma. The ovary is composed of one or more ovules and is responsible for housing the eggs. The male structures involved in sexual reproduction are the filament and the anther. The filament supports the anther which is responsible for storing and producing pollen. Pollination- the process by which pollen grain is transported from the anther to the stigma, results in sexual fusion. Wind, water, insects, birds, and small mammals all aid in the pollination of plants. The moist surface or chemicals on the stigma cause the pollen grain to germinate by growing a tube. The tube grows to eventually reach the ovary and penetrates to the ovule reaching the egg cell where a sperm nucleus splits in two fertilizes the egg (a zygote and combine with polar bodies to form the endosperm (stored fruit) - a nutritive tissue that sustains the embryo and seedling. The seed is the mature, fertilized ovule. After fertilization the ovule develop into the hard, water-resistant outer covering of the seed, called the testa, or seed coat. The zygote develops into the embryo, and the endosperm cells multiply and provide nutrition. The testa usually shows a scar called the hilum where the ovule was originally attached to the funicle. The micropyle of the ovule usually survives as a small pore in the seed coat that allows passage of water during germination of the seed. Seed germination results in new plants (propagation) SBI3U Plants-Anatomy, Growth and Function By: Laura Pepper & Suzette McLean-Fletcher The ability to produce new individuals asexually is common in plants. Under appropriate experimental conditions, nearly every cell of a flowering plant is capable of regenerating the entire plant. In nature, new plants may be regenerated from leaves, stems, or roots that receive an appropriate stimulus and become separated from the parent plant. In most cases, these new plants arise from undifferentiated parenchyma cells, which develop into buds that produce roots and shoots before or after separating from the parent. New plants can be produced from aboveground( via stem, leaves) or belowground horizontal runners (stolons of strawberries, rhizomes of many grasses), tubers (potato, Jerusalem artichoke, dahlia), bulbs (onion, garlic), corms (crocus, gladiola), bulbils on the shoot (lily, many grasses), parenchyma cells in the leaves (Kalanchoe, African violet, jade plant) and inflorescence (arrowhead). Vegetative propagation is an economically important means of replicating valuable agricultural plants asexually, through cuttings (stem, leaves, roots), layering, and grafting. Using a healthy plant, vegetative propagation is often faster, easier and cheaper than growing more plants from seeds. It takes six weeks to grow a tomato seedling to transplanting size, but you can root a stem tip cutting in half that time. In five minutes, you can multiply one petunia or coleus into several happy plants, and it will cost you nothing to start a new planting of grapes by sticking pruned branches into a bed of moist soil. A minority of flowering plants can produce seeds without the fusion of egg and sperm (known as parthenocarpy or agamospermy). This occurs when meiosis in the ovule is interrupted, and a diploid egg cell is produced, which functions as a zygote without fertilization. SBI3U Plants-Anatomy, Growth and Function By: Laura Pepper & Suzette McLean-Fletcher Advance Preparation/Teaching Ideas Prior Knowledge Before embarking on lesson students should have a good understanding of the structure of plant root, stem and leaves as well as factors affecting plant growth such as light, water, temperature and hormones (auxin and gibberellins). Teacher must review these concepts with students. A good way to do this is to show videos (you-tube) of these concepts and generate a class discussion. Advance Preparation Teacher will prepare and make ready the following facilities, equipment and materials to be used over the period of the lessons: Library- use of computers Classroom multi-media system Scalpels, small flower pots, beakers, spatulas, Rooting media, peas, water, Teaching ideas Before teaching the concept of plant reproductive systems and propagation, teacher should assess what students already know about it. This could be done using a KWL chart (students complete the KW portion; teacher collect, assess and keep chart for completion of L at end of lessons); diagnostic test or question and answer. Other strategies that could be used are: Video simulations/Gizmos (visual and auditory learners) Laboratory activities (Lab Stations) (kinesthetic, logical-mathematical learners) Computer Lab stations (Visual learners) Anticipation guide Corporative group strategies ( Interpersonal learners) Field Trip – visit to horticultural farm and /or orchard SBI3U Plants-Anatomy, Growth and Function By: Laura Pepper & Suzette McLean-Fletcher Curriculum Expectations Addressed (Grade 11 Biology, Plants: Anatomy, Growth and Function F2.4 Investigate various techniques of plant propagation (e.g., leaf cutting, stem cutting, root cutting, seed germination) [PR] F3.3 Explain the reproductive mechanisms of plants in natural reproduction and artificial propagation (e.g., germination of seeds, leaf cuttings, graphing of branches onto a host tree) Lesson Sequence Many lessons would be needed to teach this concept as it is two -part, detailed and involves several hands-on activities. Lesson 1: Sexual Reproduction in Plants Hook: A song on reproduction in plants URL: http://vimeo.com/1594115 A video will be shown to the class. Discussion will be generated. URL for video: http://vimeo.com/1594037?pg=embed&sec=1594037 Students will be divided into groups and go through a PowerPoint presentation (downloaded unto computers) which they will use to complete a worksheet on reproduction in plants. Students will go up to slide 37 for this lesson. URL from which PowerPoint and worksheet were taken: http://www.clickbiology.com/igcse-plant-reproduction-powerpointpresentation-worksheets/ (Scroll to bottom of page and click on link below student self study presentation for the PowerPoint and the link below worksheet for the worksheet) Lesson 2: Asexual Reproduction (Natural Vegetative Propagation) Students will watch video on asexual reproduction You-tube video 1: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=drcnTg7ZCoc Advantages of asexual reproduction Comparison of Sexual and Asexual Reproduction ( completion of worksheet) SBI3U Lesson 3: Plants-Anatomy, Growth and Function By: Laura Pepper & Suzette McLean-Fletcher Natural Propagation 1: Seed Germination Gizmo http://www.explorelearning.com/index.cfm?method=cResource.dspView&Re sourceID=637 (a) Teacher will group students by asking them to get into groups of 3 and assign each group to a computer. (b) Students will assemble themselves in groups of three and sit at assigned computer (c) Each student will be given a Student Exploration Sheet (as per Gizmo activity) and execute the activities on the sheet. (d) Teacher will walk around class to assist, check on progress and answer questions as they complete task. Lesson 4: Artificial Propagation Techniques: cuttings-stem, leaf, roots; grafting; layering Teaching Strategy: Computer Lab Stations, Anticipation guide http://www.youtube.com/watch?NR=1&v=GNnkYTQBlRo Cutting-stem http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ec5_9C5UIz0&feature=related Leaf cutting http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JN17smOLdsA Root cuttings http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8gwCLs8LoTs Grafting http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0jqlX6hqPno&feature=related Layering http://www.youtube.com/watch?NR=1&v=C-8pOPKyeLc Students will complete work sheet as they visit each computer station Lesson 5: Artificial Propagation Techniques continued Laboratory Activity on Artificial Propagation Students will work in groups Assessment: Lab report SBI3U Lesson 6: Plants-Anatomy, Growth and Function By: Laura Pepper & Suzette McLean-Fletcher Field Trip to horticultural farm/and or orchard Assessment: Worksheet (to be completed during trip) Written report Potential Student Difficulties and Possible Solutions Students may find it difficult to remember terminologies. A vocabulary board/wall will be made throughout the lesson and word puzzles used. Also students will dissect a flower, draw and identify parts. Students may have problems relating to vegetative structures of a plant. Actual examples will be shown and meristematic regions identified. Students may not understand how plants can be propagated artificially. Videos and video simulations will be shown and done. Students will also carry out laboratory activities. Differentiated Assessment Assessment FOR learning KWL chart Question and Answer Diagnostic Test Assessment AS learning Worksheets Lab reports Assessment OF learning Unit Test Culminating Activity Portfolio- students will maintain a portfolio throughout the concept. Culminating Activity: Students will choose how they want to do their culminating activity A journal entry on what they learned during lessons on Plant Reproductive Mechanisms and Propagation (Intrapersonal) Project-experiment demonstrating plant propagation (individual choice of presentation) (Logical, Kinesthetic) A song about what they learned (Musical) A poem/story(individual choice of presentation) (Linguistic) SBI3U Plants-Anatomy, Growth and Function By: Laura Pepper & Suzette McLean-Fletcher A PowerPoint presentation on what they learned that is taught to the class (Interpersonal) Teacher will device rubric for culminating activity which students will be given before they start activity Accommodations for ELL and IEP students Several of the differentiated teaching and assessment strategies suggested are able to help these students. Extensive use of visual aids are used- videos, PowerPoint Vocabulary wall and puzzles to help with difficulties in learning and remembering the terminologies unique to the concept Corporative strategies of working in groups, paired with non-ELL/IEP students Hands-on experimental activities Applications and Societal Issues/Implications 1. Horticulture- Artificial plant propagation is the primary technique by which this branch of science is carried out. Provides plants throughout the year. 2. Vital in maintaining varieties of plants and provides a way of keeping plants from extinction due to unfavourable natural environmental changes. 3. Agriculture- growth of fruit crops, herbaceous (vegetable) crops etc. 4. Critical in achieving and maintaining economic viability/stability for many countries, companies and persons. It is easier to grow plants from propagation than from seeds as plants grow faster and a lot of plants can be produced in negligible time. This means that fruiting time can be shortened sometimes by more than 2 years improving efficiency. Annotated References/Internet Addresses 1. http://vimeo.com/1594115 Song on reproduction in plants 2. http://vimeo.com/1594037?pg=embed&sec=1594037 Animation of plan reproduction 3. http://www.biologyreference.com/Re-Se/Reproduction-in-Plants.html Notes on sexual and asexual reproduction in plants used in the introduction and throughout the lessons SBI3U Plants-Anatomy, Growth and Function By: Laura Pepper & Suzette McLean-Fletcher 4. http://www.youtube.com/watch?NR=1&v=GNnkYTQBlRo You- tube – Vegetative and Asexual Reproduction/ propagation 5. http://www.explorelearning.com/index.cfm?method=cResource.dspView&Resour ceID=637 Gizmo used for seed germination assimilation. 6. The following sites provide short video demonstration on the various techniques of vegetative propagation. http://www.youtube.com/watch?NR=1&v=GNnkYTQBlRo Cutting-stem http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ec5_9C5UIz0&feature=related Leaf cutting http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JN17smOLdsA Root cuttings http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8gwCLs8LoTs Grafting http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0jqlX6hqPno&feature=related Layering http://www.youtube.com/watch?NR=1&v=C-8pOPKyeLc