NOTES + WORKSHEET on SALTS
advertisement
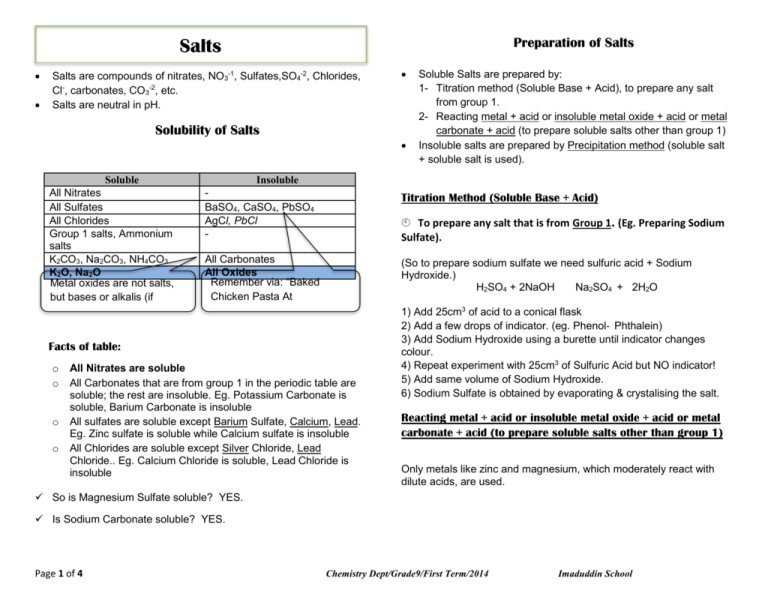
Preparation of Salts Salts Salts are compounds of nitrates, NO3-1, Sulfates,SO4-2, Chlorides, Cl-, carbonates, CO3-2, etc. Salts are neutral in pH. Solubility of Salts Soluble All Nitrates All Sulfates All Chlorides Group 1 salts, Ammonium salts K2CO3, Na2CO3, NH4CO3 K2O, Na2O Metal oxides are not salts, but bases or alkalis (if soluble) Insoluble BaSO4, CaSO4, PbSO4 AgCl, PbCl - Titration Method (Soluble Base + Acid) To prepare any salt that is from Group 1. (Eg. Preparing Sodium Sulfate). All Carbonates All Oxides Remember via: “Baked Chicken Pasta At Pastamania” (So to prepare sodium sulfate we need sulfuric acid + Sodium Hydroxide.) H2SO4 + 2NaOH Na2SO4 + 2H2O Facts of table: o o o o Soluble Salts are prepared by: 1- Titration method (Soluble Base + Acid), to prepare any salt from group 1. 2- Reacting metal + acid or insoluble metal oxide + acid or metal carbonate + acid (to prepare soluble salts other than group 1) Insoluble salts are prepared by Precipitation method (soluble salt + soluble salt is used). All Nitrates are soluble All Carbonates that are from group 1 in the periodic table are soluble; the rest are insoluble. Eg. Potassium Carbonate is soluble, Barium Carbonate is insoluble All sulfates are soluble except Barium Sulfate, Calcium, Lead. Eg. Zinc sulfate is soluble while Calcium sulfate is insoluble All Chlorides are soluble except Silver Chloride, Lead Chloride.. Eg. Calcium Chloride is soluble, Lead Chloride is insoluble 1) Add 25cm3 of acid to a conical flask 2) Add a few drops of indicator. (eg. Phenol‐ Phthalein) 3) Add Sodium Hydroxide using a burette until indicator changes colour. 4) Repeat experiment with 25cm3 of Sulfuric Acid but NO indicator! 5) Add same volume of Sodium Hydroxide. 6) Sodium Sulfate is obtained by evaporating & crystalising the salt. Reacting metal + acid or insoluble metal oxide + acid or metal carbonate + acid (to prepare soluble salts other than group 1) Only metals like zinc and magnesium, which moderately react with dilute acids, are used. So is Magnesium Sulfate soluble? YES. Is Sodium Carbonate soluble? YES. Page 1 of 4 Chemistry Dept/Grade9/First Term/2014 Imaduddin School Precipitation Method (Soluble salt+ Soluble salt) E.g. Reacting Zn with H2SO4 to prepare ZnSO4 To prepare any Insoluble salt. (Eg. Preparing Silver Chloride) AgNO3 (aq) + NaCl (aq) → NaNO3 (aq) + AgCl (s) Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + H2O(l) 1) Add Silver Nitrate with Sodium Chloride. 2) Filter out the precipitate, AgCl. 3) Wash the residue with distilled water. 4) Leave the residue to dry. To use precipitation, just make sure the salt you want to make is insoluble. The method requires you to use “Soluble salt + Soluble salt” so using the table, just find 2 salts that are soluble and contain part of the name. For example, I want to make an insoluble salt called “Calcium Sulfate”. Zn is added to H2SO4 until in excess to ensure no more H2SO4 is present. Then the mixture is filtered off to separate Zn from ZnSO 4. The filtrate (ZnSO4) is then placed in evaporating dish to evaporate most of water then it’s cooled after ZnSO4 crystals are formed. The crystals then filtered and squeezed between filter papers to dry. By Reacting Insoluble Base with Acid E.g. Reacting MgO with Acids MgO(s) + H2SO4(aq) → MgSO4(aq) + H2O(l) The same method as reaction of acid with metal is used, so refer to diagram and above explanation, substituting reactants and products. 1st, I need to find “Calcium‐~ ” that is soluble. And I also know that “All nitrates are soluble” So the 1st salt I use is Calcium Nitrate. Next, I need to find “something‐sulfate” that is soluble. I also know that all Group 1 salts are soluble.. So I can use Lithium Sulfate as my 2nd salt. By reacting 2 salts, I’ll get what I want, which is Calcium Sulphate!! Ca(NO3)2 + Li2SO4 → CaSO4 + 2LiNO3 By Reacting Carbonate with Acid E.g. Reacting CaCO3 with Acids K2CO3(s) + H2SO4(aq) →K2SO4(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) The same process is used as reaction of acid with metal, just that carbon dioxide is produced. Carbon dioxide can be tested by bubbling it into limewater which will turn limewater colourless to milky. Page 2 of 4 Chemistry Dept/Grade9/First Term/2014 Imaduddin School WORKSHEET on SALTS 6. Which pair of substances produces a precipitate when their aqueous solutions are mixed? MCQ Section A) barium nitrate, silver nitrate nitrate 1. In general, salts A) are ionic compounds B) contain hydrogen ions C) contain hydroxide ions D) turn litmus red 2. Which formula represents a salt? A )KOH B) KCl C) CH3OH A) CH3COOH B) sodium chloride, barium C) sodium nitrate, barium chloride D) sodium sulphate, barium chloride 7. From which mixture can the underlined substance be obtained by adding water, stirring and filtering? A) calcium carbonate and sodium chloride 3. Which pair of substances produce a precipitate when their aqueous solutions are mixed? A) sodium chloride and barium nitrate barium chloride B) sodium nitrate and C) sodium nitrate and silver nitrate barium chloride D) sodium sulphate and 4. Which salt can be prepared by an acid-alkali titration method? 5. A) ammonium sulphate B) copper(II) sulphate C) iron(II) sulphate D) zinc sulphate The table shows properties of four chlorides. Which is magnesium chloride? B) copper(II) sulphate and sodium chloride C) ethanoic acid and ethanol D) iron and magnesium 8. Which two reagents could be used to prepare the insoluble salt copper(II) carbonate? A) CuO(s) + Na2CO3(aq) B) CuO(s) + MgCO3(s) C) CuSO4(aq) + Na2CO3(aq) D) CuSO4(aq) + MgCO3(s) 9. The table shows the solubility of some salts of metal Y in cold water. What is metal Y? Page 3 of 4 Chemistry Dept/Grade9/First Term/2014 Imaduddin School A) barium B) magnesium C) lead D) sodium ………………………………………………………………………………… ……………..………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………… ……………..………………………………………………………………… 10. What is the best way of making zinc carbonate? A) Shake aq. zinc sulphate with aq. sodium carbonate. B) Shake aq. zinc sulphate with solid calcium hydroxide and bubble in carbon dioxide. C) Shake solid zinc hydroxide with aq.sodium hydroxide and bubble in carbon dioxide. ………………………………………………………………………………… ……………..………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………… ……………..………………………………………………………………… D) Shake solid zinc sulphate and solid calcium carbonate with water. Theory Section 11. Fertilisers are soluble salts containing one or more of the essential elements required for plant growth. (a) Ammonium chloride can be prepared by the reaction between aqueous ammonia and hydrochloric acid. Write an ionic equation for this reaction. [1] ………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………… (b) State suitable reagents and outline the experimental procedure by which a pure sample of the fertiliser potassium chloride could be prepared in the laboratory. [4] ………………………………………………………………………………… ……………..…………………………………………………………………. . ………………………………………………………………………………… ……………..………………………………………………………………… Page 4 of 4 Chemistry Dept/Grade9/First Term/2014 Imaduddin School