interpreting labels and prescription
advertisement

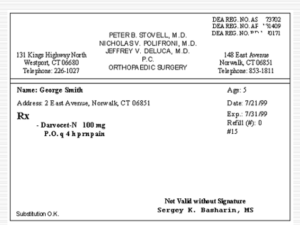
INTERPRETING LABELS AND PRESCRIPTION Objective To use a patient-centered approach to refine warning labels promoting the safe use of prescription drugs among patient. A. WORDS FOUND ON MEDICINE LABELS YOU MUST UNLOCK: Precaution- a warning Symptom- evidence of ailment such as coughs fever etc. Dosage- the amount of medicine to be taken by the patient at any one time. Formula- indicates the ingredients or contents of the medication. Manufacturer- the name of the company which manufactures the drug. Side effect- an effect of the medication such as dizziness, allergies, etc. Over- the counter Medicine- these are drugs which you can buy without a need to present a doctor’s prescription. Syrup- solution used in pharmacy. Suspension- the state in which particles of solid are mixed with fluid. Capsule- a gelatinous case containing a dosage of medicine. Drops- medication in liquid form. Sample label of a Product 1 Doctor’s Prescription Prescription may also be used as a short form for prescription drugs to distinguish from over-the-counter drugs. In reference to the entire system of controlling drug distribution (as opposed to illicit drugs), "prescription" is often used as a metaphor for healthy directions from a prescribing medical practitioner. History The concept of prescriptions dates back to the beginning of history. So long as there were medications and a writing system to capture directions for preparation and usage, there were prescriptions. Modern prescriptions are actually "extemporaneous prescriptions" from the Latin (ex tempore) for "at/from time". "Extemporaneous" means the prescription is written on the spot for a specific patient with a specific ailment. This is distinguished from a non-extemporaneous prescription which is a generic recipe for a general ailment. Modern prescriptions evolved with the separation of the role of the pharmacists from that of the physician [28]. Today the term "extemporaneous prescriptions" is reserved for "compound prescriptions" which requires the pharmacist to mix or "compound" the medication in the pharmacy for the specific needs of the patient. Predating modern legal definitions of a prescription, a prescription traditionally is composed of four parts: a "superscription", "inscription", "subscription" and "signature". The superscription section contains the date of the prescription and patient information (name, address, age, etc). The symbol "℞" separates the superscription from the inscriptions sections. In this arrangement of the prescription, the "℞" is a symbol for recipe or literally the imperative "take." This is an exhortation to the pharmacist by the medical practitioner, "I want the patient to have the following medication" [30] - in other words, "take the following components and compound this medication for the patient." The inscription section defines what the medication is. The inscription section is further composed of one or more of: a "basis" or chief ingredient indended to cure (curare) an "adjuvant" to assist its action and make it cure quickly (cito) a "corrective" to prevent or lessen any undesirable effect (tuto) a "vehicle" or "excipient" to make it suitable for administration and pleasant to the patient (jucunde) The "subscription" section contains dispensing directions to the pharmacist. This may be compounding instructions or quantities. The "signature" section contains directions to the patient [32] and is often abbreviated "Sig." [33] or "Signa." It also obviously contains the signature of the prescribing medical practitioner though the word "signature" has two distinct meanings here and the abbreviations are sometimes used to avoid confusion. 2 A. Symbols used by the Physicians which you must interpret Sig. -it is the abbreviation of signature. It is a part of a prescription which gives direction to be marked on the container of medicine. # -means number. Rx – is Recipe which means “take”, however, the original meaning of R is Eye of Horus, the god of healing. B. Commonly used medical abbreviations a) How the medicine is take O.U. - oculus uterque O.D. - oculus dexter O.S. - oculi sinister A.U. - auriculus uterque A.D. - auriculus dexter A.S. - auriculus sinister b) How much take in - both eyes - right eye - left eye - both ears - right ear - left ear cc = ml = the number of cc's or ml's to take. Remember that 5cc (or 5ml) is equal to one teaspoon. tsp = teaspoon tbs = tablespoon tab or cap = tablet or capsule gt = drop c) When to take it: qd = once a day qhs = once a day, at bedtime qam = once a day, in the morning qac = before meals qpc = after meals bid = twice a day tid = three times a day qid = four times a day q 8 hours = every 8 hours qod = every other day prn = as needed d) Common terms and abbreviations that you are likely to see in a child's chart include: 3 AGE = acute gastroenteritis (stomach virus) Allergic rhinitis = hay fever AOM or OM = acute otitis media (ear infection) ASD = atrial septal defect BMI = body mass index BOME = bilateral OME (fluid in both ears) BPD = broncho-pulmonary dysplasia CBC = complete blood count test CP = cerebral palsy FTT = failure to thrive FUO = fever of unknown origin FWLS = fever without localizing signs GER = gastroesophageal reflux HA = headache HSM = hepatospenomegaly (enlarged liver and spleen) IVH = intra-ventricular hemorrhage LAD = lymphadenopathy (enlarged lymph glands) LGA = large for gestational age MR = mental retardation Nocturnal enuresis = bedwetting OME = otitis media with effusion (fluid in the ear) Otitis externa = swimmer's ear ROP = retinopathy of prematurity SGA = small for gestational age Tinea Capitis = ringworm on the scalp Tinea Corporis = ringworm VSD = ventricular septal defect VUR = vesicoureteral reflux C. Layman’s term of various ailments compared to their Medical terms: Sore eyes (both eyes) - acute conjunctivitis (O.U.) Dizziness (spinning sensation) - vertigo Body Malaise 2˚ acute Otitis Media General Body weakness –constitutional Body Malaise 2˚ to Iron Deficiency anemia. Backache –Interscapular Nonspecifiec Myalgia. Shoulder pain- sternocleidaastoid strain Numbness of finger and/ or toes- peripheral Neuropathy D. Symptoms/signs with corresponding Medical terms to use Running nose and colds- coryza Soar throat or hoarseness- acute nasopharyngitis Coughing with ferver- acute bronchitis 4 Sample of Doctor’s Prescription 5