File - nikoo malek
advertisement

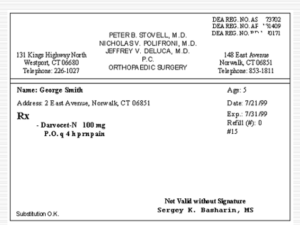
E-Prescription Distributed System E-prescription • E-prescribing is simply an electronic way to generate prescriptions through an automated data-entry process utilizing e-prescribing software and a transmission network which links to participating pharmacies Challanges Both patients and health care professionals benefit from system. Improved patient safety: • Problems resulting from poorly hand-written prescriptions are eliminated • Access to patient's medical history • Alert systems • Shorter wait for the customer at the pharmacy • No paper prescription to keep track of Convenience for the healthcare professionals: • Offers true provider mobility • Improves reporting ability Process • Patient visits a physician • Physician then writes a prescription based on examination • Physician transmits the prescription to an appropriate pharmacy using a computer or a hand-held device such as a Blackberry • Software routes the prescription through the provider’s secure server to the pharmacy • E-prescription software is able to automatically create and store electronic records Process for Creating and Managing a Prescription Electronically • System infrastructure may be based entirely on a) a device, or on a server located in the local environment b) remotely through an application service provider (ASP) environment. Process for Creating and Managing a Prescription Electronically (cont.) E-prescription Process Map: • Steps involved in e-prescription creation and management are illustrated below Sign on Identify patient Review Current pt.date Select drug Enter parameters Signature Review alerts and advisories Print or send Rx Pharmacy review and process Process for Creating and Managing a Prescription Electronically (cont.) Signing On • A user of the system—clinician, staff, etc.—signs in by performing some sort of authentication to prove his or her identity. Identifying the Patient • In order for the e-prescribing process to begin, the clinician needs to identify the patient within the e-prescribing system. Review Patient Data • After the identifying the patient in the system the clinician will have access to the patient medical history. Process for Creating and Managing a Prescription Electronically (cont.) Selecting the Drug, Entering Parameters, and Signing Functions performed by E-prescribing systems: • Review patients’ current medication list and medication history information • Work with an existing medication • Prescribe or add new medication • Complete the prescription • Output prescriptions • Other functions Process for Creating and Managing a Prescription Electronically (cont.) Review Alerts and Advisories • The prescription information generally consists of a list of drugs, mode of administration, quantity and period of administration. • drugs that a patient is allergic to are kept in a database. • patient’s expenditure would be given to the patient before discharge from hospital • After diagnosis, the doctor prescribes the right quantity and dosage of the medication. • Where a drug is not available, it is reordered from the store or the manufacturer and dispensed to patient. Process for Creating and Managing a Prescription Electronically (cont.) /Check drug Items on prescription list Dispensing Checking – drug items /Not all drugs Item on list checked /Dispensed reordering Administering /Drug not in stock or below reorder level Figure 1 System Architecture Application architecture design and deployment characteristics: • zero-layer • three-tier • 99.9% availability and connectivity • • User Interface Tier The presentation tier has application code Application code is able to render WML and JSP pages to – – – – • • mobile devices pocket PC PDAs desktop, and Smart Phone The pages are viewable through the use of PC Internet Explorer, Web and WAP browser. The WAP browser will suffice to display database queries submitted to the server. System Architecture(Cont.) As an example In Figure 2, the client is thin and typically includes a graphical users’ interface written in WML that runs from a micro browser. Middleware Client Jsp /Services Rendering Engine WML Web/ Wap browser User eHealth Services ODBC JDBC Database Figure 2 Communication Route System Architecture(Cont.) Application Server Tier • The application server tier provides access to data tier implements business logic data validation responsible for all database transaction handling • client and e-Prescription application communication is handled by HTTP and the wireless application protocol • e-Prescription server and the application server tier communication is handled by HTTP and the wireless application protocol • application server and database communication is performed via JDBCODBC drivers. System Architecture(Cont.) Database Server Tier • The data layer stores and maintains: data for the system security policy network security protocols other techniques (such as firewall, password control, secure access, antivirus, and etc) • When medications are prescribed to a patient, the details are recorded in the central server. • The pharmacist is able to retrieve a patient’s medication information in order to dispense the appropriate drugs as soon as the patient completes his encounter with the doctor. • A patient’s medication information includes: patient’s identity, drug identity, method of administration, etc. System Architecture(Cont.) The medication is monitored by the pharmacist Figure 3 depicts patient’s medication details retrieved by a physician. Figure 3 Conclusion The e-Prescription allows physicians to capture and view patients’ medication details avoids problems of prescriptions by pharmacists . The access to the patient’s medical records real-time improves patient’s care by ensuring that correct information such as the appropriate medication to be administered is retrievable and legible. In addition, the application improves efficiencies of health care services by eliminating time-consuming call-backs that may be associated with treatment processes. References 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Ikhu-Omoregbea, Nicholas. "Formal modeling and design of mobile prescription applications." 2008. Department of Computer and Information Sciences Covenant University . 15 Apr. 2009 <www.jhidc.org/index.php/jhidc/article/viewPDFInterstitial/15/49> Department of Health and Ageing. “Consultancy in Electronic Prescribing and Dispensing." June 2008. Australian Government. 15 Apr. 2009 <www.health.gov.au/internet/main/publishing.nsf/Content/.../$File/DOHA08-ePrescribing%20reportFinal290708.pdf> The eHealth Initiative and The Center for Improving Medication Management. "Electronic Prescribing: Becoming Mainstream Practice ." June 2008. eHelath Initiative. 15 Apr. 2009 <www.jhidc.org/index.php/jhidc/article/viewPDFInterstitial/15/49> Physician Assessment Study. Southeast Michigan ePrescribing Initiative (SEMI), March 2008.eHealth Initiative Blueprint: Building Consensus for Common Action. October 2007. <www.ehealthinitiative.org/blueprint> Industry Facts-at-a-Glance. 2008. National Association of Chain Drug Stores. <http://www.nacds.org/wmspage.cfm?parm1=507> National Progress Report on E-Prescribing. 2007. <http://www.surescripts.com/pdf/National-Progress-Report-on-EPrescribing-1.pdf> E-Prescribing Overview. 2008. Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. <http://www.cms.hhs.gov/eprescribing/>