SI Session 09/16/15 Chapter 6 Questions a) be a prokaryotic cell b
advertisement

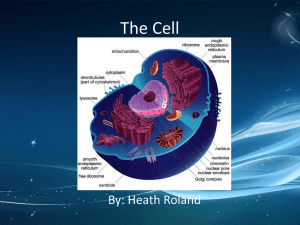
SI Session 09/16/15 Chapter 6 Questions Consider two cells with the same volume but with very different surface areas due to differences in their shapes. The cell with the larger surface area is likely to __________. a) be a prokaryotic cell b) be involved in the rapid uptake of compounds from the cell's environment c) be nearly spherical in shape d) be buried deep in the interior of an organism e) have a very high metabolic rate A particular cell has a nucleus and chloroplasts in addition to the fundamental structures required by all cells. Based on this information, this cell could be __________. a) a yeast (fungus) cell b) a cell from the intestinal lining of a cow c) a photosynthetic protist cell or a plant cell d) a bacterium What is the functional connection between the nucleolus, nuclear pores, and the nuclear membrane? A) Membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum is produced in the nucleolus and leaves the nucleus through the nuclear pores. B) The nucleolus contains messenger RNA (mRNA), which crosses the nuclear envelope through the nuclear pores. C) The nuclear pores are connections between the nuclear membrane and the endoplasmic reticulum that permit ribosomes to assemble on the surface of the ER. D) Subunits of ribosomes are assembled in the nucleolus and pass through the nuclear membrane via the nuclear pores. E) None of the listed responses is correct. A dish of animal cells was grown in the presence of radioactive phosphorous. The phosphorous largely ended up in nucleotides inside the actively growing animal cells. In which cellular structure or structures would you predict the majority of the radioactive phosphorous to accumulate? A) the Golgi apparatus B) the rough endoplasmic reticulum C) the nucleus D) the rough endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi E) Golgi and nucleus Which of the following groups is primarily involved in synthesizing molecules needed by the cell? a) lysosome, vacuole, ribosome b) smooth endoplasmic reticulum, ribosome, vacuole c) ribosome, rough endoplasmic reticulum, smooth endoplasmic reticulum d) rough endoplasmic reticulum, lysosome, vacuole e) vacuole, rough endoplasmic reticulum, smooth endoplasmic reticulum Which of the following organelles is UNLIKELY to show enhanced abundance in pancreatic cells that secrete large amounts of digestive enzymes? A) Golgi apparatus B) Transport vesicles C) Rough endoplasmic reticulum D) Free cytoplasmic ribosomes E) All of the listed organelles will show an increase in pancreatic cells secreting digestive enzymes Which of the following categories best describes the function of the rough endoplasmic reticulum? a) breakdown of complex foods b) information storage c) manufacturing d) structural support of cells e) energy processing Which of the following sequences represents the order in which a protein made in the rough endoplasmic reticulum might move through the endomembrane system? a) nuclear envelope -> lysosome b) plasma membrane -> nuclear envelope c) Golgi apparatus -> mitochondria d) Golgi apparatus -> lysosome e) Lysosome -> plasma membrane Which of the following five membranes is most likely to have a lipid composition that is distinct from those of the other four? a) endoplasmic reticulum b) lysosome membrane c) plasma membrane d) mitochondrial outer membrane e) Golgi apparatus 1. ________ is composed of DNA and protein. A) A mitochondrion B) A flagellum C) A centriole D) Chromatin E) A ribosome 2. Where is calcium stored? A) mitochondria B) smooth endoplasmic reticulum C) centrioles D) rough endoplasmic reticulum E) microtubules 3. Which of these structures is unique to plant cells? A) mitochondrion B) peroxisome C) flagellum D) central vacuole E) nucleoid region 4. Which of the following is not considered part of the endomembrane system? A) nuclear envelope B) chloroplast C) Golgi apparatus D) plasma membrane E) ER 5. Cells of the pancreas will incorporate radioactively labeled amino acids into proteins. This "tagging" of newly synthesized proteins enables a researcher to track the location of these proteins in a cell. In this case, we are tracking an enzyme that is eventually secreted by pancreatic cells. Which of the following is the most likely pathway for movement of this protein in the cell? A) ER → Golgi → nucleus B) Golgi → ER → lysosome C) nucleus → ER → Golgi D) ER → Golgi → vesicles that fuse with plasma membrane E) ER → lysosomes → vesicles that fuse with plasma membrane 6. What is a lysosome? What environment do lysosomal enzymes work best in? What’s programmed cell death? membranous sac of hydrolytic enzymes that can digest macromolecules; acidic autophagy and phagocytosis; apoptosis 7. Difference b/w prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA? Ribosomes? Circular vs linear; prokaryotes tend to use all DNA. Different subunits (explains why mitochondrial and chloroplast ribosomes are diff) 8. What network of fibrous proteins helps to maintain the shape of the nucleus? Nuclear lamina 9. What can the Golgi add to make sure cells stick together? (she wrote it on the board) Hyaluronic acid 10. Special type of peroxisome found in plant seeds? glyoxysome