DNA/RNA/Protein Synthesis Test Review
advertisement

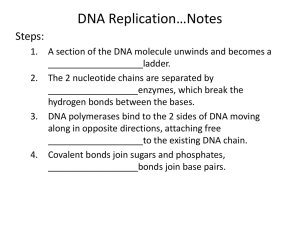
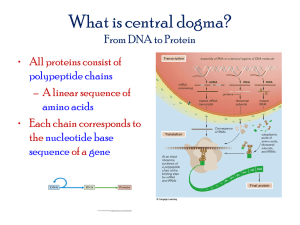
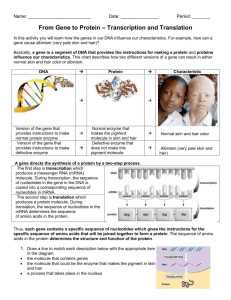
DNA/RNA/Protein Synthesis Test Review Part 1: Matching: Match the term in the first column with its corresponding description in the second column. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Nucleotide C Double Helix D Deoxyribose E Codon A Anticodon B A. group of three sequential bases of mRNA b. group of three sequential bases of tRNA c. repeating subunits/building blocks of DNA and RNA d. spiral shape of DNA e. sugar found in DNA Part 2: Multiple Choice: Choose the most correct answer. 6. DNA replication results in two DNA molecules, a. Each with two new strands b. One with two new strands and the other with two original strands c. Each with one new and one original strand. d. Each with two original strands 7. Unlike DNA, RNA contains… a. Adenine b. Uracil c. Guanine d. Thymine 8. Nitrogen bases are held together by weak bonds called… a. Hydrogen bonds b. Covalent bonds c. Ionic bonds d. Peptide bonds 9. A DNA molecule is unzipped/split in two by what type of enzyme? a. Polymerase b. Enzymease c. Helicase d. Aspartic acid 10. The sugar found in RNA is... a. Sucrose b. Deoxyribose c. Fructose d. Ribose 11. Where in the cell is the site of transcription? a. Cytoplasm b. Ribosome c. Nucleus d. Endoplasmic Reticulum 12. Where in the cell is the site of translation? a. Vacuole b. Ribosome c. Nucleus d. Endoplasmic Reticulum 13. This type of bond holds an amino acid/protein together. a. Hydrogen b. Covalent c. Peptide d. Ionic 14. Concerning complimentary base pairing, Uracil is match with… a. Thymine b. Adenine c. Cytosine d. Guanine 15. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? a. 3 b. 6 c. 9 d. 12 16. Transporting amino acids to ribosomes for assembly into needed proteins is the function of… a. DNA b. tRNA c. mRNA d. rRNA 17. Which of the following is not a type of RNA? a. Ribosomal RNA b. Messenger RNA c. Transfer RNA d. Protein RNA 18. Which of the following most accurately describes the structure of a nucleotide? a. Protein, phosphate group, nitrogen base b. Amino acid, sugar, nitrogen base c. Phosphate group, sugar, carbohydrate d. Sugar, phosphate group, nitrogen base 19. Before a cell divides, it must duplicate its DNA in a process known as… a. Replication b. Translation c. Transcription d. Transformation 20. The process by which polypeptide/proteins are assembled using the mRNA code is…. a. Replication b. Translation c. Transcription d. Transformation 21. The process by which the genetic code of DNA is copied into a strand of mRNA is... a. Replication b. Translation c. Transcription d. Transformation Part 3: Short Answers: Use the charts below to help you with questions 23. They will both give you the same answer. First, take the following DNA strand and write the corresponding mRNA strand on the line. TAC/ GCA/TTA/CGT/GCA/ACT 22. _______AUG/CGU/AAU/GCA/GCU/UGA________________________________________________ _ Next, write amino acid sequence that corresponds with your answer to 22. 23. ______MET/ARG/ASN/ALA/ALA/STOP_________________________________________________ _ Finally, write the tRNA that corresponds to your answer in 23. 24. __________UAC/GCA/UUA/CGU/CGA/ACU_____________________________________________ _ 25. Compare and contract DNA and RNA by filling in the chart below. DNA RNA Sugar deoxyribose ribose Bases (4 each) ACGT ACGU 2 1 # of strands Location in the cell nucleus Nucleus and ribosome 26. Compare and contrast the three different types of RNA Name Function mRNA messenger To take the code from DNS to the ribosomes tRNA transfer To bring amino acids to the ribosomes, match up the anti-codeon with the mRNA codon rRNA Ribosomal Make up ribosomes 27. Briefly explain what happens in transcription and where it occurs. Transcription occurs in the nucleus. The code from DNA is transferred via complementary base pairs to mRNA. 28. Briefly explain what happens in translation and where it occurs. Translation occurs at the ribosomes when the tRNA anti-codon connects to the mRNA codon. On the other end of the tRNA is an amino acids. The amino acids eventually connect to form a polypeptide chain which later becomes a protein. 29. Explain why a change in the DNA sequence may or may not causes a different protein (mutation) to be created. It the change in the DNA causes a change in the amino acid which is coded for then there can be a change in a protein which can cause a problem. If the new codon codes for the same amino acid then there will not be a problem. 30. If the 1st C was deleted in the DNA Sequence: TAC ATG CCG GCA, what would happen? (Hint: transcribe the DNA into mRNA) AUG/UAC/GGC/CGU: original AUU/ACG/GCC/GU: With deletion Different amino acid sequence would result 31. Explain the 3 aspects of processing that need to occur before mRNA can leave the nucleus. Poly A tail a the 3’ end 5’ cap introns taken out and exons “glued” together