World Cities 2
advertisement

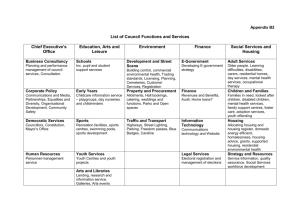
World Cities 2 Homework from Friday: 1. When did world cities emerge and why? 2. Look at your notes, Name at major world cities at the top of the global hierarchy. 3. What is meant by Cultural Authority in world cities. 4. What is meant by economic Authority in World Cities? 5. What are TNC’s & why do they generally locate in World Cities? 6. What features of modern global networks foster the growth of World Cities? 7. Where does Sydney fit in the hierarchy of world cities? 8. What is happening to small rural centres at the bottom of the hierarchy of settlements? From last lesson 9. Examine the results of urban growth in large Cities. (Page 115) Process -------- Social & Spatial ---- Land use Change and expansion response Urbanisation Urban Dynamics Results Consider the difference between the developed and developing world 10. Examine the role of Urbanisation in Cultural Change. Page 115 Look at the list of TNC’s What goods and/or services do they provide? Where are the head offices ? In what other ways have Cultural changes taken place? What is culture? And list some elements of a culture. What is cultural homogenisation? How has Globalisation promoted it? What is cultural imperialism? How has globalistion promoted it? Note global trends in the arts, music, language, religion, etc. Glitteratti is a term that might be applied to the famous trend setters of a society. Who are they and how do they influence global trends? So how do Global cities attract cultural Authority? Facilities for the arts, education, libraries and information storage, Entertainment Venues, Sports Venues, centres of Legal authority, Media Concentrations, information nodes (internet,phone,satillite,etc.), Religious Centres, centres of cuisine, Focus of Society events, Fashion centres Following on from Fridays lesson: 11. Discuss the impact of deregulation and liberalisation of global capital? TNC’s, decline of national financial influence, decline of communism global markets for capital, internationalisation of labour, separation of command-control –production-consumption. Telecommunications increases connectivity, Increase in mobility of capital, New Capital flows from resource rich countries, Increase in competition between financial centres ( page 116-120) 12. How does the importance of the stock market and headquarters of TNC’s influence the importance of a global city as a command centre? (page 120) 13. Describe the changes in capital flows in the past 40 years.( Page 122) transfer of funds from Developed world to developing world, decline of old industrial centres, new industrial areas in the developing world command and control in developed world, production in developing world. Increased consumption in developing world. 14. How has this influenced world cities in developed and developing world? Rise of resource processing, manufacturing, and services in developing cities Decline in old world cities, this might be taken up by new services and technology 15. What is meant by the term connectivity and how does it influence world cities? Measure of knowledge, information and direction of flow – service industries Information technology, focii of info. Centres, speed of info transfer, linguistic elements, Look at list and Diagram on page 122 16. Copy the Figure 2.1.16 Explain in your own words what it means? (page 123) command and controlnational centresregional centres 17. Look at Figure 2.1.3 Rankings of Stock Exchanges. What does this tell us about Global cities? 18. Look at Figure 2.1.4 Headquarter of TNC’s What does this tell us about Global cities? 19. Describe Australia’s Network of Global Cities (page 124) 20. Summarise London as a Global City (Page 125-126) Qu 9. Results of Urban Growth on large cities Urbanisation Urban Dynamics Results Process -------- Social & Spatial ---- Land use Change and expansion response Social Responses of U.G. Spatial Responses of U.G. Socio-Economic Class Rich Top 5% of Pop’n 70% of wealth Power, Authourity Command and Control Exclusive suburbs, Gated Gated communities, exurban settlements land use leaders of prime sites Middle Class Top 10% of Pop’n Technologically enhanced Aspirational, Upwardly Mobile Gentrification, some of the exclusive suburbs better urban sprawl white flight Urban renewal Lower Middle Class Salarymen, 30% of population Service Industry and Public Service Deskilled as technology provides Alternatives Urban intensifcation, Urban Sprawl Urban decline Working Class Wage and Contract workers 40% of Pop’n Deskilled, marginalised workers Poor quality Urban Sprawl Units & multifamily housing Urban decay and deurbanisation Underclass Unemployed, semi employed, Welfare cases and undocumented 15% of Population Unskilled marginalised population Ghetto formation, Ethnic Neighbourhoods inner-mixed core areas Urban decay