Experimental details - The Royal Society of Chemistry
advertisement

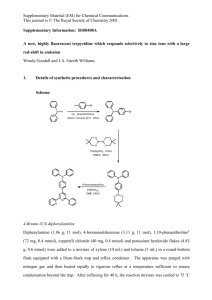
# Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications # This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2004 Electronic Supplementary Information Direct arylation of aromatic C-H bonds catalyzed by Cp*Ir complexes Ken-ichi Fujita,* Mitsuru Nonogawa and Ryohei Yamaguchi* a Graduate School of Human and Environmental Studies, Kyoto University, Kyoto 606-8501, Japan b Graduate School of Global Environmental Studies, Kyoto University, Kyoto 606-8501, Japan Experimental Section: General: All reactions were carried out under an atmosphere of argon. NMR spectra were recorded on JEOL A-500 and EX-270 spectrometers. Gas chromatography analyses were performed on a Shimadzu GC-14A gas chromatograph with capillary column (Shimadzu CBP1-M25-025). Benzene was distilled from Na / benzophenone. Anisole and toluene were distilled from CaH 2. The catalysts [Cp*IrHCl]2,1 [(Cp*Ir)2(-H)3]Cl,2 [Cp*IrCl2]2,3 Cp*Ir(cod)4 and [IrCl(cod)]25 were prepared according to literature methods. Other reagents were used as obtained from commercial sources. Procedure for the arylation of benzene with 4-iodoanisole under various conditions shown in Table 1: Under an atmosphere of argon in a heavy-walled glass reactor, iodoanisole (0.50 mmol), catalyst (5.0%Ir), KOtBu (1.65 mmol) and benzene (20 mmol) were placed. The reactor was sealed, and the mixture was stirred at 80 ˚C for 30 (or 17) hours. The yield of 4-methoxybiphenyl was determined by GC analysis using decane as an internal standard. Procedure for the arylation of benzene with various aryl iodides shown in Table 2: Under an atmosphere of argon in a heavy-walled glass reactor, aryl iodide (0.50 mmol), [Cp*IrHCl]2 (5.0 or 10.0%Ir), KOtBu (1.65 mmol) and benzene (20 mmol) were placed. The reactor was sealed, and the # Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications # This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2004 mixture was stirred at 80 ˚C for 30 hours. The yield of product was determined by GC analysis using decane as an internal standard. The product was isolated by Kugelrohr distillation and identified by spectral comparison with literature data.6 Procedure for the arylation of anisole and toluene with iodobenzene shown in eqn. 1 and 2: Under an atmosphere of argon in a heavy-walled glass reactor, iodobenzene (0.50 mmol), [Cp*IrHCl]2 (10.0%Ir), KOtBu (1.65 mmol) and anisole or toluene (20 mmol) were placed. The reactor was sealed, and the mixture was stirred at 80 ˚C for 30 hours. The yield of product was determined by GC analysis using decane as an internal standard. References 1. Gill, D. S.; Maitlis, P. M. J. Organomet. Chem. 1975, 87, 359. 2. White, C.; Oliver, A. J.; Maitlis, P. M. J. Chem. Soc., Dalton Trans. 1973, 1901. 3. Ball, R. G.; Graham, W. A. G.; Heinekey, D. M.; Hoyano, J. K.; McMaster, A. D.; Mattson, B. M.; Michel, S. T. Inorg. Chem. 1990, 29, 2023. 4. Booth, B. L.; Haszeldine, R. N.; Hill, M. J. Organomet. Chem. 1969, 16, 491. 5. Herde, J. L.; Lambert, J. C.; Senoff, C. V. Inorg. Synth. 1974, 15, 18. 6. (a) The Aldrich Library of 13 C and 1H FT NMR Spectra volume 2. (b) Old, D. W.; Wolfe, J. P.; Buchwald, S. L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 9722. (c) Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, D.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, T. Y.; Zhang, H. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2003, 1, 1643.