acute angle - Community School 13
advertisement
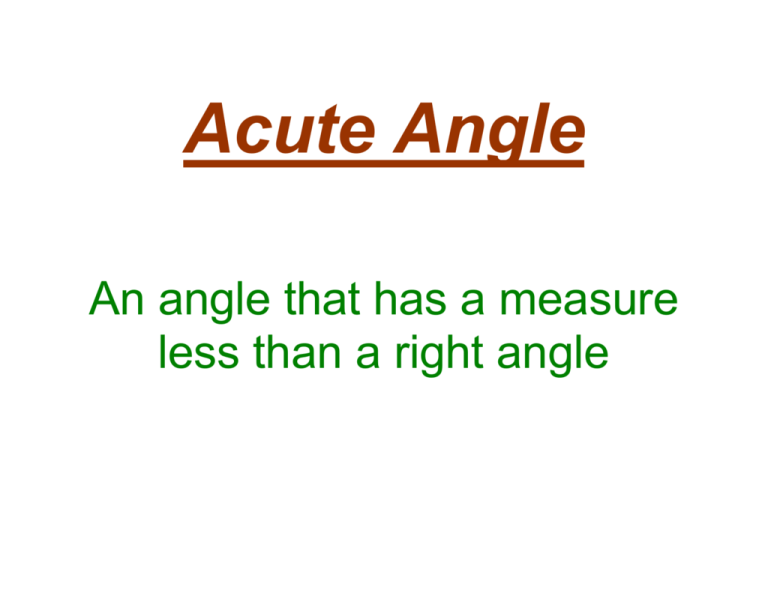
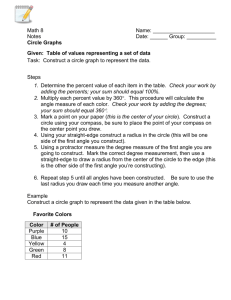
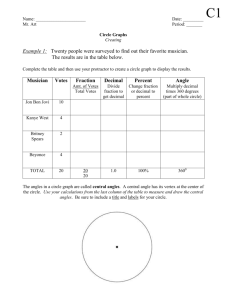
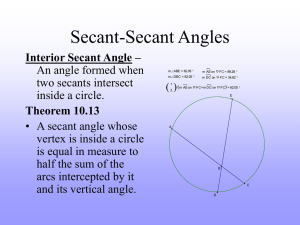
Acute Angle An angle that has a measure less than a right angle Addend Any of the numbers that are added Angle A figure formed by two rays that meet at a common end point Area The number of square units needed to cover a flat surface Array An arrangement of objects in rows and columns Average One way to find a number that best represents all the numbers in a set Bar Graph A way to show information that uses bars to stand for data Benchmark A number used as a point of reference Calendar A table that shows the days, weeks, and months of a year in order Capacity The amount a container can hold when filled Cardinal A number that tells how many Centimeter (cm) A unit of length in the metric system Certain An event that will always happen Circle graph A graph in the shape, circle that shows data as a whole up of different parts Closed figure A shape that begins ends at the same point Congruent Figures Figures that have the same size and shape Cumulative Frequency The sum of the frequency of data as they are collected Cup (c) A customary unit for measuring capacity Decimal A number that uses place value and a decimal point to show values less than one, such as tenths and hundredths Decimal point A period used in decimal numbers to separate the whole number part from the decimal part Decimeter (dm) A unit of length in the metric system Denominator The number below the bar in a fraction. It tells the total number of equal parts Difference An answer to a subtraction Dimension A measure in one direction Dividend The number that is being divided in a division problem Divisor The number that divides the dividend Equation A number sentence with an equals sign to show that two amounts are equal Factor A number that is multiplied by another number to find a product Foot (ft) A unit of length in the customary system Interval The distance between two numbers on the scale of a graph Inverse Opposite operations, such as multiplication and division, that and each other Line A straight path in a plane, extend in both directions with no endpoints Line graph A graph that uses a line to show how data change over a period time Line plot A diagram that shows the frequency of data as they are collect Line segment A part of a line between two endpoints Line symmetry A figure has line symmetry when it can be folded about a line so that its two parts are identical Liter (L) A metric unit of capacity Mass The amount of matter of an object Mean One way to find a number that best represents all the numbers in a set Median The middle number in an ordered series of numbers Mode The number that is listed the most often in a set of data Multiple A number that is the product of a given number and another whole Net A two-dimensional pattern of a threedimensional figure Nominal A number that names something Numerator The number above the bar in a fraction. It tells how many parts are being considered Obtuse angle An angle that has a measure greater than a right angle Ordinal A number that tells position or order Outcomes Possible results of an experiment Pint (pt) A customary unit for measuring capacity Plane A flat surface that extends will end in all directions Pint The name of a location on an object and in space Predict To tell what will happen when doing experiments Probability The chance that a given event will occur Product The answer to a multiplication problem Range The difference between the greatest and least numbers in a set of data Scale A series of numbers placed at fixed distances on a graph to help label the graph Square unit The unit used to measure area Standard Form A way to write numbers by using digits Sum The answer to an addition problem Survey A collection of data that lists choices Tally table A way to organize data that uses tally marks to show how often something Happens Volume The measure of the space a solid figure occupies Axis Either of two lines drawn perpendicular to each other in a graph. Center The point from which all points in a circle are equally distant Chord A line segment that connects two points the circle Common Denominator A number that is the denominator of two or more fractions Common Factor A number that is a factor of or more given numbers Compatible numbers Numbers which are to compute with mentally Compensation Adjusting one number of an operation to make computations easier and balancing the adjustment by changing the of number Composite number A whole number great than one that has more than two factors Equal ratios Ratios that show the same comparison Formula An equation that states a rule Greatest Common Factor (GCF) The greatest number that is a factor of two or more numbers Negative Integers Integers that are less than zero Opposites Numbers that are the same distance away from zero Origin The point where the two axes of the coordinate plane intersect. The origin is represented by the ordered pair Outcome A result in an experiment Overestimate The result of using larger numbers to estimate a sum or product. The estimate is larger than the actual answer