shown corresponding
advertisement

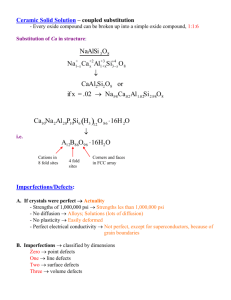
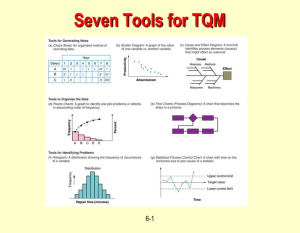
SQC HW#4 Eric Klopp 3/9/05 14. What information is provided by the operating characteristic curve of a control chart? The operating characteristic curve provides information such as the process mean and the probability of that mean falling between the control limits. 18. Consider the control chart shown here. Does the pattern appear random? The pattern does, in fact, appear to be random. 22. Sketch warning limits on the control chart in exercise 4-19. Do these limits indicate any potential out-of-control conditions? There does appear to be several points that exceed the warning limit. This could quite possibly indicate an out-of-control condition. 23. Apply the Western Electric rules to the control chart presented in exercise 4-19. Would these rules result in any out-of-control signals? Two of the rules apply to this exercise: Two out of three consecutive points plot outside the two-sigma warning limit, and Four out of five consecutive points plot at a distance of one-sigma or beyond from the center line. These would definitely result in out-ofcontrol signals. 24. Consider the time-varying process behavior shown in Figs. a-e. Match each of these several patterns of process performance to the corresponding x and R charts shown in Figs. 1-5. a) #2 b) #4 c) #5 d) #1 e) #3 SQC HW#4 Eric Klopp 3/9/05 26. A car has gone out of control during a snowstorm and struck a tree. Construct a cause-and-effect diagram that identifies and outlines the possible causes of the accident. Driver error Reckless driving Passenger error Distracting driver Fatigue/ Inattentiveness Struck a tree Mechanical Failure Car failure wind and ice Slippery roadway Fierce act of God Outside forces 29. Develop a flow chart for the process that you follow every morning from the time you awake until you arrive at your school. Identify the value-added and nonvalue-added activities. to living room Value added Non-value added Shut off alarm put on coat and back pack walk to school do business take shower wake up to bathroom to get dressed living room to shower put on walk to coat and school back pack to bedroom get dressed check email to make eat kitchen breakfast put on walk to coat and school back pack SQC HW#4 Eric Klopp 3/9/05 31. Develop a check sheet to record “defects” you have in your personal life. Use the check sheet to keep a record of these “defects” for one month. Use a Pareto chart to analyze these data. What are the underlying causes of these “defects”? Defect Overeating Not doing homework Skipping class Watching too much tv Snacking between meals Picking on roommates Leaving dishes on counter top Forgetting to take out trash Monthly Data Check Sheet Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 ||| | ||||| | || Week 4 || |||| | ||| |||||| |||| ||| || |||| || ||| ||||||| ||| | || | |||| || | | | Pareto Chart for Monthly Data 18 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 wa tc hi ng to pi o ck m in uc g h o n sn tv ro ac om kin m g at be es tw ee n le m av ea in ls g o di ve sh re es at fo on in rg g et co t in un g te to rt ta op ke ou no tt td ra oi sh ng ho m ew or sk k ip pi ng cl as s 0 There are several underlying causes of these “defects”, but I think the main ones are stress and laziness. The stress of getting school work done and performing well may cause the poor eating habits, which are considerable “defects.” The laziness factor causes results like watching too much tv and leaving the dirty dishes on the kitchen counter top. This type of analysis can be beneficial to observe defects that may go unnoticed as well as make it easier to think of solutions to prevent these defects from occurring.