3-7 Similar Triangles - MOM 213-215
advertisement
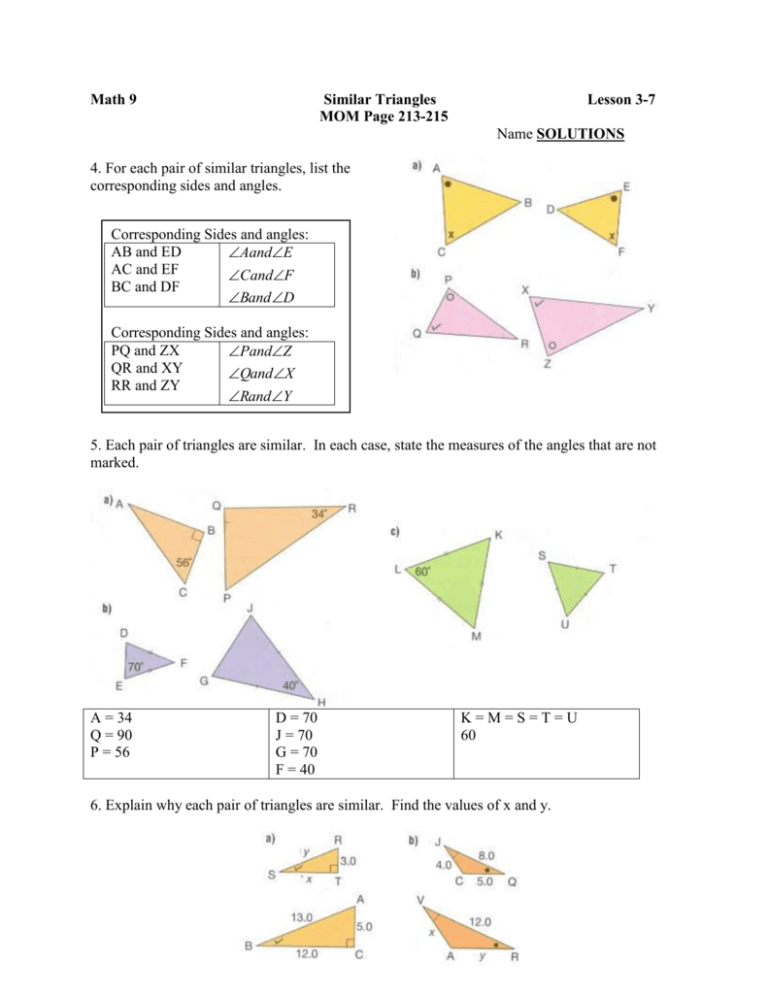
Math 9 Similar Triangles MOM Page 213-215 Lesson 3-7 Name SOLUTIONS 4. For each pair of similar triangles, list the corresponding sides and angles. Corresponding Sides and angles: AB and ED AandE AC and EF CandF BC and DF Band D Corresponding Sides and angles: PQ and ZX PandZ QR and XY QandX RR and ZY Rand Y 5. Each pair of triangles are similar. In each case, state the measures of the angles that are not marked. A = 34 Q = 90 P = 56 D = 70 J = 70 G = 70 F = 40 K=M=S=T=U 60 6. Explain why each pair of triangles are similar. Find the values of x and y. S B T C ThereforeR A J V Q R ThereforeC C Therefore RST is similar to ABC Therefore JCQ is similar to VAR RT RS ST AC AB BC 3 y x 5 13 12 3 y 5 13 3(13) 5 y 39 5 y JC JQ CQ VA VR AR 4 8 5 x 12 y 4 8 x 12 4(12) 8 x 48 8 x 7. 8 y 3 x 5 12 3(12) 5 x 36 5 x 7 .2 x 8 5 12 y 5(12) 8 y 60 8 y 7 .5 y 6x 8. State the ratios of the corresponding sides of each pair of similar triangles. Find each value of x. xy yz xz pq qr pr 11 yz x 6 qr 4 11 x 6 4 4(11) 6 x 44 6 x 7 .3 x TN NC TC EQ QS ES 7 NC 10 12 QS x 7 10 12 x 7 x 12(10) 7 x 120 x 17.14 9. State which triangles are similar. Find the values of x and y. XYZ PQR XY YZ XZ PQ QR PR x 6 4 8 10 y 10 x 8(6) XY YZ XZ PQ QR PR x 6 4 8 10 y 6 y 4(10) 10 x 48 x 4 .8 6 y 40 y 6.67 PST PQR PS PT ST PQ PR QR 10 y x 3 24 10 x 20 10 y (20) 10(24) 200 20 y 240 20 y 40 y2 10. For each diagram, name two similar triangles. Find the length of CE. CAB CED ACE ABD CA CB CE CD 10 CB CE CD 10 8 x 4 8 x 10(4) 8 x 40 x5 AC AE CE AB AD BD AC 21 CE BC 7 4 21 x 7 4 7 x 21( 4) 7 x 84 x 12 AB ED 8 4 PS PT ST PQ PR QR 10 y x 3 24 10 x 20 20( x 3) 24( x) 20 x 60 24 x 60 4 x 15 x 11. For this picture of an ironing board, explain how you know that AEC is similar to BED . The floor and the board are parallel lines Therefore: A = B ( Z pattern) C = D ( Z pattern) E = E (Opposite angles) Therefore: AEC BED 12. Explain why each pair of triangles are similar. Find the values of x and y. F B E C ThereforeD A K G L H ThereforeJ I Therefore FED is similar to BCA Therefore KLJ is similar to GHI FE FD DE BC BA AC 6 x 8 y 15 12 6 8 y 12 6(12) 8 y 72 8 y 9 y KL KJ JL GH GI IH 18 x 15 12 6 y 18 15 12 y 12(15) 18 y 180 18 y 10 y x 8 15 12 8(15) 12 x 120 12 x 10 x x 18 6 12 6(18) 12 x 108 12 x 9x 13. Name a pair of similar triangles in each diagram. Explain how you know the triangles are similar. P T R S Q Q Alternate Interior Alternate Interior Opposite Angles X V Y W U U Corresponding Angles Corresponding Angles Shared Angle XYU VWU PRQ TSQ 15. For each diagram, name two similar triangles. Find the values of x and y. RSQ is similar to RTP BCD is similar to FED BC CD BD FE ED FD y 1.2 1.4 4.8 x 5.6 y 1.4 4.8 5.6 1.4(4.8) 5.6( y ) 6.72 5.6 y 1.2 y 1. 2 1. 4 x 5.6 1.2(5.6) 1.4 x 6.72 1.4 x 4.8 x RS SQ RQ RT TP RP 12 x 6 y 12 15 9 12 6 y 12 9 6( y 12) 12(9) 6 y 72 108 x 6 15 9 6(15) 9 x 90 9 x 10 x 6 y 108 72 6 y 180 y 30 GHJ is similar to LKJ GH GJ HJ LK LJ KJ 6.10 16.2 y x 12.96 12 16.2 y 12.96 12 16.2(12) 12.96( y ) 194.4 12.96 y 15 y 6.10 16.2 x 12.96 16.2 x 6.1(12.96) 16.2 x 79.056 16. In each diagram, the triangles are similar. For each pair of triangles, write the ratio of sides AB that is equal to . BC FD DE DE EF ED DF 17. The two triangles in each diagram are similar. Find each length represented by x. 21 x 42 14 42( x) 21(14) 42 x 294 x7 2 .0 1 .5 2 .4 x 1.5( 2.4) 2( x ) 3 .6 2 x x 1 .8 x 10 15 20 20( x) 10(15) 20 x 150 x 7.5 19. Name a pair of similar triangles in this figure. Explain how you know the triangles are similar. DGE is similar to FDE Because: Both have a right angle, and E is common to both triangles. DGF is similar to EDF Because: Both have a right angle, and E is common to both triangles DGE is similar to FGD Because: Both have a right angle, and P is common to both triangles 20. In each figure, name a pair of similar triangles. Explain how you know they are similar. Find the values of x and y. ADC is similar to ABE Because: A=A, D=B, C=E IFG is similar to IHF 20 18 8 y 8 x 6 20 18 8 x 8(18) 20 x 15 y 13.2 y 13.2 x 15 15 13.2 y 13.2 15 15(15) 13.2(13.2 y ) 144 20 x x 7 .2 20 8 y 8 6 8(8 y ) 20(6) 64 8 y 120 8 y 120 64 8 y 56 y7 BDE is similar to BAC 15 8 17 17 y 12 15 x 8 15 12 17 y 12(15) 8(17 y ) 180 136 8 y 180 136 8 y 44 8 y 5.5 y 8 17 12 15 x 12(17) 8(15 x) 204 120 8 x 204 120 8 x 84 8 x 10.5 x 3.84 15 x 13.2 3.84(13.2) 15( x) 50.76 15 x 3.38 x 225 174.24 13.2 y 225 174.24 13.2 y 50.76 13.2 y 3.84 y RQS is similar to RPQ 4 y x 10 8 4 4 y 10 8 4(8) 10( y ) 32 10 y 3 .2 y 4 x 10 4 4( 4) 10 x 16 10 x 1 .6 x MOM Page 221-223 Name SOLUTIONS 4. State which triangles are similar? Find the values of x and y. Y = U given w = S given X = T Sum of Triangle D = Z given E = A given C = B Sum of Tri. F = K given G = I given H = J Sum of Tri. YWX UST DEC ZAB FGH KIJ YW WX YX US ST UT y 6 x 10 8 12 DE EC DC ZA AB ZB 18 9 20 y 12 x FG GH FH KI IJ KJ x 8 12 18 y 15 y 6 10 8 10(6) 8 y 60 8 y 7.5 y 6 x 8 12 8 x 6(12) 8 x 72 x9 18 9 y 12 9 y 18(12) 9 y 216 y 24 9 20 12 x 9 x 12( 20) 9 x 240 x 26.7 x 12 18 15 15 x 18(12) 15 x 216 x 14.4 12 8 15 y 12 y 15(8) 12 y 120 y 10 5. In each figure, state which triangles are similar, then find the value of x. A = D Corresponding angles B= E Corresponding angles C = C Common Angle. L = N Alternate Interior K = P Alternater Interior M = M Opposite angles ABC DEC LKM NPM AB BC AC DE EC DC x 12 AC 6 8 DC LK KM LM NP PM NM x 12 LM 5 4 NM x 12 6 8 8 x 6(12) 8 x 72 x9 x 12 5 4 4 x 5(12) 4 x 60 x 15 V = Z Alternate Interior W = Y Alternate Interior X = X Opposite angles E = D Corresponding angles B= C Corresponding angles A = A Common Angle. VWX ZYX EBA DCA VW WX VX ZY YX ZX 6 WX x 15 YX 25 EB BA EA DC CA DA 9 x EA 18 6 x DA 6 x 15 25 15 x 6( 25) 15 x 150 x 10 9 x 18 6 x 9(6 x) 18 x 54 9 x 18 x 54 9 x 6x 6. To find the distance PQ across a farm pond, Marty marks out points R and S so that RS is parallel to PQ. By measuring, she finds that RS = 5.7 m, OP = 19.5 m, and OS = 4.2 m. What is the distance PQ? P = S, Q = R, O = O Therefore: PQO SRO PQ QO PO x 19.5 SR RO SO 5 .7 4 .2 x QO 19.5 4.2 x (5.7)(19.5) 5.7 RO 4 .2 4.2 x 111.15 x 26.46 The distance of PQ is 26.46 m. 7. Two trees cast shadows as shown. How tall is the evergreen tree? 14 5 x 8 5 x 14(8) 5 x 112 x 22.4 The evergreen tree is 22.4 m tall. PAGE 222 10. The shadow of a telephone relay tower is 32.0 m long on level ground. At the same time, a boy 1.8 m tall casts a shadow 1.5 m long. What is the height of the tower? 1.8 1.5 h 32 1.5h 1.8(32) 1.5h 57.6 h 38.4 The height of the tower is 38.4 m. 11. Karen is 37.5 m from a church. She finds that a pencil, 4.8 cm long, which is held with its base 60 mm from her eye, just blocks the church from her sight. How high is the church? 37.5 h 0.06 0.48 0.06h 37.5(0.48) 0.06h 18 h 300 The height of the church is 300 m. 12. In each figure, state which triangles are similar? Find the values of x and y. A = B corresponding angles E = D corresponding angles C = C common angle x 12 y 10 6 8 10 AEC BDC x 12 6 8 8 x 72 12 y 10 8 10 8 y 80 120 x9 8 y 40 y5 14. To find the distance across a river, Elinka uses the sketch and the measurements shown below. Find the distance across the river. A = A common angle D = B corresponding E = C corresponding Therefore ADE ABC AD DE AE AB BC AC x 24 AE x 48 60 AC x 24 x 48 60 60 x 24( x 48) 60 x 24 x 1152 36 x 1152 x 32 The distance across the river is 32 m. 15. To calculate the height of a building, Rudolf uses the height of a pole and the length of the shadows cast by the pole and the building, as shown in the diagram. How tall is the building? 3 . 5 1 .5 x 6 1.5 x 3.5(6) The building is 14 m tall. 1.5 x 21 x 14 PAGE 223 17. a pole 3.8 m high casts a shadow that measures 1.3 m. A nearby tree casts a shadow 7.8 m long. Find the height of the tree. 3 .8 1 .3 x 7.8 1.3 x 3.8(7.8) 1.3 x 29.64 x 22.8 The height of the tree is 22.8 m. 19. To determine the height of a tree, Jerry places a 2 m rod 24 m from the tree. He finds that he can align the top of the rod with top of the tree when he stands 1.9 m from the rod. Jerry’s eyes are 1.6 m from the ground. What is the height of the tree? 0.4 1.9 x 24 1.9 x 0.4(25.9) 1.9 x 10.36 x 5.45 x 2 7.45 The height of the tree is 7.45m.