Ch58Test_File - Milan Area Schools
advertisement

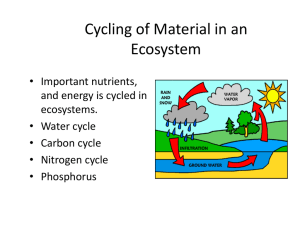
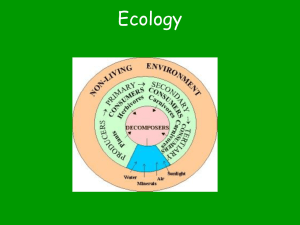
58 Earth System Science TEST FILE QUESTIONS Fill in the Blank 1. In temperate lakes, the depth at which the temperature abruptly changes from warm surface temperatures to cold deeper temperatures is the _______. Answer: thermocline 2. The cycling of water between the oceans, atmosphere, and land is known as the _______. Answer: hydrological cycle 3. The layer of the atmosphere in which humans live (the one closest to the ground) is the _______. Answer: troposphere 4. The movement of an element through a living organism and the physical environment is called its _______. Answer: biogeochemical cycle 5. The addition of nutrients, especially phosphorus, to a lake will result in blooms of algae that die and decompose, using all of the oxygen in the lake. This process is called _______. Answer: eutrophication 6. With a very few exceptions, all of the energy available to living organisms ultimately comes from the _______. Answer: sun 7. _______ is a new field of inquiry that focuses on Earth as a whole. Answer: Earth system science 8. A _______ is a group of entities that interact to yield some product. Answer: system 9. Waters in zones of upwelling are rich in _______. Answer: mineral nutrients 10. The layer of the atmosphere that extends from the top of the troposphere up to about 50 km and contains very little water vapor is the _______. Answer: stratosphere 11. Deposits of organic molecules that are eventually transformed into deposits of oil, gas, or coal are known as _______. Answer: fossil fuels 12. _______ is the principal process that removes nitrogen from the biosphere and returns it to the atmosphere. Answer: Denitrification 13. The rate of CO2 movement to deep ocean waters depends on a circulation pattern called the _______. Answer: ocean conveyor belt 14. A _______ is an area in a body of water that results from flows of nitrogen-enriched water. Answer: “dead zone” 15. Human activity has most seriously disturbed the _______ biogeochemical cycle. Answer: carbon 16. The troposphere is transparent to visible light and traps most outgoing infrared light. This property results in the _______ of Earth. Answer: warming Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following elements is not a major component of living systems? a. Carbon b. Nitrogen c. Oxygen d. Hydrogen e. Potassium Answer: e 2. Erosion from poor farming practices leads to large losses of soil to the sea. What is the likely fate of the elements in the soil? a. Most of the elements will be rapidly recirculated by ocean currents and reintroduced into terrestrial ecosystems. b. Most elements will dissolve and eventually cycle into the atmosphere. c. Most elements will dissolve in the soil and move into freshwater ecosystems, where they will eventually be reintroduced into terrestrial ecosystems. d. Tidal forces will quickly return most of the soil to the shore, where the elements will collect. e. Most elements will settle to the bottom of the oceans, where they will remain for millions of years until bottom sediments are elevated by movements of Earth’s crust. Answer: e 3. Excluding human-induced effects, most elements enter freshwater systems from a. rainfall. b. oceans (through tidal movements). c. actions of animals. d. weathering of rocks (via groundwater). e. plants and plant parts decaying in streams, lakes, and rivers. Answer: d 4. In a temperate zone lake in the middle of summer, a. most nutrients are near the surface of the lake, and O2 is evenly distributed throughout all depths of the lake. b. most nutrients are near the bottom of the lake, and most O2 is near the surface of the lake. c. nutrients and O2 are evenly distributed throughout all depths of the lake. d. nutrients are evenly distributed throughout all depths of the lake, and O2 is near the surface of the lake. e. most nutrients and O2 are found near the surface of the lake. Answer: b 5. At which of the following temperatures is water most dense? a. 16°C b. 8°C c. 4°C d. 2°C e. 0°C Answer: c 6. Most of Earth’s nitrogen is in a. the atmosphere. b. the oceans. c. freshwater systems. d. soil. e. organisms. Answer: a 7. The gas that is removed from the atmosphere by plants and algae is a. N2. b. O2. c. CO2. d. methane. e. water vapor. Answer: c 8. One difference between gases such as O2 and CO2 and minerals such as phosphorus and calcium that do not have a gas phase is that a. there is relatively little variation from site to site in the concentration of gases, whereas solids tend to remain where they are, creating local abundances and shortages of these minerals. b. gases such as O2 and CO2 are never found in a rock (solid) phase or dissolved in water, whereas minerals without a gaseous phase are frequently found as rocks or dissolved in water. c. gaseous elements (and compounds) are essential to living organisms, whereas minerals without a gaseous phase are not. d. gases are modified by living organisms, whereas minerals without a gaseous phase are not. e. the relative proportions of different gases in the atmosphere change radically over short periods of time, whereas the relative proportions of different solid minerals remain fairly constant. Answer: a 9. Most of the world’s carbon is found a. as CO2 in the atmosphere. b. in living organisms. c. as bicarbonate and carbonate ions dissolved in the oceans. d. as carbonate minerals in sedimentary rock. e. in the decaying remains of dead organisms. Answer: d 10. Photosynthesis and respiration are central to which cycle? a. Nitrogen cycle b. Carbon cycle c. Phosphorus cycle d. Sulfur cycle e. Hydrological cycle Answer: b 11. For the past 150 years there has been a major new input to the carbon cycle. What is it? a. There are more humans releasing large quantities of CO2 as respiration. b. Increased animal farming has resulted in greater CO2 releases. c. Industrialization has resulted in the burning of fossil fuels such as oil and coal, which releases CO2 into the atmosphere. d. Changes in ocean currents have lead to the release of large quantities of CO2. e. Global warming has increased the release of CO2 from carbonate minerals. Answer: c 12. Why is nitrogen often in short supply in terrestrial ecosystems? a. There is very little free nitrogen in the air. b. Atmospheric nitrogen is primarily in the stratosphere and does not come into contact with terrestrial ecosystems. c. Atmospheric nitrogen cannot be used by most organisms. It needs to be converted to useful forms by bacteria and cyanobacteria. d. Nitrogen solubility in water is very low and therefore atmospheric nitrogen enters cells very slowly. e. Atmospheric nitrogen varies widely from location to location. As a result local shortages occur frequently. Answer: c 13. The phosphorus cycle differs from the carbon cycle in that a. phosphorus does not enter living organisms, whereas carbon does. b. the phosphorus cycle does not include a gaseous phase, whereas the carbon cycle does. c. the phosphorus cycle includes a solid phase, whereas the carbon cycle does not. d. the primary reservoir of the phosphorus cycle is the atmosphere, whereas the primary reservoir for the carbon cycle is rock. e. phosphorus passes through living organisms many times, whereas carbon flows through living organisms only once. Answer: b 14. Acid precipitation a. occurs naturally when clouds are formed by evaporation over land. b. occurs naturally when clouds are formed by evaporation over oceans. c. occurs as a result of the burning of fossil fuels that contain sulfur and nitrogen compounds. d. occurs because of carbon monoxide emissions by automobiles. e. occurs when large forest tracts are logged or otherwise deforested. Answer: c 15. The two main human-induced causes of increased CO2 levels are a. the burning of fossil fuels and the burning of forests. b. the burning of fossil fuels and the raising of cattle. c. modern agricultural fertilizers and the raising of cattle. d. pollution-induced mortality of oceanic algae and the burning of forests. e. modern agricultural fertilizers and pollution-induced mortality of oceanic algae. Answer: a 16. If CO2 levels double, as they may by the middle of the next century, many serious consequences are likely. Which of the following is the one result that would not be expected? a. World mean temperature will increase 3–5°C. b. Droughts in the central regions of continents will become more common and more severe. c. Precipitation in coastal areas will increase. d. Polar ice caps will melt, raising sea levels and flooding coastal cities and agricultural areas. e. The destruction of the ozone layer by CO2 will allow more ultraviolet light to reach Earth. Answer: e 17. In the movement of energy and nutrients through ecosystems, energy _______, and nutrients _______. a. flows; flow b. flows; cycle c. cycles; cycle d. cycles; flow e. flows; either cycle or flow Answer: b 18. Which of the following does not influence a terrestrial ecosystem? a. Solar energy fluxes b. Earlier successional stages c. Local species richness d. Global atmospheric circulation e. Eutrophication Answer: e 19. The major differences between ocean and freshwater compartments of the global ecosystem exist because a. of the much greater depth of the oceans. b. the oceans turn over only once a year. c. freshwater systems receive input only from groundwater. d. temperature varies only with depth in freshwater systems. e. nutrient recycling is less rapid in freshwater systems. Answer: a 20. Which global ecosystem compartment is characterized by very slow movement of materials and exchange of gases, mostly via organisms? a. Oceanic b. Freshwater c. Atmospheric d. Terrestrial e. Both a and b Answer: d 21. Which of the following comparisons of the troposphere and stratosphere compartments of the global ecosystem is true? a. Most water vapor resides in the troposphere. b. Vertical circulation of air occurs mostly in the stratosphere. c. Circulation of the stratosphere influences ocean currents more directly. d. The stratosphere represents most of the mass of the atmosphere. e. Most weather events occur in the stratosphere. Answer: a 22. Which of the following statements regarding the hydrological cycle is false? a. Most input to the oceans occurs via runoff from rivers. b. The amount of water that evaporates from the surface of the oceans is greater than the amount that falls as rain over them. c. The amount of water that evaporates from the surface of the land is less than the amount that falls as rain over it. d. Water found in sedimentary rock is constantly exchanged with the ocean. e. The energy driving the hydrological cycle is heat from the sun. Answer: d 23. In biogeochemical cycles, elements that cycle the most quickly a. are found in organisms. b. are scarce. c. have a gaseous phase. d. do not become fixed into sediment. e. do not accumulate in the higher trophic levels. Answer: c 24. Which of the following biogeochemical cycles is characterized by a major reservoir that is gaseous, and a major inorganic form that can be utilized only by a small group of bacteria and cyanobacteria? a. Carbon cycle b. Nitrogen cycle c. Phosphorus cycle d. Sulfur cycle e. Oxygen cycle Answer: b 25. In which of the following biogeochemical cycles is the gaseous phase a major greenhouse gas? a. Carbon cycle b. Nitrogen cycle c. Phosphorus cycle d. Sulfur cycle e. More than one cycle Answer: a 26. Which of the following biogeochemical cycles lacks a gaseous phase? a. Carbon cycle b. Nitrogen cycle c. Phosphorus cycle d. Sulfur cycle e. Oxygen cycle Answer: c 27. Which of the following biogeochemical cycles has a gaseous phase made up of emissions from volcanoes and fumaroles? a. Carbon cycle b. Nitrogen cycle c. Phosphorus cycle d. Sulfur cycle e. Oxygen cycle Answer: d 28. The land compartment of Earth is connected to the atmospheric compartment through a. runoff from rivers. b. organisms that process chemical elements. c. zones of upwelling. d. chemical elements that enter groundwater. e. None of the above Answer: b 29. In the human-induced condition called eutrophication, the main biogeochemical cycle that is altered is the _______ cycle; the effect is the creation of _______ conditions and a decrease in species diversity. a. hydrological; aerobic b. phosphorus; anaerobic c. hydrological; aerobic d. phosphorus; aerobic e. nitrogen; anaerobic Answer: b 30. In the human-induced condition called acid precipitation, the main biogeochemical cycles that are altered are the _______ cycles; one effect in lakes is the _______ of populations of nitrifying bacteria. a. phosphorus and nitrogen; increase b. phosphorus and nitrogen; decrease c. nitrogen and sulfur; decrease d. nitrogen and sulfur; increase e. phosphorus and sulfur; decrease Answer: c 31. Which of the following occurrences is not considered to be a likely consequence of global warming? a. Melting of the polar ice caps b. Flooding and increased precipitation in coastal areas c. Increased ozone depletion d. Average worldwide temperature increase of 3–58° e. Droughts in central areas of continents Answer: c 32. Rain and snow become acidified when the burning of fossil fuels releases the acid forms of the elements a. phosphorus and sulfur. b. sulfur and nitrogen. c. nitrogen and chlorine. d. phosphorus and chlorine. e. nitrogen and phosphorus. Answer: b 33. Primary production is higher in zones of upwelling because a. water in these zones conducts nutrients poorly. b. nutrient levels are lower in these zones. c. a thermocline exists in these zones. d. water is more dense at 4ºC. e. the water in these areas has a greater concentration of nutrients. Answer: e 34. Which of the following gases is not part of Earth’s atmosphere? a. O2 b. N2 c. Chlorine d. Water vapor e. CO2 Answer: c 35. In a generalized biogeochemical cycle, fluxes between _______ are slower than fluxes between _______. a. rocks and soils; organisms and the atmosphere b. oceans and the atmosphere; fresh water and the atmosphere c. organisms and the atmosphere; rocks and soils d. magma and igneous rock; metamorphic rock and magma e. nitrogen and phosphorus; carbon and water Answer: a 36. The process that redistributes nutrients in freshwater lakes is called a. upwelling. b. eutrophication. c. the hydrological cycle. d. turnover. e. denitrification. Answer: d STUDY GUIDE QUESTIONS Knowledge and Synthesis Questions 1. Zones of upwelling near the shores of land masses have high primary production because such zones a. bring nutrients from the seafloor up to the surface. b. are characterized by clear water that permits light to penetrate to an unusually great depth. c. bring warm water to the surface. d. trap nutrients washed into the ocean from nearby land masses. 2. Which of the following features would be characteristic of oceans but not of freshwater ecosystems? a. Receives material from land mostly via groundwater b. Seasonal mixing of materials c. Elements buried in bottom sediments for long periods of time d. Bottom waters frequently lacking oxygen 3. In the following diagram, the temperature of a freshwater lake is plotted against depth. This temperature profile would be most characteristic of the lake during a. winter. b. spring. c. summer. d. fall. 4. Based on data in the graph from Question 3, the thermocline for the lake is located between a. 0 and 20 meters. b. 20 and 30 meters. c. 30 and 50 meters. d. 50 and 80 meters. 5. Which of the following features would be characteristic of the stratosphere but not of the troposphere? a. Most ultraviolet radiation is absorbed here. b. Most water vapor resides here. c. Most of the mass of the atmosphere lies here. d. Circulation of this layer influences ocean currents. 6. Which of the following compartments of the global ecosystem is characterized by very slow movement of materials within it? a. Oceans b. Fresh waters c. Atmosphere d. Land 7. In which of the following compartments of the global ecosystem would circulation of materials be affected by Earth’s revolution around the sun? a. Oceans b. Fresh waters c. Atmosphere d. All of the above 8. Which of the following statements about biogeochemical cycles is not true? a. Most elements remain longest in the living portion of their cycle. b. Gaseous elements cycle more quickly than elements without a gaseous phase. c. You may have some atoms in your body that were once part of a dinosaur. d. Biogeochemical cycles all include both organismal and nonliving components. 9. Next to each of the following features, place a c, n, p, or s if it is characteristic of the biogeochemical cycles of carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, or sulfur. (Note: Some features may apply to more than one cycle.) _____ Major reservoir is atmospheric _____ Major reservoir is in sedimentary rock _____ Often in short supply in ecosystems _____ Fossil fuel reserve is part of this cycle _____ Involved in cloud formation _____ Lacks a gaseous phase _____ Includes a form that is a greenhouse gas _____ Most fluxes involve organisms 10. Which of the following statements is not a major concern about our altering of the carbon cycle? a. The Greenland and Antarctic ice caps may melt if global warming continues. b. The burning of fossil fuels adds compounds of sulfur to the atmosphere. c. The increase in atmospheric CO2 exceeds the ability of the oceans to absorb the increase. d. CO2 is a gas that traps infrared radiation. 11. Which of the following statements concerning acid precipitation is false? a. Acids that enter the atmosphere primarily affect ecosystems located less than 100 kilometers from the source of the pollution. b. The effects of acidification of lakes appear to be quickly reversible if their pH can be returned to normal. c. Regulation of emission sources has raised the pH of precipitation in many parts of the eastern United States in the last two decades. d. Sulfuric acid and nitric acid from the burning of fossil fuels are the major causes of acid precipitation. 12. The process by which a lake ecosystem is altered by eutrophication involves several stages, each causing the next. Which of the following stages would occur second in the chain of causation? a. Algal blooms occur. b. Oxygen levels drop in deeper water. c. Phosphorus input from sewage and agricultural runoff increases. d. Respiratory demand from decomposers increases. Answers Knowledge and Synthesis Answers 1. a. Low concentrations of mineral nutrients limit the primary production of most ocean waters. In zones of upwelling, nutrient-rich water is brought to the surface from the ocean bottom, thereby enhancing the growth of photosynthesizing plankton. 2. c. Most elements remain in bottom sediments of the ocean for millions of years, until they are elevated above sea level by movements of Earth’s crust. 3. c. The steep thermocline evident in this temperature profile would typically be established only by mid- to late summer. 4. b. The range of depths over which the temperature changes most abruptly is 20 to 30 meters. 5. a. The ozone that shields the surface of Earth from most incoming ultraviolet radiation is located in the stratosphere. 6. d. Unlike their behavior in air and water, elements on land move slowly and usually only short distances. 7. d. The revolution of Earth around the sun (combined with the tilt of Earth’s axis) is the cause of the seasons. Circulation patterns of materials in the oceans, fresh waters, and the atmosphere are all affected by seasonal changes in temperature, precipitation, and prevailing wind direction. 8. a. Most elements cycle through organisms more quickly than they cycle through the nonliving world. 9. n. Major reservoir is atmospheric c., p. Major reservoir is in sedimentary rock n., p. Often in short supply in ecosystems c. Fossil fuel reserve is part of this cycle s. Involved in cloud formation p. Lacks a gaseous phase n., c. Includes a form that is a greenhouse gas n. Most fluxes involve organisms 10. b. The addition of compounds of sulfur to the atmosphere has more to do with acid precipitation than it does with global warming. 11. a. Acid precipitation is a regional, not a local, environmental problem. Acids may travel hundreds of kilometers before they settle to Earth in precipitation or as dry particles. 12. a. The correct sequence is: 1. Phosphorus input from sewage and agricultural runoff increases. 2. Algal blooms occur. 3. Respiratory demand from decomposers increases. 4. Oxygen levels drop in deeper water. TEXTBOOK SELF QUIZ QUESTIONS 1. Earth is in chemical disequilibrium because a. Earth has a moon. b. organisms dissipate energy as heat. c. most continents are in the Northern Hemisphere. d. Earth has living organisms that maintain the O2, N2, and H2O of the atmosphere. e. Earth is tilted on its axis. 2. Zones of marine upwelling are important because a. they help scientists measure the chemistry of deep ocean water. b. they bring to the surface organisms that are difficult to observe elsewhere. c. ships can sail faster in these zones. d. they increase marine productivity by bringing nutrients back to surface ocean waters. e. they bring oxygenated water to the surface. 3. Which of the following is not true of the troposphere? a. It contains nearly all of the atmospheric water vapor. b. Materials enter it primarily at the intertropical convergence zone. c. It is about 17 km deep in the Tropics. d. Most global air circulation takes place there. e. It contains about 80 percent of the mass of the atmosphere. 4. The hydrological cycle is driven by the a. flow of water into the oceans via rivers. b. evaporation (transpiration) of water from the leaves of plants. c. evaporation of water from the surface of the oceans. d. precipitation falling on the land. e. fact that less water falls on the ocean as precipitation than evaporates from its surface. 5. Carbon dioxide is called a greenhouse gas because a. it is used in greenhouses to increase plant growth. b. it is transparent to heat, but traps sunlight. c. it is transparent to sunlight, but traps heat. d. it is transparent to both sunlight and heat. e. it traps both sunlight and heat. 6. The ocean conveyor belt carries water to the deep ocean in the a. North Pacific Ocean b. South Pacific Ocean c. North Atlantic Ocean d. South Atlantic Ocean e. Indian Ocean 7. The cycle of phosphorus differs from the cycles of carbon and nitrogen in that a. it lacks a gaseous phase. b. it lacks a liquid phase. c. only phosphorus is cycled through marine organisms. d. living organisms do not need phosphorus. e. The phosphorus cycle does not differ importantly from the carbon and nitrogen cycles. 8. The sulfur cycle influences the global climate because a. sulfur compounds are important greenhouse gases. b. sulfur compounds help transfer carbon from the atmosphere to the oceans. c. sulfur compounds in the atmosphere are particles around which water condenses to form clouds. d. sulfur compounds contribute to acid precipitation. e. The sulfur cycle does not influence the global climate. 9. Acid precipitation results from human modifications of a. the carbon and nitrogen cycles. b. the carbon and sulfur cycles. c. the carbon and phosphorus cycles. d. the nitrogen and sulfur cycles. e. the nitrogen and phosphorus cycles. 10. Acid precipitation may change lakes by a. making phosphorus more available to plants, thereby increasing productivity. b. making nitrogen more available to plants, thereby increasing productivity. c. increasing populations of nitrogen-fixing microorganisms. d. accelerating the carbon cycle within lakes. e. causing the local extinction of species that cannot tolerate the lower pH. Answers 1. d 2. d 3. e 4. e 5. c 6. c 7. a 8. c 9. d 10. e ONLINE QUIZ QUESTIONS 1.A new field of inquiry that focuses on Earth as a whole is known as a. Earth ecology. b. planet conservation. c. Earth environmentalism. d. Earth system science. e. Earth biology. Answer: d 2.A group of entities that interact to yield some product is called a a. system. b. mechanism. c. product producing group. d. machine. e. community. Answer: a 3.Which of these qualities does not make Earth an unusual planet? a. solar radiation as an energy input b. large moon c. continental drift d. moderate surface temperature e. presence of life Answer: a 4.These waters are rich in mineral nutrients and most of the world’s fisheries are concentrated here. a. Equatorial currents b. Lakes and rivers c. Groundwater d. Zone of upwelling e. Water turnover. Answer: d 5.The thin layer of gases surrounding the Earth is/are the a. atmosphere. b. greenhouse gases. c. vapor layer. d. gas layer. e. nitrogen zone. Answer: a 6.The cycling of water through the oceans, atmosphere, fresh water, and land is known as the a. water cycle. b. hydrological cycle. c. vapor cycle. d. biogeochemical cycle. e. physical cycle. Answer: b 7.The pattern of movement of a chemical element through organisms and the four compartments of the physical environment is called its a. water cycle. b. hydrological cycle. c. vapor cycle. d. biogeochemical cycle. e. physical cycle. Answer: d 8.The addition of nutrients to bodies of water is known as a. denitrification. b. the hydrological cycle. c. eutrophication. d. the carbon cycle. e. the “dead zone”. Answer: c 9.Rain or snow whose pH is lowered by the presence of sulfuric acid and nitric acid, derived in part from the burning of fossil fuels, is called a. the water cycle. b. the sulfur cycle. c. the carbon cycle. d. acid precipitation. e. poison precipitation. Answer: d 10.As a result of high fertilization rates, great quantities of _______ are accumulating in agricultural soils. a. water b. sulfur c. phosphorus d. carbon e. nitrogen Answer: c