Prof. Jin`s CV - Purdue University
advertisement
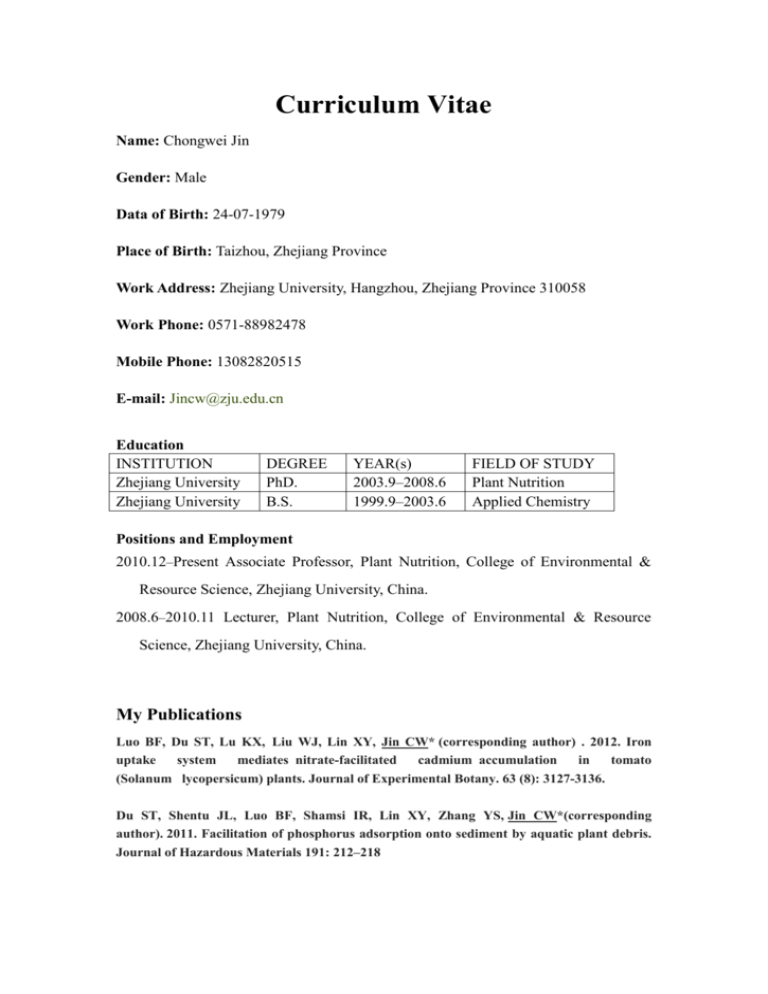
Curriculum Vitae Name: Chongwei Jin Gender: Male Data of Birth: 24-07-1979 Place of Birth: Taizhou, Zhejiang Province Work Address: Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province 310058 Work Phone: 0571-88982478 Mobile Phone: 13082820515 E-mail: Jincw@zju.edu.cn Education INSTITUTION Zhejiang University Zhejiang University DEGREE PhD. B.S. YEAR(s) 2003.9–2008.6 1999.9–2003.6 FIELD OF STUDY Plant Nutrition Applied Chemistry Positions and Employment 2010.12–Present Associate Professor, Plant Nutrition, College of Environmental & Resource Science, Zhejiang University, China. 2008.6–2010.11 Lecturer, Plant Nutrition, College of Environmental & Resource Science, Zhejiang University, China. My Publications Luo BF, Du ST, Lu KX, Liu WJ, Lin XY, Jin CW* (corresponding author) . 2012. Iron uptake system mediates nitrate-facilitated cadmium accumulation in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) plants. Journal of Experimental Botany. 63 (8): 3127-3136. Du ST, Shentu JL, Luo BF, Shamsi IR, Lin XY, Zhang YS, Jin CW*(corresponding author). 2011. Facilitation of phosphorus adsorption onto sediment by aquatic plant debris. Journal of Hazardous Materials 191: 212–218 Jin CW, Du ST, Shamsi IR, Luo BF, Lin XY. 2011. NO synthase-generated NO acts downstream of auxin in regulating Fe-deficiency-induced root branching that enhances Fe-deficiency tolerance in tomato plants. Journal of Experimental Botany 62(11): 3875–3885 Jin CW, Li GX, Yu XH, Zheng SJ. 2010. Plant Fe status affects the composition of siderophore-secreting microbes in the rhizosphere. Annals of Botany 105: 835-841 Chen WW, Yang JL, Qin C,Jin CW, Mo JH, Ye T, Zheng SJ. 2010. Nitric oxide acts downstream of auxin to trigger root ferric-chelate reductase activity inresponse to iron deficiency in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiology. 154: 810-819 Jin CW, Du ST, Zhang YS, Lin XY, Tang CX. 2009. Differential regulatory role of nitric oxide in mediating nitrate reductase activity in roots of tomato (Solanum lycocarpum). Annals of Botany 104: 9-17 Jin CW, Du ST, Chen WW, Li GX, Zhang YS, Zheng SJ. 2009. Elevated carbon dioxide improves plant Fe nutrition through enhancing the Fe-deficiency-induced responses under Fe-limited conditions in tomato. Plant Physiology 150:272-280 Jin CW, Du ST, Wang Y, Condon J. Lin XY, Zhang YS. 2009. Carbon dioxide enrichment by composting in greenhouses and its effect on vegetable production. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science-Zeitschrift fur Pflazenernahrung und Bodenkunde 172: 418-424 Jin CW, Du ST, Zhang YS,Tang CX, Lin XY. 2009. Atmospheric nitric oxide stimulates plant growth and improves the quality of spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.). Annals of Applied Biology 155: 113-120 He XX*, Jin CW*(Co-first author), Li GX, Yu YH, You GY, Zhou XP, Zheng SJ. 2008. Use of the modified viral satellite DNA Vector to silence mineral nutrition-related genes inplants: Silencing of the tomato ferric reductase gene, FRO1, as an example. Science in China Series C-Life Science 51: 402-409 Jin CW, You GY, Zheng SJ. 2008. The iron deficiency-induced phenolics secretion plays multiple important roles in plant iron acquisition underground. Plant Signaling and Behavior. 3(1): 60-61 Jin CW, Chen WW, Meng ZB, Zheng SJ. 2008. The iron-deficiency-induced increase of root branching is important for enhancing ferric chelate reductase activity. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology 50: 1557-1562. Jin CW, Du ST, Zhang K, Lin XY. 2008. Copper contamination in tea leaves and factors affecting it. Food Chemistry and Toxicity. 46(6): 2054-2061 Jin CW, He XX, Zheng SJ. 2007. The Iron-deficiency Induced Phenolics Accumulation May Involve in Regulation of Fe(III) Chelate Reductase in Red Clover. Plant Signaling and Behavior. 2(5):327-335 Jin CW, You GY, Tang CX, Wu P, Zheng SJ. 2007. Iron-deficiency-induced Secretion of Phenolics Facilitates the Reutilization of Root Apoplastic Iron in Red Clover (Trifolium pratense L.). Plant Physiology. 144: 278-285. Jin CW, He YF, Tang CX, Wu P, Zheng SJ. 2006. Mechanisms of microbial enhanced iron uptake in red clover. Plant, Cell & Environment. 29: 888-897 Jin CW, Zheng SJ, He YF, Zhou GD, Zhou ZY. 2005. Lead contamination in tea garden soils and factors affecting its bioavailability. Chemosphere. 59:1151-1159. Jin CW, He YF, Zhou GD, Shi JL, Zhang K, Zheng SJ. 2005. Lead contamination in tea leaves and non-edaphic factors affecting it. Chemosphere. 61: 726-736.
![Jiye Jin-2014[1].3.17](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005485437_1-38483f116d2f44a767f9ba4fa894c894-300x300.png)