Gases and Gas Laws Review Gas Structure and Measurement
advertisement

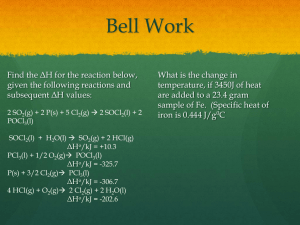
Gases and Gas Laws Review Gas Structure and Measurement Devices 1. List 5 properties of gases. (Various answers) Low Density, Easily Compressed, High Fluidity, No definite shape, No definite volume 2. What creates pressure in gases? Gas particles bouncing against objects around them. 3. What is STP? Standard Temperature (0 °C or 273.15 K) and Pressure (1 atm) Conversions 4. Convert 31°C to K. 31 °C + 273.15 = 304.15 K 5. Convert 750 Torr to kPa. 750 Torr x 101.325 kPa 1 760 Torr 100. kPa = 6. Convert 2.04 atm to psi. 2.04 atm 1 x 14.696 psi 1 atm = 30.0 psi 7. Convert 36.2 in Hg to mm Hg. 36.2 in Hg x 760 mm Hg 1 29.921 in Hg = 919 mm Hg 8. If you didn’t have the conversion factor between the 2 for the problem above but you had 1 in = 2.54 cm, show how you could convert it. 36.2 in Hg 1 x 2.54 cm Hg 1 in Hg x 10 mm Hg 1 cm Hg = 919 mm Hg Gas Law Calculations 9. If a gas is at 1.7 psi and has a volume of 3.5 L, what will its volume be if the pressure is increased to 831 Torr? P1 V1 = P2V2 P1 = 1.7 psi V1 = 3.5 L P2 = 831 Torr V2 = ? 1.7 psi x 760 Torr = 87.91507893 Torr 1 14.696 psi 87.91507893 Torr (3.5 L) = 831 Torr(V2) V2 = 0.370 L 10. An open manometer is filled with mercury. The mercury level is 12 mm higher on the side open to the atmosphere. What is the total pressure of the gas, in kPa, if the atmospheric pressure is 100.8 kPa? 12 mm Hg x 101.325 kPa 1 760 mm Hg 1.599868421 kPa = 100.8 kPa + 1.599868421 kPa = 102 kPa 11. Calculate the pressure (in Torr) inside a television picture tube given that its volume is 500. mL, the temperature is 23 oC and it contains 1.00 mg of nitrogen gas. R = 0.08206 atm L mol-1 K-1 P=? V = 500. mL n = see below T = 23 °C 23 °C + 273.15 = 296.15 K 1.00 mg N2 1 x 1 g N2 1000 mg N2 x 1 mol N2 28.02 g N2 = 3.5689 x 10-5 mol 500. mL x 1 L = 0.500 L 1 1000 mL 0.08206 atm L mol-1 K-1 = P (0.500 L) 3.5689 x 10-5 mol (296.15 K) 0.001734633 atm x 760 Torr 1 1 atm = P = 0.001734633 atm 1.32 Torr 12. What is the density of carbon dioxide at 37.0 oC and 1.05 atm? D = ? M = 44.01 g/mol P = 1.05 atm R = 0.08206 atm L mol-1 K-1 T = 37.0 °C 37.0 °C + 273.15 = 310.15 K D = 44.01 g/mol (1.05 atm) 0.08206 atm L mol-1 K-1 (310.15K) D = 1.82 g/L 13. The initial temperature of a 1.00 liter sample of argon is 20.° C. The pressure is decreased from 720 mm Hg to 360 mm Hg and the volume increases to 2.14 liters. What was the change in temperature of the argon? P1V1/ T1 = P2V2/ T2 P1 = 720 mm Hg T2 = ? V1 = 1.00 L T1 = 20. °C P2 = 360 mm Hg V2 = 2.14 L 20 °C + 273.15 = 293.15 K 720 mm Hg (1.00 L) 293.15 K = 360 mm Hg (2.14 L) T2 T2 = 314 K 14. What volume will 120 grams of chlorine gas occupy at STP? 120 g Cl2 1 x 1 mol Cl2 70.90 g Cl2 x 22.4 L Cl2 1 mol Cl2 = 37.9 L Cl2 15. What is the new volume of gas if 12g of N2 is released from a container that was 5.17 L and originally held 2.3 moles of N2? 12 g N2 1 x 1 mol N2 28.02 g N2 = 0.428265525 mol N2 2.3 mol N2 - 0.428265525 mol N2 = 1.871734475 mol N2 V1/ n1 = V2/ n2 V1 = 5.17 L 5.17 L 2.3 mol n1 = 2.3 mol = V2 = ? V2 1.871734475 mol n2 = 1.871734475 mol V2 = 4.21 L 16. A closed manometer is filled with mercury and attached to a container of helium. The difference in height of mercury between the two arms is 521 mm. What is the pressure of the helium, in Torr? Pgas = 521 mm Hg 521 mm Hg x 760 Torr 1 760 mmHg = 521 Torr 17. A sample of hydrogen gas effuses through a porous container 9 times faster than an unknown gas. Estimate the molar mass of the unknown gas. 9 1 = (M)1/2 (2.02 g/mol)1/2 M = 164 g/mol 18. At STP, a 22.4L container would have a. _1__ moles of H2, a mass of _2.02__ g, and _6.02 x 1023_____ molecules. b. _1__ moles of He, a mass of _4.00__ g, and __6.02 x 1023_____ atoms. c. _1__ moles of H2O, a mass of _18.02_ g, and _6.02 x 1023_____ molecules. 19. Find the partial pressure of a sample of oxygen collected over water when the temperature is 10.0°C. The total pressure is 750. mmHg. The vapor pressure of water is 9.209 mmHg at 10.0°C. 750. mm Hg – 9.209 mm Hg = 741 mm Hg 20. A container with two gases, helium and argon, is 30.0% by volume helium. Calculate the partial pressure of helium and argon if the total pressure inside the container is 4.00 atm. % of Ar = 100% - 30.0% = 70.0% PHe = 30.0% x 4.00 atm = 1.2 atm PAr = 70.0% x 4.00 atm = 2.8 atm 21. Given: CaCO3(s) CO2(g) + CaO(s) How many grams of calcium carbonate will be needed to form 4.29 liters of carbon dioxide if the reaction occurs at 1.00 atm and 300 K? R = 0.08206 atm L mol-1 K-1 P = 1.00 atm V = 4.29 L n= ? T = 300 K 0.08206 atm L mol-1 K-1 = 1.00 atm (4.29 L) n (300 K) n = 0.174262735 mol CO2 0.174262735 mol CO2 1 x 1 mol CaCO3 1 mol CO2 x 100.09 g CaCO3 1 mol CaCO3 = 17.4 g CaCO3 22. If 50.2 liters of oxygen are consumed during the combustion reaction of benzene (C6H6) at 756 mm Hg and 98.3°C, how many liters of water vapor will be formed? 2C6H6 + 15O2 12CO2 + 6H2O R = 0.08206 atm L mol-1 K-1 P = 756 mm Hg 756 mm Hg x 1 atm 1 760 mm Hg V = 50.2 L n= ? T = 98.3 °C 0.994736842 atm = 98.3 °C + 273.15 = 371.45 K 0.08206 atm L mol-1 K-1 = 0.994736842 atm (50.2 L) n (371.45 K) n = 1.638249503 mol O2 1.638249503 mol O2 1 x 6 mol H2O 15 mol O2 0.655299801 mol H2O = 0.08206 atm L mol-1 K-1 = 0.994736842 atm (V) 0.655299801 mol (371.45 K) V = 20.1 L H2O 23. Given the unbalanced equation: 4 NH3(g) + 5 O2(g) 4 NO(g) + 6 H2O(g) How many grams of NO will be produced when 26.8 L of water vapor are produced at STP? 26.8 L H2O 1 x 1 mol H2O 22.4 L H2O x 4 mol NO x 30.01 g NO = 23.9 g NO 6 mol H2O 1 mol NO 24. If magnesium is added to hydrochloric acid, hydrogen gas and magnesium chloride are made. If 2.91 L of a 4.2 M solution of HCl is used, what volume of hydrogen gas will be produced at 1.4 atm and 25°C? Mg + 2HCl H2 + MgCl2 4.2 M HCl = x / 2.91 L 12.222 mol HCl 1 x x = 12.222 mol HCl 1 mol H2 = 6.111 mol H2 2 mol HCl R = 0.08206 atm L mol-1 K-1 P = 1.4 atm V = ? n= 6.111 mol T = 25 °C 25 °C + 273.15 = 298.15 K 0.08206 atm L mol-1 K-1 = 1.4 atm (V) 6.111 mol (298.15 K) V = 107 L H2 25. How many liters of CO2 are made if 9.5 L of acetylene (C2H2) react in a combustion reaction with 13.7 L of oxygen at 762Torr and 99°C? 2C2H2 + 5O2 4CO2 + 2H2O R = 0.08206 atm L mol-1 K-1 762 Torr 1 x P = 762 Torr V = 9.5 L 1 atm 760 Torr n= ? T = 99 °C 1.002631579 atm = 99 °C + 273.15 = 372.15 K 0.08206 atm L mol-1 K-1 = 1.002631579 atm (9.5 L) n (372.15 K) 0.311900053 mol C2H2 x 4 mol CO2 1 2 mol C2H2 = n = 0.311900053 mol C2H2 0.623800106 mol CO2 0.08206 atm L mol-1 K-1 = 1.002631579 atm (V) 0.623800106 mol (372.15 K) V = 19.0 L CO2 R = 0.08206 atm L mol-1 K-1 762 Torr 1 x P = 762 Torr V = 13.7 L 1 atm 760 Torr n= ? T = 99 °C 1.002631579 atm = 99 °C + 273.15 = 372.15 K 0.08206 atm L mol-1 K-1 = 1.002631579 atm (13.7 L) n (372.15 K) 0.449792708 mol O2 1 x 4 mol CO2 5 mol O2 = n = 0.449792708 mol O2 0..359834166 mol CO2 0.08206 atm L mol-1 K-1 = 1.002631579 atm (V) 0..359834166 mol (372.15 K) V = 11.0 L CO2