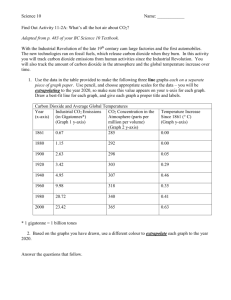
Paper - The Polesworth School
advertisement

Q1. Crude oil is used to make useful substances such as alkenes and plastics. (a) The alkene shown is ethene. (i) Tick ( ) the correct formula for ethene. Formula ( ) CH4 C2H4 C2H6 (1) (ii) Tick ( ) the name of the plastic formed when many ethene molecules join together. Name of plastic ( ) Poly(ethene) Poly(ethanol) Poly(propene) (1) (b) Read the article about plastics and then answer the questions. THE PROBLEM WITH PLASTIC WASTE The UK produces about 3 million tonnes of plastics from crude oil every year. Most of the litter found on UK beaches is plastic waste. 80% of the plastics produced end up in landfill sites. The UK recycles only 7% of plastic waste. (i) Draw a ring around the correct answer in the box to complete the sentence. Litter that is plastic waste needs to be removed from beaches decomposes because it is flammable . is not biodegradable (1) (ii) Suggest a problem caused by 80% of the plastics going to landfill sites. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (iii) The UK government has set a target to recycle 30% of plastic waste. How are resources saved by recycling more plastics? .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (Total 5 marks) Q2. Billions of years ago, the Earth’s early atmosphere was probably like the atmosphere of Venus today. The table shows a comparison of the atmospheres of the Earth and Venus today. Percentage composition of atmosphere Name of gas Nitrogen Earth today Venus today 78 3.5 Oxygen 21 a trace Argon 0.97 a trace Carbon dioxide 0.03 96.5 Average surface temperature 20 ºC 460 ºC (a) Use the names of gases from the table to complete the sentences. (i) In the Earth’s atmosphere today, the main gas is .................................................. . (1) (ii) In the Earth’s atmosphere billions of years ago, the main gas was ............................................................ . (1) (b) (i) Scientists do not know the accurate composition of the Earth’s early atmosphere. Suggest why. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (ii) Use information from the table to answer this question. Water vapour is present in the atmospheres of the Earth and Venus today. The Earth’s surface is mainly covered by water. Suggest why there is no water on the surface of Venus. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (c) The diagram shows how carbon dioxide is removed from the Earth’s atmosphere. Describe what happened to the carbon dioxide in the Earth’s early atmosphere. Use the diagram to help you. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (3) (Total 7 marks) Q3. Energy is released by burning fuels. (a) The bar chart shows the energy in kilojoules, kJ, released by burning 1 g of five different fuels. (i) Which fuel releases the least energy from 1 g? .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (ii) How much energy is released by burning 1 g of coal? Energy = ......................... kJ (1) (iii) Coal burns in oxygen and produces the gases shown in the table. Name Formula Carbon dioxide CO2 Water vapour H2O Sulfur dioxide SO2 Use information from the table to name one element that is in coal. .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (iv) Use information from the bar chart to calculate the mass of petrol that will release the same amount of energy as 1 g of hydrogen. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... Mass = ......................... g (1) (b) Hydrogen can be made from fossil fuels. Hydrogen burns rapidly in oxygen to produce water only. A lighthouse uses electricity generated by burning hydrogen. (i) Use information from the bar chart and the diagram above to suggest two advantages of using hydrogen as a fuel. 1 ......................................................................................... ............................... .................................................................................................. ......................... 2 ......................................................................................... ............................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (2) (ii) Suggest one disadvantage of using hydrogen. .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (Total 7 marks) Q4. The diagram shows a circuit that is used in a torch. Electrons flow through this circuit. (a) Why is copper used for the wire? ............................................................................................................ ......................... (1) (b) The diagram shows the structure of an atom of lithium. Name the particle labelled Z. ............................................................................................................ ......................... (1) (c) The table shows some properties of the metals used in the electrical circuit. Metal Melting point in °C Boiling point in °C Reaction with oxygen Copper 1083 2582 Reacts slowly to form a thin oxide layer on surface Lithium 179 1317 Reacts rapidly to form oxide 3370 5930 Reacts only when very hot to form oxide Tungsten (i) Use information from the table to suggest the order of reactivity for copper, lithium and tungsten. most reactive .......................................................... .......................................................... least reactive .......................................................... (2) (ii) The filament wire glows because it gets very hot. Use information from the table to suggest one reason why tungsten is used for the filament wire in the light bulb. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (d) The gas used in the light bulb is argon. Draw a ring around the correct word in the box to complete the sentence. dense. Argon is used in the light bulb because it is solid. . unreactive. (1) (Total 6 marks) Q5. An advert for some crisps claims that they now contain only 30% saturated fat because they are cooked in sunflower oil. The crisp company used bromine water to compare percentage unsaturation of sunflower oil with four other vegetable oils, A, B, C and D. Volume of bromine water added until the bromine colour just remains (cm3) Oil (i) Percentage unsaturation (%) Test 1 Test 2 Test 3 Average Sunflower 25.4 28.0 27.0 26.8 A 13.0 14.0 15.0 14.0 35 B 23.2 11.2 24.0 23.6 59 C 19.9 21.1 20.2 20.4 51 D 9.5 8.8 9.3 9.2 23 What is the range of percentage unsaturation for oils A, B, C and D? Range = ................................................ % (1) (ii) Describe and explain what happens to the first drops of bromine water that are added to these oils. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (2) (iii) The average for oil B is given as 23.6 cm3. Explain how this average has been calculated. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (1) (iv) The results did not show that sunflower oil contains 30% saturated fat. Explain why. (You will need to calculate the percentage unsaturation of sunflower oil.) ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (2) (Total 6 marks) Q6. Limestone contains calcium carbonate, CaCO3. At a cement works, limestone is mixed with clay and heated in a kiln. (a) (i) When methane is burned in this process the waste gases contain carbon dioxide and nitrogen. Explain why. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (2) (ii) Complete the symbol equation for the thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate. CaCO3 → ......................... + ......................... (2) (b) A different fuel is burnt at the cement works. Suggest one reason the company may give for using this different fuel at the cement works. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (1) (c) The cement works continue to burn the different fuel. Local residents are concerned because more children are suffering asthma attacks. Residents have also noticed that parked cars are becoming dirty because of smoke particles from the chimney. The table shows the possible medical risk from smoke particles. Particle size in mm Medical effect Larger than 0.4 No medical risks known 0.3 and smaller Causes asthma attacks 0.2 and smaller May cause cancer It is also recommended that to avoid damage to health, the concentration of any particles should be no higher than 2 parts per million (ppm). Scientists were brought in to monitor the emissions from the cement work’s chimney. They positioned four sensors around the cement works to monitor airborne smoke particles. These four sensors only detect particle sizes larger than 0.5 mm and measure the concentration of particles in ppm. The scientists reported that the particle sensors showed that the average concentration of particles was 1.8 ppm. The scientists concluded that there was no risk to health. (i) Explain why the local residents objected to the positions of the four sensors. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (2) (ii) What evidence did the scientists use to conclude that there was no risk to health? .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (iii) The local residents were still concerned that there was a risk to health, even though the average concentration of particles was 1.8 ppm. Explain why. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (3) (Total 11 marks) Q7. In 1935 C.F. Richter designed a scale for comparing the size of earthquakes. A newspaper reported that an earthquake off the coast of Kent had caused plaster to come down from ceilings, house tiles to loosen and church bells to ring. The epicentre is the place on the surface of the Earth directly above where the earthquake occurs. (a) Suggest why the earthquake in Kent was reported and why most earthquakes in the UK are not reported. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (2) (b) Explain how earthquakes are caused. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (3) (c) People living in Kent were not warned about this earthquake. In terms of what is happening within the Earth, explain the problems of trying to predict earthquakes. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (2) (Total 7 marks) Q8. The hip joint between the femur and pelvis sometimes has to be replaced. Early hip replacement joints were made from stainless steel. Stainless steel is an alloy of iron, chromium and nickel. The diagram below represents the particles in stainless steel. (a) Use the particle diagram to complete the percentages of metals in this stainless steel. The first one has been done for you. Element Percentage (%) Iron, Fe 72 Chromium, Cr Nickel, Ni (2) (b) Pure iron is a relatively soft, metallic element. (i) Why is iron described as an element? .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (ii) Suggest why pure iron would not be suitable for a hip replacement joint. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (iii) Use the particle diagram to help you to explain why stainless steel is harder than pure iron. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (2) (Total 6 marks) Q9. Crude oil is a resource from which fuels can be separated. (a) The name of the main fuel fractions and one of the hydrocarbons in each fraction are shown in the table. (i) How does the number of carbon atoms in a hydrocarbon affect its boiling point? .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (ii) Suggest the lowest temperature to which crude oil needs to be heated to vaporize all the hydrocarbons in the table. Temperature = ................................................ °C (1) (iii) Dodecane boils at 216 °C. At what temperature will dodecane gas condense to liquid? Temperature = ................................................ °C (1) (b) The bar chart shows the relative supply and demand for the petrol and diesel fractions. (i) How does the relative supply and demand for petrol and diesel fractions cause problems for an oil company? .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (2) (ii) Suggest one way an oil company could solve these problems. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (Total 6 marks) Water sold in plastic bottles has a high ‘carbon cost’. Q10. The ‘carbon cost’ depends on the amount of carbon dioxide emitted in making and transporting the product. The more carbon dioxide emitted, the higher the ‘carbon cost’. (a) Plastic water bottles are made from a polymer. The polymer is made from ethene. Ethene is made by cracking hydrocarbons. (i) Name the polymer made from ethene. .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (ii) Ethene can be made by cracking the hydrocarbon pentane, C5H12. C5H12 → C2H4 + C3H8 Explain why there is a ‘carbon cost’ for the process of cracking a hydrocarbon. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (2) (b) The diagram shows information about water sold in plastic bottles in the UK. The diagram also shows the average distances that water and plastic bottles are transported. Suggest how the high ‘carbon cost’ of water sold in plastic bottles could be reduced. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (3) (Total 6 marks) Q11. Earthquakes are common in certain places on Earth. (a) The diagram shows the layered structure of the Earth. Choose one word from the box to complete the label on the diagram. atmosphere core plate (1) (b) In 1935 C.F. Richter designed a scale for comparing the size of earthquakes. A newspaper reported that an earthquake off the coast of Kent had caused plaster to come down from ceilings, house tiles to loosen and church bells to ring. (i) Earthquakes happen often in the UK. Suggest why most of these earthquakes are not reported in the newspapers. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (ii) Draw a ring around the number which best shows the size of the earthquake in Kent. 1 4 6 8 (1) (iii) State what causes earthquakes. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (iv) Why were people living in Kent not warned about this earthquake? .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (Total 5 marks) Q12. An advert for crisps claims that they now contain only 30% saturated fat because they are cooked in sunflower oil. (a) The oil is extracted from sunflower seeds. The diagram shows how this can be done. Draw a ring around the correct word in each box to complete the sentences. (i) evaporating. The oil is obtained from crushed sunflower seeds by filtering. pressing. (1) (ii) burn The oil does not dissolve in water. melt (1) (b) Draw a ring around the correct word in the box to complete the sentence. Carbon carbon double bonds in sunflower oil can be detected bromine. by reacting with iron. oxygen. (1) (c) Water has a boiling point of 100 °C. Sunflower oil has a boiling point above 232 °C. Suggest why sunflower oil and not water is used to make crisps from thin slices of potato. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (2) (Total 5 marks) Limestone has been called the Earth’s most useful rock. Q13. (a) Limestone contains calcium carbonate, CaCO3. (i) Complete the table to show the number of atoms of each element in the formula of calcium carbonate. Calcium has been done for you. Element Number of atoms in the formula CaCO3 Calcium, Ca 1 Carbon, C Oxygen, O (2) (ii) The diagram below represents a carbon atom. Use words from the box to label the parts of this atom. bond electron molecule nucleus (2) (b) At a cement works, limestone is mixed with clay and heated in a kiln. Use the information in the diagram to answer these questions. (i) Name the fuel that is used to heat the limestone and clay. .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (ii) Limestone contains calcium carbonate, CaCO3. Draw a ring around the correct gas in the box to complete the sentence. argon. The gas formed when calcium carbonate decomposes is carbon dioxide. nitrogen. (1) (c) The cement works starts to burn a different fuel. Local residents are concerned because more children are suffering asthma attacks. Residents have also noticed that parked cars are becoming dirty because of smoke particles from the chimney. The table shows the possible medical risk from smoke particles. (i) Particle size in mm Medical effect Larger than 0.4 No medical risks known 0.3 and smaller Causes asthma attacks 0.2 and smaller May cause cancer Give two reasons why local residents are concerned about the cement works burning a different fuel. 1 ......................................................................................... ............................... .................................................................................................. ......................... 2 ......................................................................................... ............................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (2) (ii) The company operating the cement works stated that smoke particles from the chimney had not changed since it started burning the different fuel. If you were a local resident, what evidence would you like to see to help you decide if the company’s statement is true or not? .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (2) (Total 10 marks) Q14. Iron is the main structural metal used in the world. (a) The diagram represents the particles in iron, Fe. Draw a ring around the correct word in the box to complete the sentence. atoms Iron is described as an element because all the compounds metals are the same. (1) (b) Stainless steel is mostly iron. The diagram represents the particles in stainless steel. Use the correct words from the box to complete the sentences about alloys. metal structure mixture molecule polymer smart Stainless steel is an alloy because it is a ........................................................................... of iron, chromium and nickel. An alloy is made up of more than one type of ................................................................ . Stainless steel alloys are harder than iron because the different sized atoms added change the ............................................................................... . An alloy that can return to its original shape after being deformed is called a ..................................................................... alloy. (4) (c) In the UK, we use about 1.8 billion steel cans every year but only 25% are recycled. Used steel cans are worth about £100 per tonne. Recycling saves raw materials and reduces waste that would end up in landfill. Producing steel by recycling used cans saves 75% of the energy that would be needed to produce steel from iron ore. This also reduces carbon dioxide emissions. (i) Give two reasons, from the information above, to explain why recycling used steel cans is a good idea. 1 ......................................................................................... ............................... .................................................................................................. ......................... 2 ......................................................................................... ............................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (2) (ii) Suggest how the local council could increase the percentage of used steel cans that are recycled. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (Total 8 marks) Q15. Air is a mixture of gases and contains various pollutants. The gases are useful and can be separated by fractional distillation of liquid air. The table gives information about some of the gases in air. Name of gas Formula Melting point in °C Boiling point in °C Helium He –272.2 –269.0 Oxygen O2 –219.0 –183.0 Nitrogen N2 –210.0 –195.9 Argon Ar –189.0 –185.9 Carbon dioxide CO2 –78.5 –78.5 Water vapour H2O 0.0 100.0 To separate these gases: • • • • (a) the air is filtered water is removed first carbon dioxide is then removed by absorption the gases remaining are compressed and cooled to –200 °C. The air is filtered before the gases are separated. Suggest why. ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ (1) (b) Water vapour and carbon dioxide are removed before the gases are compressed and cooled. Use the information in the table to suggest why. ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ (2) (c) After the water and carbon dioxide have been removed, which gas stays liquid over the greatest temperature range? ............................................................................................................ ............ (1) (d) After the water and carbon dioxide have been removed, the four gases that are left are compressed and cooled to –200 °C. (i) Which gas does not liquefy? .................................................................................................. ............. (1) (ii) The three liquefied gases are then allowed to warm up. Give the order in which the three liquefied gases would vaporise. 1st ................................................... 2nd .................................................. 3rd ................................................... (1) (Total 6 marks) Q16. An advert for crisps claimed that they are healthier because they are cooked in sunflower oil. (a) A student found the following information about four oils that are used to make crisps. Rapeseed oil Sunflower oil Olive oil Corn oil Saturated fat (%) 6.6 12.0 14.3 14.4 Polyunsaturated fat (%) 29.3 63.3 8.2 51.3 Melting point (°C) +5 –18 –12 –15 One hypothesis is that oils are thought to be healthier if they are: • low in saturated fat • high in polyunsaturated fat. (i) Use the table to decide which oil should be healthiest. Explain your decision by comparing this oil with other oils from the table that you think are less healthy. Healthiest oil is ..................................................................................... Explanation ......................................................................................... .. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. (2) (ii) These oils can be hardened by reacting them with hydrogen. A student said that hardening would make sunflower oil healthier. Is this student’s claim correct? Explain your answer. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. (2) (b) A mixture of the olive oil, water and egg yolk was shaken and left to stand. The olive oil and water do not separate. The diagram shows a simple model of how a stable mixture of olive oil and water is produced by the addition of egg yolk. Use this simple model to explain how the molecules in the egg yolk are able to produce a stable mixture of olive oil and water. ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ (3) (Total 7 marks) Q17. This question is about the use hydrocarbons and the production of compounds from hydrocarbons. (a) The equation shows a reaction involving hydrocarbons. C8H18 → C2H4 + C6H14 Hydrocarbon J Hydrocarbon L Hydrocarbon K Choose the correct processes from the box to complete the sentences. combustion hydration polymerisation (i) thermal decomposition Hydrocarbons K and L are produced by ........................................... . (1) (ii) Ethanol can be produced from hydrocarbon K by .............................. . (1) (iii) Describe a test to distinguish between hydrocarbons K and L and give the result of the test. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. (2) (b) Hydrocarbon J burns completely in oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water vapour. 2 C8H18 + H2O (i) 25 O2 → 16 CO2 + 18 When 114g of hydrocarbon J burns completely in 400g of oxygen it produces 162g of water vapour. What mass of carbon dioxide would be produced from burning 114g of hydrocarbon J? Show clearly how you work out your answer .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. Answer = ................................. g (2) (ii) The mass of carbon dioxide produced is greater than the 114g of hydrocarbon J that was burned. Explain why. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. (2) (c) Two different processes are used to produce ethanol. Process 1 Process 2 Fermentation of a sugar solution by yeast in a reaction vessel. Reaction of ethene (from crude oil) with steam in a reactor. The reaction vessel has to be emptied, cleaned and refilled every few days. The reaction is only stopped if there is a fault in the reactor. The process produces a 15% ethanol solution in water. (i) The process produces 100% ethanol. Give one advantage that Process 1 has over Process 2. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. (1) (ii) What advantages to a manufacturer of ethanol, does Process 2 have over Process 1? .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. (2) (Total 11 marks) Q18. Copper is found in the Earth’s crust as an ore containing copper sulfide. Large areas of land, where this ore was once quarried, are contaminated with low percentages of copper sulfide. Copper would be too expensive to extract from this contaminated land using the traditional method of quarrying and then heating in a furnace. (a) The percentage of copper ore in the contaminated land is low. (i) It would be too expensive to extract from this land by the traditional method. Explain why. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. (1) (ii) Extracting copper from this land by the traditional method would have a major environmental impact. Give one reason why. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. (1) (b) One way to extract the copper from land that contains low percentages of copper sulfide is by bioleaching. Bioleaching uses bacteria. The bacteria produce a solution of copper sulfate. It is possible to get copper from a solution of copper sulfate using scrap iron. (i) It is economical to use scrap iron to get copper. Give one reason why. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. (1) (ii) Why can iron be used to get copper from copper sulfate solution? .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. (1) (c) A new way to extract the copper from land that contains low percentages of copper sulfide is phytomining. Phytomining uses plants. Plants are grown on this land and absorb copper compounds through their roots. (i) Use this information to give two advantages of phytomining compared to the traditional method. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. (2) (ii) Use this information to suggest one disadvantage of phytomining compared to the traditional method. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. (1) (Total 7 marks) Q19. Limestone contains calcium carbonate, CaCO3 (a) The flow chart shows the stages in the limestone cycle. Write the name of the correct calcium compound in each empty box to complete the flow chart. (3) (b) Limestone is heated with clay to make cement. Cement is mixed with sand to make mortar. A student investigated the strength of six mortar mixtures. Each mortar mixture contained 100cm3 cement but each contained a different volume of sand. To do the investigation the student: • added and stirred water into each mortar mixture • put each mixture into the same sized moulds • left each mixture to set hard • dropped a metal ball from increasing heights until the mortar cracked • recorded the results in a table. Volume of sand in cm3 Volume of cement in cm3 Height the metal ball was dropped from to crack the mortar in cm 700 100 24 600 100 30 500 100 36 400 100 37 300 100 48 200 100 54 (i) What happens to the strength of the mortar as the volume of sand increases? .................................................................................................. ............. (1) (ii) The student was worried about an anomalous result. Which result was anomalous? Volume of sand = ................. cm3 Explain why you have chosen this result. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. (2) (c) The student repeated the investigation but used six concrete mixtures. From the results the student concluded correctly that concrete was stronger than mortar. Suggest one reason why concrete is stronger than mortar. ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ (1) (Total 7 marks) Q20. (a) The chemical equation for a reaction of sodium is shown below. 2Na + Cl2 → 2NaCl Describe this reaction of sodium in terms of the names of the substances and the numbers of the atoms involved. ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ (3) (b) Use the periodic table on the data sheet to help you to answer this question. (i) Complete the electronic structure of sodium. (2) (ii) How is the electronic structure of sodium different from the electronic structure of chlorine? .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. (1) (Total 6 marks) Q21. Evidence shows that the Earth formed from a molten ball of rocks and minerals. Before 1900 many scientists thought that the Earth’s mountains and continents formed in fixed positions when the molten ball of rocks and minerals cooled and wrinkled. (a) In 1912 Alfred Wegener suggested his hypothesis of continental drift. The areas of rocks shown on Map 1 contain fossils of the same type of animals. Today animals in Africa are different from animals in South America. Map 1 Map 2 Wegener suggested his hypthesis that all of the continents, including Africa and South America, had been joined together but then drifted slowly apart. In 1920 other scientists stated that all of the continents were in fixed positions, including Africa and South America, and that they had once been joined together by a land bridge. (i) Use the information to suggest two pieces of evidence that may have led Wegener to propose his hypothesis that continents move. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. (2) (ii) Suggest why, in 1920, other scientists thought that Wegener’s hypothesis was wrong. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. (2) (b) In 1962 scientists produced the theory of plate tectonics. The theory of plate tectonics supported Wegener’s hypothesis that continents move. Tectonic plates move a few centimetres a year. Complete the sentences about what causes the movement of the Earth’s tectonic plates. Deep inside the Earth ........................................ processes release large amounts of energy. These processes heat up the substances in the Earth’s ........................................ producing convection currents. (2) (Total 6 marks) Q22. Most plastic bags are made from poly(ethene). Poly(ethene) is a polymer made from ethene. Ethene is made by cracking saturated hydrocarbons from crude oil. (a) Use words from the box to complete the sentences about cracking. alkanes alkenes catalyst fuel gas Cracking involves heating the .......................................... to make a vapour. The vapour is either passed over a hot ............................................... or mixed with steam and heated to a very high temperature so that thermal decomposition reactions happen. (2) (b) Poly(ethene) molecules are made from ethene molecules by a polymerisation reaction. Describe what happens in a polymerisation reaction. ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ (2) (c) In this question you will be assessed on using good English, organising information clearly and using specialist terms where apropriate. There are millions of plastic bags in use. After use most of these plastic bags are buried in landfill sites. The amount sent to landfill could be reduced if the plastic bags: • could be reused • could be recycled by melting and making into new plastic products • could be burned to release energy Use the information above and your knowledge and understanding to give the positive and negative environmental impacts of using these methods to reduce the amount of plastic bags sent to landfill. ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ (6) (Total 10 marks) Q23. Atoms are made up of three main particles called protons, neutrons and electrons. Use the periodic table on the data sheet to help you to answer these questions. (a) Sodium is in Group 1 of the periodic table. (i) Why are potassium and sodium in the same Group of the periodic table? .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. (1) (ii) How many protons are in an atom of sodium? ..................................... (1) (iii) The atomic number of sodium is 11. How many neutrons are in an atom of sodium with mass number 23? ...................................... (1) (iv) Each sodium atom has 11 electrons. Complete the electronic structure of sodium. (2) (b) The chemical equation for a reaction of sodium is shown below. 2Na + Cl2 → 2NaCl Describe this reaction of sodium in terms of the names of the substances and the numbers of the atoms involved. ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ (3) (Total 8 marks) Q24. This is a headline from a newspaper. ‘Why is a 2p coin made in 1991 now worth 3.3p?’ (a) The bar chart shows the percentages of metals in UK coins in 1991. Use the bar chart to answer these questions. (i) Which metal is in all of these coins? ................................................... (1) (ii) Which coin does not contain zinc? ...................................................... (1) (iii) What is the percentage of nickel in a 50p coin? ............................... % (1) (b) Suggest two reasons why a 2p coin made in 1991 is now worth 3.3p. ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ (2) (Total 5 marks) Q25. Useful fuels can be produced from crude oil. Crude oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons. (a) The table shows the boiling points of four of these hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbon Boiling point in °C methane, CH4 –162 butane, C4H10 0 pentane, C5H12 +36 decane, C10H22 +175 Tick ( ) two statements that are correct about these hydrocarbons. Statement Tick ( ) decane has the largest molecules pentane is a liquid at 40°C methane and butane are gases at 20°C methane has the highest boiling point butane does not boil (2) (b) Natural gas supplied to homes and schools is mainly methane. The diagram shows an apparatus to investigate the two substances produced when natural gas burns completely in air. (i) Name the liquid that collects in the U-tube. ........................................ (1) (ii) Name the gas that turns the limewater cloudy .................................... (1) (c) Some crude oil contains sulfur. Petrol and diesel fuels are produced from crude oil. The sulfur must be removed from these fuels before they are burned. Explain why. ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ (2) (Total 6 marks) Q26. Limestone and the products of limestone have many uses. (a) Limestone is quarried. Photograph © Lonny Kalfus / Getty Images Quarrying limestone has impacts that cause environmental problems. Tick ( ) two impacts that cause environmental problems. Impact of quarrying Tick ( ) Puts off tourists Causes dust pollution Increases jobs Increases traffic (2) (b) Limestone contains calcium carbonate, CaCO3. When it is heated calcium carbonate produces calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. The word equation for this reaction is: calcium carbonate → calcium oxide + carbon dioxide (i) Complete the sentence. The reaction when calcium carbonate is heated is called thermal ........................................... (1) (ii) 100 g of calcium carbonate was heated and produced 56 g of calcium oxide. Calculate the mass of carbon dioxide produced. .................................................................................................. ............. ....................................... g (1) (c) The flow chart shows the stages in the limestone cycle. Complete the names of the calcium compounds formed in the flow chart. (2) (Total 6 marks) Q27. Billions of years ago, the Earth’s early atmosphere was probably like the atmosphere of Venus today. The table shows the temperature and the percentage composition of the atmospheres of the Earth and Venus today. Percentage (%) composition of atmosphere Name of gas Earth today Venus today Nitrogen 78 3.5 Oxygen 20.6 a trace Argon 0.97 a trace Carbon dioxide 0.03 96.5 Water vapour 0.4 a trace 20 °C 460 °C Average surface temperature (a) Use information from the table to help you to answer each part. (i) In the Earth’s atmosphere today, the main gas is ............................... . (1) (ii) In the Earth’s atmosphere billions of years ago the main gas was ............................................................. (1) (iii) The Earth’s surface is mainly covered with water. There is no water on the surface of Venus. Suggest why. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. (2) (b) The diagram shows part of the Earth and ways that carbon dioxide can be removed from the Earth’s atmosphere. Give three ways that carbon dioxide can be removed from the Earth’s atmosphere. ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ ............................................................................................................ ............ (3) (c) In the Earth’s atmosphere the percentage of carbon dioxide has remained at about 0.03% for many thousands of years. The graph shows the percentage of carbon dioxide in the Earth’s atmosphere over the last 50 years. (i) What was the percentage of carbon dioxide in the Earth’s atmosphere in 1965? .................................................................................................. ............. ......................................... % (1) (ii) What change has happened to the percentage of carbon dioxide in the Earth’s atmosphere over the last 50 years? .................................................................................................. ............. (1) (iii) Suggest one reason for this change. .................................................................................................. ............. .................................................................................................. ............. (1) (Total 10 marks) Q28. Many plants produce useful oils. (a) The diagram shows some apparatus used to obtain oil from plant material. Four parts of the apparatus are labelled, A, B, C and D. Use the information in the diagram to complete the sentences. Steam is made in part . Oil from the plant material is vaporised in part Steam and oil vapour are condensed in part . . (3) (b) A student investigated a mixture of a plant oil and water. (i) A mixture of the plant oil and water was shaken and left to stand for 10 minutes. Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete the sentence. dissolves. The plant oil separates from the water because it floats. sinks. (1) (ii) A mixture of the plant oil, water and egg yolk was shaken and left to stand for 10 minutes. The mixture did not separate. Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete the sentence. a compound. The plant oil, water and egg yolk make an emulsion. a fat. (1) (Total 5 marks) Q29. A substance made of only one type of atom is called an element. The chemical symbols and positions of six elements in the periodic table are shown. Draw a straight line from each description to its correct symbol. Description Symbol Al A metal with a low density that does not corrode easily Fe It has properties similar to those of sodium, Na He It is a transition metal Li It is a noble gas O (Total 4 marks) Q30. A limestone quarry is in an area of natural beauty and near several villages. The company operating the quarry wants planning permission to build a new cement works in the quarry. The diagram shows some of the substances used and produced at a cement works. (a) Limestone is mainly calcium carbonate, CaCO3. Write the correct number in the box to complete each sentence. (i) The formula shows that calcium carbonate, CaCO3, contains different elements. (1) (ii) Calcium carbonate, CaCO3, contains a total number of atoms. (1) (b) The company wants the new cement works because the nearest cement works is 100 km from the quarry. The company argues that a new cement works sited inside the quarry would reduce carbon dioxide emissions. Suggest why the new cement works might reduce carbon dioxide emissions. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (1) (c) Residents from the villages near the quarry are concerned that there will be atmospheric pollution from the new cement works. (i) Name and explain how one of the emissions from the chimney causes atmospheric pollution. Name of emission: ......................................................................................... .. Explanation: ......................................................................................... ............ .................................................................................................. ......................... (2) (ii) Suggest what the company could do to reduce this atmospheric pollution. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (Total 6 marks) Q31. (a) Limestone is a hard rock that is used as a building material. Limestone was used by the Egyptians to make plaster. Reaction 1 – calcium carbonate, CaCO3, was decomposed by heating limestone CaCO3 → CaO + CO2 Reaction 2 – water was added to the solid produced to make slaked lime CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2 Reaction 3 – a mixture of slaked lime and water was used as plaster. After the plaster had set it became even harder with age Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O (i) Name the solid formed when calcium carbonate decomposed. .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (ii) Use the reactions to explain how the plaster became even harder with age. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (3) (b) A gardener wanted to make a step up to his greenhouse door. He decided to use a mixture of cement and sand to make mortar. He experimented using mixtures with different cement to sand ratios. • The mortar mixtures were put in the same sized mould. • Each mortar mixture was allowed to set hard. • He then dropped a metal ball from increasing heights until the set mortar cracked. • He recorded his results in a table. (i) Volume of sand in cm3 Volume of cement in cm3 Height the metal ball dropped to crack the set mortar in cm 800 100 17 700 100 24 600 100 30 500 100 36 400 100 37 300 100 48 200 100 54 What is the relationship between the volume of sand and the strength of the mortar? .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (ii) The gardener was not sure about some of his results. Use the results to explain why. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (2) (Total 7 marks) Q32. There are many ideas about the formation of the Earth and its atmosphere from a molten ball of rock and minerals. (a) One idea is that the Earth’s early atmosphere and average surface temperature were probably like that of Venus today. The table shows information about the Earth and Venus today. Percentage composition of atmosphere Name of gas Earth today Venus today Nitrogen 78 3.5 Oxygen 21 a trace Argon 0.97 a trace Carbon dioxide 0.03 96.5 Average surface temperature 20 °C 460 °C There is a variable amount of water vapour in both atmospheres. (i) How was the Earth’s early atmosphere formed? .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (ii) The Earth’s average surface temperature decreased over time. At what temperature would oceans have started to form? Temperature = ......................... °C (1) (iii) Describe how the evolution of plants changed the Earth’s atmosphere. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (2) (b) Another idea was that the Earth’s mountains and continents formed in fixed positions as the molten ball of rock and minerals cooled and wrinkled. Wegener, in 1915, had the idea that the Earth’s crust and the upper part of the mantle had cracked into plates that were able to move. His idea meant that the mountains and continents were not in fixed positions. (i) Give one piece of evidence that led to Wegener’s idea being accepted. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (ii) Describe what causes the Earth’s tectonic plates to move. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (3) (Total 8 marks) Q33. The demand for iron and steel is high. (a) Iron that is extracted from its oxide by carbon reduction in a blast furnace is called cast iron. Cast iron contains about 4% carbon. This carbon makes cast iron very brittle. Carbon steels can be made by the following processes. • Blowing oxygen into molten cast iron to remove most of the carbon. • Adding a calculated amount of carbon. Sometimes different metals may also be added to the molten carbon steels. (i) Suggest how blowing oxygen into molten cast iron removes most of the carbon. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (2) (ii) Why are different metals sometimes added to molten carbon steels? .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (b) The percentage of iron and steel recycled in the UK has been increasing. Year %iron and steel recycled 1998 25 2000 35 2002 42 2004 46 2006 57 The UK government has set targets for the percentage of iron and steel to be recycled. In 2006 the target was exceeded. Suggest two reasons why the UK government wants to encourage recycling of iron and steel. 1 .................................................................................................. ................................ ............................................................................................................ ......................... 2 .................................................................................................. ................................ ............................................................................................................ ......................... (2) (Total 5 marks) Q34. Margarine is manufactured using ‘hard’ plant oils. A margarine company tested several plant oils to determine their hardness for use in its margarine. In the test iodine solution was used to find the iodine value. The units are grams of iodine that react with 100 g of oil. Plant oils with lower iodine values are harder and are less unsaturated. Plant oil Melting point in °C Iodine value Coconut 25 10 Palm 35 54 Olive –6 81 Castor –18 85 Peanut 3 93 Rapeseed –10 98 Sunflower –17 125 Soya bean –16 130 (a) Do the results in the table indicate that there is a relationship between the melting point of a plant oil and its hardness? Explain your answer. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (2) (b) The company stated that some of the plant oils were brown and that this may have affected the results. Explain why the company considered the colour of plant oils to be a problem with this test. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (2) (c) A consumer group stated that the test should not be carried out by the margarine company but by independent scientists. Explain why. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (2) (d) The company intends to use sunflower oil to make its margarine. Explain how the company could process the sunflower oil to make it suitable for the manufacture of margarine. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (3) (Total 9 marks) Q35. (a) PEX is a material that is used as an alternative to copper for hot water pipes. PEX is made from poly(ethene). (i) Describe how ethene forms poly(ethene). .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (2) (ii) PEX is a shape memory polymer. What property does a shape memory polymer have? .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (iii) The simplified structures of poly(ethene) and PEX are shown. Poly(ethene) PEX Poly(ethene) is a thermoplastic that softens easily when heated. Suggest and explain how the structure of PEX changes this property. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (3) (b) Copper was considered to be the most suitable material to use for hot water pipes. PEX is now used as an alternative material for hot water pipes. Copper is extracted from its ore by a series of processes. 1 The low-grade ore is powdered and concentrated. 2 Smelting is carried out in an oxygen flash furnace. This furnace is heated to 1100 °C using a hydrocarbon fuel. The copper ore is blown into the furnace with air, producing impure, molten copper. 3 Oxygen is blown into the impure, molten copper to remove any sulfur. The copper is cast into rectangular slabs. 4 The final purification of copper is done by electrolysis. PEX is made from crude oil by a series of processes. 1 Fractional distillation 2 Cracking 3 Polymerisation 4 Conversion of poly(ethene) into PEX Suggest the possible environmental advantages of using PEX instead of copper for hot water pipes. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (4) (Total 10 marks) Q36. Hot air balloons burn hydrocarbons to heat the air. (a) The hot air contains these gases: nitrogen, N2 oxygen, O2 argon, Ar carbon dioxide, CO2 water vapour, H2O (i) Argon is an element. What is an element? .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (ii) Name one other gas in the hot air that is also an element. .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (b) Propane, C3H8, can be represented as: H H H H │ │ │ C C C H │ H │ H │ H Use the correct words from the box to complete the sentences. bond (i) carbon compound element mixture Propane is a ....................................... and is made up of atoms of hydrogen and ....................................... (2) (ii) Each line between the atoms in propane represents a chemical ....................... (1) (Total 5 marks) Q37. Use the correct words from the box to complete the sentences. higher oxygen (i) hydrogen saturated lower unsaturated Animal and vegetable oils that contain .................................. fats can be hardened. (1) (ii) When oils are hardened with .................................. gas, a chemical change takes place, producing margarine which has a .................................. melting point than the original oil. (2) (Total 3 marks) Q38. Plastics are used to make many everyday items, such as the body of the kettle. (a) Complete the sentences by drawing a ring around the correct words. catalysts (i) The plastic is made from many small molecules called monomers polymers (1) (ii) Propene is produced by cracking some of the fractions that are crude oil separated from limestone metal ores (1) (b) After a few years the kettle no longer worked. • • • Some parts of the kettle are made of plastic. Some parts of the kettle are made of stainless steel. The owner of the kettle disposed of it in a landfill site. Consider these statements. Suggest three reasons why the kettle should not be disposed of in a landfill site. 1 .................................................................................................. ............................... ............................................................................................................ ........................ 2 .................................................................................................. ............................... ............................................................................................................ ........................ 3 .................................................................................................. ............................... ............................................................................................................ ........................ (3) (Total 5 marks) Q39. Global warming is thought to be happening because of the increased burning of fossil fuels. The concentration of carbon dioxide in the air from 1905 to 2005 has been calculated. (a) Draw a line of best fit for these points. (1) (b) (i) What was the concentration of carbon dioxide in 1955? .................................................................................................. ................ ppm (1) (ii) In what year did the concentration of carbon dioxide reach 350 ppm? .................................................................................................. ........................ (1) (c) Use the graph to describe, in as much detail as you can, what happened to the concentration of carbon dioxide from 1905 to 2005. ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ (2) (Total 5 marks) Q40. Copper metal is used for electric wires. An alloy of copper, called brass, is used for pins and terminals of electric plugs. (a) Copper metal is relatively soft and flexible. Give another reason why copper is used for electric wires. ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ (1) (b) Brass is an alloy. What is an alloy? ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ (1) (c) Open-cast mining of copper ore makes a very large hole. (i) Suggest one environmental problem that is caused by opencast mining of copper ore. .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ (1) (ii) Some copper ores contain copper sulfide, CuS. Copper sulfide is heated in air to produce copper and sulfur dioxide. CuS + O2 → Cu + SO2 Suggest one environmental problem caused by heating copper sulfide in air. .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ (1) (d) The amount of copper-rich ores is estimated to last only a few more years. New houses need several kilometres of copper wire. (i) Explain why the need to use so much copper will cause a problem in the future. .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ (1) (ii) Suggest two ways in which society could overcome this problem. 1 ......................................................................................... .............................. .................................................................................................. ........................ 2 ......................................................................................... .............................. .................................................................................................. ........................ (2) (Total 7 marks) Q41. A map of the world shows that the outline of South America looks as if it would fit into the west coast of Africa. • Alfred Wegener in 1920 suggested his idea that the continents had been joined together but then slowly drifted apart. • Other scientists in 1920 said that the continents were fixed on solid Earth and had been joined by a land bridge. Modern South American animals are different from modern African animals. Most fossils of animals found in South America and Africa are exactly the same. (a) Consider the information above. (i) What evidence gave Wegener the idea that the continents of South America and Africa had been joined? .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ (1) (ii) Suggest two reasons why the other scientists in 1920 thought that Wegener was wrong. 1 ......................................................................................... .............................. .................................................................................................. ........................ 2 ......................................................................................... .............................. .................................................................................................. ........................ (2) (b) Complete the sentences by writing in the correct words. Recent evidence has supported Wegener’s idea. The Earth’s .................................. and the upper part of the mantle are now thought to be composed of tectonic plates. Heat released by radioactive processes causes convection currents within the Earth’s .................................. These convection currents cause the plates to move a few centimetres per ................................... (3) (Total 6 marks) Q42. Aluminium has many uses because of its low density, good electrical conductivity, flexibility and resistance to corrosion. The main steps in the extraction of aluminium are shown in the flow chart. (a) Use the information in the flow chart to suggest the benefits of recycling aluminium. ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ (3) (b) Pure aluminium is rarely used for the construction of large objects. Small amounts of other metals are usually mixed with aluminium. Explain why. ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ (2) (Total 5 marks) Q43. Since 2000 there has been a lot more research into alternative, environmentally-friendly fuels for road transport. Several pollutants are found in the exhaust emissions produced when fossil fuels are used for road transport. Carbon monoxide (CO) interferes with the way that red blood cells carry oxygen. Carbon dioxide (CO2) increases the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and causes global warming. Oxides of nitrogen (NOx) are produced at high temperatures when nitrogen and oxygen from the atmosphere combine. Sulfur dioxide (SO2) is produced when sulfur impurities in the fuel combine with oxygen in the atmosphere. Tiny particles of solids are produced when the fuel does not burn completely. This increases the level of particulates (PM10) in the atmosphere. (a) Name the environmental effect caused by: (i) oxides of nitrogen (NOx) and sulfur dioxide (SO2) .................................................................................................. ........................ (1) (ii) the increased level of particulates (PM10). .................................................................................................. ........................ (1) (b) Diesel obtained from crude oil is often called fossil diesel. Biodiesel can be made from many vegetable oils. One research project compared the exhaust emissions when fossil diesel or biodiesel were used as fuels. Some of the relative amounts of these exhaust emissions are shown in the bar chart. (i) Use your knowledge and the information above to explain the environmental benefits of using biodiesel as a sustainable, low pollution fuel. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (3) (ii) Biodiesel is called a green fuel. This is because the life-cycle emission of carbon dioxide from biodiesel is less than that from fossil diesel. Use your knowledge and the information above to explain why biodiesel’s contribution to global warming is considered to be much less than that of fossil diesel. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (3) (Total 8 marks) Q44. Crude oil is the source of many useful materials. Crude oil is separated into fractions by fractional distillation. (a) Describe how the naphtha fraction separates from the other fractions. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (2) (b) The naphtha fraction is often used to make other useful materials. This involves the cracking of hydrocarbons in the naphtha fraction. For example: decane C10H22 (i) → → hexane C6H14 + + ethene C2H4 Balance the symbol equation given above. (1) (ii) Describe how cracking is carried out. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (2) (iii) Why does ethene have different chemical properties from decane and hexane? .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (2) (c) Ethene is used as the starting material for many polymers. The most common polymer is poly(ethene). One hydrocarbon molecule in poly(ethene) will contain thousands of carbon atoms. Complete the diagram to show the bonds in ethene. H H C C H H (1) (d) Read the following information. Landfill, Incineration, Recycling and Re-use of Poly(ethene) People could be encouraged to re-use their poly(ethene) bags and containers. Recycling poly(ethene) saves raw materials and energy needed to make new plastic. When polymers are recycled the plastics must be collected, transported, sorted into different types by hand and washed. This requires the use of fossil fuels and is expensive. Poly(ethene) can be burnt in an incinerator with other household waste. The heat released could be used to make steam to drive an electric generator. Surplus heat could be used to heat greenhouses used for growing vegetables. Incineration at too low a temperature can produce harmful substances. The residue (ash) has to go to landfill. Landfill is probably the easiest way to dispose of polymers and it is cheap. Polymers are often mixed in with other household rubbish. Household waste does not get sorted into different materials because it is disposed of in the same hole in the ground. When the hole is eventually full, the waste is covered by a layer of soil to stop it smelling. The waste gets compressed under its own weight. Most polymers, such as poly(ethene), are not biodegradable so will remain in the ground forever. You are asked to decide which option for the disposal of poly(ethene) will be put forward in your area. You decide that recycling is the best option. Suggest one economic argument and one environmental argument that will be made against recycling. For each argument made, how will you persuade those making the argument to accept your option? (You must use only one sentence for each argument made against your decision and only one sentence for your response to it.) ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (4) (Total 12 marks) Q45. Hydrogen is an element. (a) The diagram shows the parts of a hydrogen atom. Use words from the box to label the diagram. electron group nucleus symbol (2) (b) Hydrogen can be used as a clean fuel for cars. (i) When hydrogen burns in air, it reacts with another element. Complete the word equation for this reaction. hydrogen + ................................. → water (1) (ii) Suggest one reason why hydrogen is called a clean fuel. .................................................................................................. ....................... .................................................................................................. ....................... (1) (Total 4 marks) Q46. Most electricity in the UK is generated in power stations that burn fossil fuels. The diagram lists some of the substances released into the air when fossil fuels are burned. (a) (i) Which one of the substances released into the air causes acid rain? .................................................................................................. ....................... (1) (ii) In the sentence below, draw a ring around the correct answer. The type of environmental pollution caused by global dimming smoke particle is global warming rising sea levels (1) (iii) Suggest how the burning of fossil fuels may cause climate change. .................................................................................................. ....................... .................................................................................................. ....................... .................................................................................................. ....................... .................................................................................................. ....................... (2) (b) The table shows the percentage of electricity generated by different energy sources. Energy sources Percentage (%) Renewables Nuclear Coal Gas and Oil 8 20 32 40 Complete the bar chart to show the percentage of electricity generated by coal and by gas and oil. (2) (Total 6 marks) Q47. A headline from 27 December 2004 read: (a) Use words from the box to complete the sentences about earthquakes. convection radioactive tectonic volcanic The earthquake was caused by the movement of two of the Earth’s ......................................................... plates. The energy for this movement comes from the heat released by natural ......................................................... processes. (2) (b) It was estimated that 300 000 people died as a result of the tsunami in 2004. Some newspapers criticised scientists for not predicting the tsunami, because if people had been warned they could have moved to safety. (i) Suggest why we can only estimate that 300 000 people died as a result of the tsunami. .................................................................................................. ....................... .................................................................................................. ....................... .................................................................................................. ....................... .................................................................................................. ....................... (2) (ii) Explain why scientists could not have predicted the tsunami. .................................................................................................. ....................... .................................................................................................. ....................... .................................................................................................. ....................... .................................................................................................. ....................... (2) (Total 6 marks) Q48. The label on a bottle of salad dressing shows that the dressing contains the following ingredients. Ingredients Water Vegetable oil Egg yolk Sugar Flour Vinegar Salt (a) Extract of spices Preservative E202 Emulsifier E405 One of the main ingredients in salad dressing is vegetable oil. (i) Use the correct word from the box to complete the sentence about the extraction of vegetable oil. crushed evaporated hardened To extract the vegetable oil, the fruits or seeds of plants are first ......................................................... . (1) (ii) The liquids can be separated from the solid parts of the fruits or seeds by filtering. Suggest one reason why separation by filtering is better than separation by distilling. .................................................................................................. ....................... .................................................................................................. ....................... (1) (b) (i) A mixture of vegetable oil and water is shaken and left to stand for several minutes. The diagram shows the result. Complete the following sentence. The vegetable oil and water .................................................................................... . (1) (ii) A mixture of vegetable oil, water and egg yolk is shaken and left to stand for several minutes. The diagram shows the result. Use words from the box to complete the sentence. additive distil emulsion extract mix separate The egg yolk causes vegetable oil and water to ........................................................ and form an ..................................................... . (2) (Total 5 marks) Q49. Tablet containers are often made from two different polymers. (a) Ethene, C2H4, and propene, C3H6, can be made from crude oil. (i) Complete the following sentence. Ethene and propene are called hydrocarbons because they are made up of carbon and ..................................................... atoms only. (1) (ii) Ethene molecules are used to form poly(ethene) molecules. Complete the diagram to show the poly(ethene) molecule. Ethene molecules Poly(ethene) molecule (2) (b) The tablet containers could be disposed of in a landfill site or could be recycled. (i) Suggest two reasons why disposing of the tablet containers in a landfill site could cause problems. 1 ......................................................................................... .............................. .................................................................................................. ........................ 2 ......................................................................................... .............................. .................................................................................................. ........................ (2) (ii) Suggest one reason why recycling the tablet containers would be difficult. .................................................................................................. ..................... .................................................................................................. ..................... (1) (Total 6 marks) Q50. Metals and their alloys have many uses. (a) Dentists use a smart alloy to make braces that gently push teeth into the right position. What is meant by a smart alloy? ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ (1) (b) Pure copper is made up of layers of copper atoms. Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc. Why are the physical properties of brass different from the physical properties of pure copper? ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ (2) (c) Nearly all zinc is obtained from ores that also contain lead. The metals zinc and lead can be extracted by reducing their oxides using carbon. (i) Choose one element from the box below to complete the sentence about the reduction of zinc oxide. lead nitrogen oxygen Zinc oxide is reduced by carbon, which takes away.................................................. to leave zinc metal. (1) (ii) The melting points and boiling points of lead and zinc are given in the table. Metal Lead Zinc Melting point in °C 328 420 Boiling point in °C 1740 907 The furnace operates at a temperature of 1200 °C. Suggest how the lead metal and zinc metal are separated in the furnace. .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ (2) (Total 6 marks) Q51. Limestone is mainly calcium carbonate. (a) Quicklime is produced by heating limestone. (i) Complete the word equation for this reaction by writing the chemical name of the solid and the gas produced. calcium carbonate → ................................. + ................................. . (2) (ii) What is the name for this type of chemical reaction? .................................................................................................. ........................ (1) (b) Quicklime is used in self-heating cans. The diagram shows a self-heating can designed to raise the temperature of coffee to 60 °C. The button on the base of the can is pushed. The foil separator breaks, allowing water to mix with the quicklime. After about 3 minutes, the can is opened by the ring pull. Insulating materials are used inside the walls of the can to prevent either the lips or the fingers from being burned. (i) Explain why the coffee becomes hot. .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ (2) (ii) Suggest two reasons why it is not possible to re-use this selfheating can. 1 ......................................................................................... .............................. .................................................................................................. ........................ 2 ......................................................................................... .............................. .................................................................................................. ........................ (2) (Total 7 marks) Q52. The hydrocarbons in crude oil can be separated into useful fractions. Fraction Boiling point in °C Carbon chain length Relative % in crude oil Relative % demand Naphtha 20–180 5–9 10 20 Gasoline (petrol) 20–200 5–10 10 20 Kerosene (paraffin) 180–260 10–16 15 23 Diesel 260–340 14–20 20 25 Fuel oil 370–600 20–70 45 12 (a) Why does gasoline (petrol) have a lower boiling point than fuel oil? ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ (1) (b) Suggest why gasoline (petrol) costs more than fuel oil. ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ (2) (c) Describe how fuel oil can be changed into gasoline (petrol). ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ (2) (Total 5 marks) Q53. Titanium is used in aircraft, ships and hip replacement joints. Titanium is as strong as steel but 45% lighter, and is more resistant to acids and alkalis. Most titanium is produced from its ore, rutile (titanium oxide), by a batch process that takes up to 17 days. Titanium reactors produce about 1 tonne of the metal per day. Iron blast furnaces produce about 20 000 tonnes of the metal per hour. (a) Give one property of titanium that makes it more useful than steel for hip replacement joints. ............................................................................................................ ........................ (1) (b) In the reactor magnesium is used to produce titanium. If carbon were used instead of magnesium, no titanium would be produced. What does this tell you about the relative reactivities of carbon, magnesium and titanium? ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ (2) (c) The use of titanium is limited because it is expensive. Explain why titanium costs more than steel. ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ (3) (Total 6 marks) Q54. A company compared the relative ‘unsaturation’ of five oils. Bromine water was added from a burette to equal amounts of each oil until the bromine water remained orange-yellow. The volume added was recorded. Type of oil Volume of bromine water added in cm3 Maize 25.6 Olive 6.1 Palm 4.9 Soya Bean 29.9 Sunflower 25.1 (i) What would you see when the first few drops of bromine water are added to each oil? ............................................................................................................ ....................... (1) (ii) What do these results tell you about sunflower oil compared with the other oils? ............................................................................................................ ....................... ............................................................................................................ ....................... ............................................................................................................ ....................... ............................................................................................................ ....................... (2) (Total 3 marks) Q55. A large reservoir is surrounded by trees. Planners need to protect the environment. The distance around the reservoir is many kilometres. There will be only one road access to a car park a few kilometres from the reservoir. From the car park people would be transported to accommodation, activities or places of interest by steam train. (a) Coal contains carbon and small amounts of sulfur. The steam train would cause environmental problems if coal were used as the fuel. Explain why. ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ (4) (b) The planners have stated that, as a result of using the steam train, there must be no overall increase of carbon dioxide added to the atmosphere. The steam train would be considered as ‘carbon neutral’ if wood, from the surrounding forest, were used as the fuel. Suggest why. ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ (3) (Total 7 marks) Q56. Scientists study the atmosphere on planets and moons in the Solar System to understand how the Earth’s atmosphere has changed. (a) Millions of years ago the Earth’s atmosphere was probably just like that of Mars today. The table shows data about the atmospheres of Mars and Earth as they are now. Mars Earth nitrogen 3% nitrogen 78% oxygen trace oxygen 21% water trace water trace carbon dioxide 95% carbon dioxide trace Average surface temperature –23 °C Average surface temperature 15 °C Suggest what has caused the main gases in the Earth’s atmosphere of millions of years ago to change to the present-day atmosphere. ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ (2) (b) Titan is the largest moon of the planet Saturn. It has an atmosphere that, like the Earth’s, contains mainly nitrogen. Methane is the other main gas. Main gases in Titan’s atmosphere Percentage (%) Boiling point in °C Nitrogen 95 –196 Methane 5 –164 Average surface temperature –178 °C When it rains on Titan, it rains methane! Explain why. ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ (2) (c) Ultraviolet radiation from the Sun produces simple alkenes, such as ethene and propene, from methane in Titan’s atmosphere. (i) Draw the structure of propene, C3H6, to show the covalent bonds. (1) (ii) Explain how propene molecules form a polymer. You should name the polymer formed. .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ (3) (Total 8 marks) Q57. Lithium metal is used in alkaline batteries. (a) The diagram shows the atoms in lithium metal. Why is lithium metal described as an element? ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (1) (b) The diagram below represents a lithium atom. Choose words from the box to label parts of the atom. bond electron molecule nucleus (2) (Total 3 marks) Q58. A vegetable oil can be extracted from olives. (a) The diagram shows the first step in this extraction. Use the correct word from the box to complete the sentence about this first step. evaporating filtering pressing The olive oil is extracted by ................................................................... the olives. (1) (b) The contents from the mortar are tipped into a beaker. The mixture is left to settle. (i) What is the name of the colourless liquid? .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (ii) How can the olive seeds and skins be removed from the liquids? .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (Total 3 marks) Q59. When electricity passes through a thin wire, the wire gets hot. If the wire gets very hot, it may glow. This idea is used in filament lamps. (a) The table shows some metals and their melting points. Metal Aluminium Melting point in °C 660 Copper 1084 Iron 1540 Tungsten 3410 Which metal in the table should be used to make the wire in a filament lamp? Give a reason for your answer. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (2) (b) The table shows some gases. Gas Argon Carbon dioxide Oxygen Sulfur dioxide Which gas in the table should be used in a filament lamp? Give a reason for your answer. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (2) (Total 4 marks) Q60. Limestone contains calcium carbonate. (a) Calcium carbonate has the formula CaCO3. Complete the sentence by writing in the correct numbers. The formula of calcium carbonate is made up of 1 calcium atom, ............ carbon atom(s) and ............ oxygen atom(s). (2) (b) When limestone is heated it forms two other compounds. (i) State one safety precaution that you should take when heating limestone. .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (ii) Name the white solid produced. .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (iii) Why does a piece of limestone lose mass as it is heated? .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (d) A company wants to quarry limestone. There are some houses near the quarry. Residents in the houses say that they do not want a quarry next to them. (i) Suggest two reasons why they do not want the quarry next to them. 1 ......................................................................................... ............................... .................................................................................................. ......................... 2 ......................................................................................... ............................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (2) (ii) Suggest one possible benefit to the residents of having a quarry near their houses. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (Total 8 marks) Q61. Polymers are used to make many materials that people need. (a) Plastic bags are used to carry, protect and store food. Plastic bags are made from polymers. (i) Ethene is the small molecule (the monomer) used to make the polymer for this plastic bag. Name the polymer that is made from ethene. .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (ii) Use the correct word from the box to complete the sentence about ethene. condensing corroding cracking Ethene is made by breaking down large hydrocarbon molecules into smaller hydrocarbon molecules by a process called ..................................................... (1) (iii) The hydrocarbon ethene has the formula C2H4 Complete the sentence about ethene. Ethene is a hydrocarbon made up of carbon and .......................................... atoms. (1) (b) The hydrocarbons used to make ethene come from crude oil. The properties of hydrocarbons are linked to the number of carbon atoms in their molecules. Number of carbon atoms 5 6 7 8 9 Boiling point in °C 36 69 99 125 151 (i) Use the data in the table to complete the bar chart. (2) (ii) What happens to the boiling point of a hydrocarbon as the number of carbon atoms increases? .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (iii) All the hydrocarbons in the table are found in petrol. Petrol is one of the fractions separated from crude oil. Describe how the fractions are separated from crude oil. .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (2) (c) Most plastic bags that are made of hydrocarbons are not biodegradable. Used plastic bags can be: • dumped into large holes, which is called landfill • burned to give out heat energy, which would produce large amounts of gases. Would burning used plastic bags be better for the environment than dumping them in landfill? Explain your answer. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (2) (Total 10 marks) Q62. (a) Two hundred years ago, scientists thought that the Earth was about 400 million years old. This estimate came from the idea that the centre of the Earth was still molten. More recently, measurement of radioactivity in rocks has shown that the Earth is much older than 400 million years. Suggest one reason why scientists now know that the Earth is much older than 400 million years. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (1) (b) About one hundred years ago there was a scientist called Alfred Wegener. He found evidence that the continents, such as South America and Africa, had once been joined and then drifted apart. Use the diagram to suggest two pieces of evidence that could be used to show that the continents had once been joined. 1 .................................................................................................. ................................ ............................................................................................................ ......................... 2 .................................................................................................. ................................ ............................................................................................................ ......................... (2) (c) About fifty years ago, new evidence convinced scientists that the Earth’s crust is made up of tectonic plates that are moving very slowly. Give two pieces of evidence that have helped to convince these scientists that the tectonic plates are moving. 1 .................................................................................................. ................................ ............................................................................................................ ......................... 2 .................................................................................................. ................................ ............................................................................................................ ......................... (2) (Total 5 marks) Q63. Life on Earth would not exist without the atmosphere. Billions of years ago the composition of the Earth’s atmosphere was very different from the composition today. (a) Label the pie chart below to show the percentages and names of the two main gases in the Earth’s atmosphere today. (2) (b) There is evidence that the composition of the Earth’s atmosphere is still changing. One possible reason is that many power stations generate electricity by burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil or natural gas. Sulfur dioxide, SO2, is produced when coal burns in air. (i) What environmental problem does sulfur dioxide cause? .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (ii) How could this environmental problem be reduced in coalfired power stations? .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (iii) Gas-fired power stations burn methane, CH4, in air. Complete the word equation for this reaction. methane + ............................... → carbon dioxide ............................... (2) (c) Excess carbon dioxide should be prevented from entering the atmosphere. Explain why. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (2) (d) Carbon dioxide is produced when fossil fuels burn in power stations. The diagram represents one idea to prevent excess carbon dioxide from entering the atmosphere. Use the diagram to explain how carbon dioxide can be prevented from entering the atmosphere. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (2) (Total 10 marks) Q64. Many everyday items are made from iron. (a) Haematite is an ore of iron. Haematite contains iron oxide, Fe2O3. (i) What is the meaning of the term ore? .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (ii) Iron can be produced by reacting iron oxide with carbon in a blast furnace. What type of reaction produces the iron? .................................................................................................. ......................... .................................................................................................. ......................... (1) (iii) The word equation for this reaction is: iron oxide + dioxide carbon → iron + carbon Complete and balance the symbol equation for this reaction. .....Fe2O3 + ................... .....C → ................... + (2) (b) Pure iron is relatively soft and not very strong. The iron from the blast furnace is very hard and brittle. It contains about 4% carbon and is used as cast iron. Explain the differences in the properties of pure iron and cast iron by referring to the diagrams. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (3) (c) The diagram shows the way in which iron is extracted, used and recycled. Explain why the recycling of iron is necessary for sustainable development. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (3) (Total 10 marks) Q65. This information was taken from a label on a packet of crisps. Main ingredients: Potatoes, vegetable oil, Worcester sauce flavour, colourings, flavourings, salt. Nutritional information (per 100 g): Energy 2040 kJ Protein 6.5 g Carbohydrate 55 g of which sugars Fat 3g 27 g of which saturates unsaturates 9g 18 g Fibre 4.5 g Sodium 1.2 g Saturated fats are linked to heart problems. In order to claim that their crisps are healthy, the manufacturer keeps the proportion of saturated fats low. (i) What type of fat contains double carbon carbon bonds? ............................................................................................................ ......................... (1) (ii) The colour of bromine water is orange. What is seen when bromine water is shaken with: an unsaturated fat ........................................................................................................ a saturated fat? ............................................................................................................ (2) (iii) Unsaturated vegetable oils can be hardened to make them useful as spreads. Describe how unsaturated vegetable oils are hardened. ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... ............................................................................................................ ......................... (2) (Total 5 marks) Q66. Crude oil is a mixture of mostly alkanes. (a) Crude oil is separated into useful fractions by fractional distillation. (i) Describe and explain how the mixture of alkanes is separated by fractional distillation. .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ (3) (ii) The table gives the name and formula for each of the first three alkanes. Complete the table to show the formula of butane. Name of alkane Formula Methane CH4 Ethane C2H6 Propane C3H8 Butane (1) (b) The structural formula of methane, CH4, is: H H │ C │ H H Draw the structural formula of propane, C3H8 (1) (c) The relative amounts of and the market demand for some hydrocarbons from the fractional distillation of crude oil are shown in the graph. (i) Why is the market demand for the C5 – C8 fraction higher than the market demand for the C21 – C24 fraction? .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ (1) (ii) Cracking is used to break down large hydrocarbon molecules into smaller hydrocarbon molecules. Complete the symbol equation by writing in the formula of the other hydrocarbon. C20H42 C16H34 + 2 .......................................... (1) (iii) The C5 – C8 fraction has low supply and high market demand. Suggest three ways in which the oil industry could overcome this problem. 1 ......................................................................................... ................................ .................................................................................................. .......................... 2 ......................................................................................... ................................ .................................................................................................. ........................ 3 ......................................................................................... .............................. .................................................................................................. ........................ (3) (Total 10 marks) Q67. Crude oil is a natural resource from which useful fuels can be separated. (a) Crude oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons. Complete the sentence about a hydrocarbon molecule. A hydrocarbon molecule is made up of ....................................... and carbon atoms only. (1) (b) Many fuels come from crude oil. Some of these fuels are shown in the diagram. Suggest two properties of these fuels that allow them to be separated from crude oil. ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ (2) (c) Fuels from crude oil burn to provide heat energy. When a fuel burns, it combines with oxygen in the air and produces carbon dioxide and water. When there is not enough oxygen, the fuel burns and also produces carbon monoxide and carbon particles. Draw a straight line from each substance that links it to a possible environmental problem. One has been done for you. (3) (Total 6 marks) Q68. Iron ore is the main source of iron. (a) This was the headline in a newspaper. ‘Village protests against quarry’ The dotted line ( ---- ) on the map is drawn around the area from which a company wants to quarry iron ore. (i) Give one reason that the company could give for the need to quarry the iron ore. .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ (1) (ii) The people who live in the village do not want the quarry because it would decrease the value of their homes. Suggest two other reasons why the villagers do not want the quarry. 1 ......................................................................................... .............................. .................................................................................................. ........................ 2 ......................................................................................... .............................. .................................................................................................. ........................ (2) (b) Iron ore contains the compound iron oxide, Fe2O3. (i) Iron is extracted from its oxide in the blast furnace. Complete the word equation for the extraction of iron. iron oxide + ............................................................... → iron + carbon dioxide (1) (ii) This diagram represents pure iron. Use the diagram to explain why pure iron is described as an element. .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ (2) (iii) Pure iron is relatively soft. The iron from the blast furnace is hard and brittle. The diagram below represents iron from the blast furnace. Use the diagram to explain why iron from the blast furnace is hard and brittle. .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ (2) (Total 8 marks) Q69. The Earth is shaped like a ball and is surrounded by an atmosphere. (a) The diagram shows the layered structure of the Earth. Choose words from the box to complete the labels on the diagram. core mantle plate (2) (b) Some theories suggest that the Earth’s early atmosphere was like the atmosphere of Mars today. The bar charts show the three most common gases in each atmosphere today. (i) Use the bar charts to complete the sentence by writing in the correct gases. In the atmosphere of Mars today there is mainly ......................................... and no ......................................... . (2) (ii) Use the bar charts to complete the sentence by writing in the correct number. These theories suggest that there was about ......................................... % nitrogen in the Earth’s early atmosphere. (1) (iii) The atmosphere of the Earth today has much more nitrogen than in the early atmosphere. Denitrifying bacteria released most of this nitrogen into the atmosphere. There are other differences between the Earth’s early atmosphere and the atmosphere of the Earth today. Use the bar charts to describe and explain two of these other differences. .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ (3) (Total 8 marks) Q70. Limestone contains the compound calcium carbonate, CaCO3. (a) Limestone is used to make cement in a rotary kiln. Use the information in the diagram to name the two main waste gases from this rotary kiln. 1 .................................................................................................. ............................... 2 .................................................................................................. ............................... (2) (b) Columns used as supports for buildings can be made from materials such as limestone blocks or concrete. From the diagrams, name which you think is the better material for making a column. ............................................................................................................ ........................ Give three advantages for your choice of material. 1 .................................................................................................. ............................... ............................................................................................................ ........................ 2 .................................................................................................. ............................... ............................................................................................................ ........................ 3 .................................................................................................. ............................... ............................................................................................................ ........................ (3) (Total 5 marks) Q71. Copper is a widely used metal. The main ore of copper contains copper sulfide. Copper can be extracted from copper sulfide in a three stage process. (a) In the first stage of extraction the copper sulfide is heated in air. (i) Balance the symbol equation for the reaction. Cu2S + ........O2 → .........CuO + SO2 (1) (ii) Explain why there would be an environmental problem if the gas from this reaction were allowed to escape into the atmosphere. .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ (2) (b) In the second stage copper oxide, CuO, is reduced using carbon. Describe and explain what happens during this reaction. ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ (2) (c) During the third stage the copper can be purified as shown in the diagram. (i) What is the name of the type of process used for this purification? .................................................................................................. ........................ (1) (ii) Give one use of purified copper. .................................................................................................. ........................ (1) (d) Copper-rich ores are running out. New ways of extracting copper from low grade ores are being researched. Recycling of copper may be better than extracting copper from its ores. Explain why. ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ (3) (Total 10 marks) Q72. The Earth is shaped like a sphere and is surrounded by an atmosphere. (a) The diagram shows a section of the layered structure of the Earth. (i) Complete the diagram by writing in the missing label. (1) (ii) Earthquakes within the Earth’s crust can be sudden and disastrous. Scientists cannot accurately predict when earthquakes will occur. Explain why. To obtain full marks you must support your answer with a description of what causes earthquakes. .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ (4) (b) Some theories suggest that the Earth’s early atmosphere was like the atmosphere of Mars today. The atmosphere of Mars today The atmosphere of Earth today Carbon dioxide % 95 0.03 Nitrogen % 3 Gases (i) Argon % 1.5 0.97 Oxygen % 0.5 21 Complete the table by writing in the percentage of nitrogen in the atmosphere of Earth today. (1) (ii) Use the information in the table to describe the changes that have happened to two of the gases in the Earth’s atmosphere. Explain what has caused these changes. .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ (4) (Total 10 marks) Q73. (a) The diagrams show the results of shaking a vegetable oil with the substances indicated. (i) Give a reason for the result in Flask 1. .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ (1) (ii) Explain the result in Flask 2. .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ (2) (b) Saturated fats are linked to heart problems. Oils that are unsaturated help to prevent heart disease. A company wants to make a ‘healthy’ soft margarine. The company tested the same volume of different vegetable oils by shaking each with three drops of iodine solution. The results are shown in the table. Vegetable oil (i) Time in minutes for the colour of iodine to ‘disappear’ Olive oil 3.5 Peanut oil 3.0 Soya oil 1.5 Sunflower oil 1.0 Why does iodine react with the molecules in these oils? .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ (1) (ii) Use the company results to evaluate which one appears to be the most ‘healthy’ vegetable oil to use in the soft margarine. .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ (2) (c) The ingredients of soft margarine include hydrogenated vegetable oil. (i) Why is hydrogenated vegetable oil used in soft margarine? .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ (1) (ii) Describe how vegetable oils are hydrogenated. .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ (2) (Total 9 marks) Q74. Known crude oil reserves are being used up rapidly. Crude oil is used to produce many useful fuels, such as petrol. One way to conserve crude oil reserves would be to increase the production of bio-fuels. (a) Ethanol can be produced for use as a bio-fuel. Cars can be powered by ethanol or ethanol–petrol mixtures. Sugar cane can be fermented to give a mixture of water (boiling point 100 °C) and ethanol (boiling point 78 °C). (i) How can ethanol be separated from water? .................................................................................................. ........................ .................................................................................................. ........................ (1) (ii) Ethanol, C2H5OH, burns to release heat energy. Complete the balanced symbol equation by writing in the formulae of the two products. C2H5OH + 3O2 2......... + 3......... (2) (b) The cost of producing a bio-fuel, such as ethanol, by fermentation, is at least three times higher than the production cost of petrol. It costs less to produce ethanol from alkanes. In the production, the vapour of an alkane is passed over a hot catalyst. Ethene is then converted into ethanol. (i) What has happened to the hexane to produce ethene? .................................................................................................. ........................ (1) (ii) Complete the structural formula for ethene, C2H4. C C (1) (iii) Name the compound that is added to ethene to produce ethanol, C2H5OH. .................................................................................................. ........................ (1) (c) As explained in parts (a) and (b), ethanol can be made using either sugar or alkanes as the starting material. Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of using these two starting materials to produce ethanol. ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ ............................................................................................................ ........................ (4) (Total 10 marks) Q75. (a) Complete this sentence about crude oil. Crude oil is mainly a mixture of compounds called ...................................... which contain carbon and hydrogen only. (1) (b) The diagram shows a laboratory experiment used to separate crude oil. Complete each sentence by choosing the correct words from the box. condensation distillation melting evaporation sublimation The main process taking place at A is ....................................................................... The main process taking place at B is ....................................................................... This method of separating crude oil is called ............................................................ (3) (c) Complete this sentence by crossing out the word in each box that is wrong. The first one has been done for you. This method of separating crude oil works because the the molecules are, the they are. their boiling point and the volatile (1) (Total 5 marks) M1. (a) (i) C2H4 1 (ii) poly(ethene) 1 (b) (i) is not biodegradable 1 (ii) not enough landfill sites / space accept landfill sites are filling up or plastics remain for years or plastics not broken down ignore cost / waste of resources / not biodegradable / wildlife 1 (iii) less (crude) oil / fuels / energy used accept (crude) oil is a non-renewable resource 1 [5] M2. (a) (i) nitrogen / N2 1 (ii) carbon dioxide / CO2 1 (b) (i) humans / scientists had not evolved accept it was billions / millions of years ago allow too long ago 1 (ii) temperature is above 100°C or any water would evaporate / boil accept Venus is too hot 1 (c) any three from: • used by plants • used for photosynthesis accept plants take in carbon dioxide and give out oxygen for the first two bullet points ie 2 marks • dissolves in oceans / seas allow absorbs into oceans / seas • used to form the shells / skeletons of marine organisms • locked up as limestone / carbonates • locked up as fossil fuels / oil / coal 3 [7] M3. (a) (i) wood 1 (ii) 30 (kJ) 1 (iii) carbon / C or hydrogen / H or sulfur / S or oxygen / O 1 (iv) 3 / three (g) 1 (b) (i) releases most energy accept releases a lot of energy / burns rapidly ignore references to cost 1 no harmful gases / no or less pollution formed / no global warming / no climate change / no greenhouse gas accept produces water (only) /steam accept does not produce sulfur dioxide / carbon dioxide / carbon monoxide / particles / smoke 1 (ii) any one from: • expensive • difficult to produce accept large volume needed • not available in large quantities • explosive / dangerous • not a natural fuel / resource allow will run out / non-renewable • made from fossil fuels • difficult to store 1 [7] M4. (a) conducts (electricity) or accept flexible allows electrons / current to flow ignore conducts heat 1 (b) electron 1 (c) (i) lithium>copper>tungsten or Li>Cu>W all correct allow 1 mark for one metal in the correct position 2 (ii) has high / highest melting point accept has high / highest boiling point or can withstand the highest temperature 1 (d) unreactive 1 [6] M5. (i) 23 to 59 accept 36 1 (ii) decolourise or (orange to) colourless ignore discolours / fades do not allow oil decolourises 1 (because bromine reacts with the) (carbon) double bond ignore alkenes or reference to unsaturation 1 (iii) any one from: • an anomalous result (11.2) / Test 2 accept • (= 23.6) 11.2 / Test 2 is ignored when averaging accept average of tests 1 and 3 1 (iv) unsaturation 67% average was less than it should be / only 26.8 cm3 1 (this means there is) 33% saturated fat it should have been 28.0 cm3 to give a percentage of 70% 1 [6] M6. (a) (i) oxygen / air reacts with carbon / methane (to form carbon dioxide) accept from the decomposition / reaction of calcium carbonate ignore CO2 from the air 1 nitrogen is (unreacted) from the air 1 (ii) CaO 1 CO2 any order ignore words any incorrect balancing max 1 mark 1 (b) any one from: • more energy / efficient allow converse for present fuel • from a sustainable / renewable resource • produces less / no carbon dioxide / greenhouse gases / global warming ignore no pollution / environmental damage • more profit or money for local economy accept fuel is cheap(er) • more readily available it = different fuel 1 (c) (i) any two from: • not near where people / residents live accept not between cement works and where people live ignore sensors are unsightly • not positioned where concentration of particles was likely to be highest • not positioned downwind 2 (ii) the average / concentration was 1.8(ppm) or the average / concentration was below 2(ppm) accept 1.8(ppm) is less than 2.0 (ppm) 1 (iii) any three from: • children / people suffering asthma attacks • result was an average • readings (at some (2/3) sensors) could have been higher than 2ppm • sensors did not detect particles below 0.5mm • small particles / particles below 0.5mm / 0.4mm / 0.3mm / 0.2mm could (still) cause cancer / asthma ignore global dimming or cars becoming dirty or position of sensors 3 [11] M7. (a) (Kent reported because) damage was caused or it was above 3 (on the Richter scale) accept description of damage 1 (others not reported because) no vibrations / not felt / not noticed allow below 3 (on Richter scale) ignore no damage 1 (b) movement of (tectonic) plates allow collision of plates or plates rubbing together or plates pushing against each other 1 any two from: • vibration / (shock)waves (in the earth) or p and s waves accept sudden jolts / slips • caused by convection currents (in the mantle) • heat / energy released from radioactive processes 2 (c) any two from: scientists do not know: • what happens under the crust / mantle / under the surface accept anything under the crust • where forces / pressures are building up • how to measure these forces / pressures • when these forces / pressures reach their limit accept there is no pattern ignore random / speed of movement 2 [7] M8. (a) (Chromium =) 20 1 in correct order (Nickel =) 8 accept Chromium = 8 and Nickel = 20 for 1 mark 1 (b) (i) (because iron is made up of only) one type of atom 1 (ii) not strong ignore soft / corrosive / flexible accept it rusts / corrodes or that it could wear away accept could change shape / bend accept layers / atoms could slide (over each other) 1 (iii) has different sized atoms / particles or structure is different/distorted / disrupted accept not in layers or not regular 1 so it is difficult for layers / atoms / particles to slip / slide (over each other) accept layers cannot slip / slide 1 [6] M9. (a) (i) the greater the number (of carbon atoms), the higher its boiling point do not accept hydrocarbons for carbon atoms allow converse allow melting point 1 (ii) accept answers in the range 344 to 350 1 (iii) 216 1 (b) (i) EITHER shortage of petrol or demand for petrol is higher than supply diesel is in excess or supply of diesel is higher than demand 1 OR petrol low supply and diesel high supply (1) petrol high demand and diesel low demand (1) petrol / diesel not specified = max 1 1 (ii) any one from: • use diesel to make petrol accept crack diesel or description of cracking • make diesel cheap(er) (than petrol) or make petrol more expensive accept lobby the government to reduce the tax on diesel / increase tax on petrol • mix ethanol with petrol ignore biodiesel 1 [6] M10. (a) (i) polyethene / poly(ethene) accept polythene / polyethylene 1 (ii) needs heat / energy / high temperature / fuel (for cracking) ignore other processes 1 produces carbon dioxide / CO2 ignore use of CO2 or ‘produces carbon’ 1 (b) any three from: • use water from local sources or water from close to home • recycle bottles in the UK / close to home accept do not recycle in other countries / Asia • (reduction in distance travelled) would reduce CO2 emitted by transport accept use of transport with low / no carbon dioxide emissions • use tap water • use glass bottles / waxed cartons / metal bottles do not accept ‘do not use plastic bottles’ without an alternative material • do not put in landfill or recycle more • reuse / refill plastic bottles • tax imported water / plastic bottles (to offset carbon cost) • make more / all plastic bottles in UK answers must be about the reduction of carbon cost 3 [6] M11. (a) core 1 (b) (i) 3 or below / low on the Richter scale accept vibrations not felt / causes no damage ignore references to injuries 1 (ii) 4 1 (iii) movement of (Earth.s / tectonic) plates allow plates collide 1 (iv) (earthquakes) cannot be predicted / sudden / without warning / random ignore under / in the sea 1 [5] M12. (a) (i) pressing 1 (ii) dissolve 1 (b) bromine 1 (c) temperature needs to be high / above 100 °C allow melting point 1 or (sunflower oil has a) high(er) boiling point or boiling point of water is not high enough any one from: • remove water / make potato crisp(er) accept water makes potato soft / soggy • adds / gives flavour 1 [5] M13. (a) (i) 1 1 3 1 (ii) nucleus 1 electron 1 (b) (i) methane / CH4 accept natural gas ignore air do not allow other gases 1 (ii) carbon dioxide 1 (c) (i) any two from: • medical risks • asthma • cancer • dirt • causes global warming / global dimming / greenhouse effect / acid rain ignore death accept effect on health accept difficulty breathing/ lung disease allow smoke particles allow harmful for the environment 2 (ii) any two from: • have a test done / scientific evidence • independent (evidence) • comparison of smoke particles / when different fuels used • medical evidence or more / less asthma attacks or cancer or dirt on cars 2 [10] M14. (a) atoms 1 (b) mixture 1 metal 1 structure 1 smart 1 (c) (i) any two from: • saves raw materials / iron ore • saves energy / fuels accept cheaper / saves money • make new / useful items • make money / it is economic • reduces pollution allow less harmful for the environment • decreases cost of steel cans • reduces carbon dioxide emissions • decreases waste materials / use of landfill 2 (ii) any one from: • provide information / education of the need to recycle • legislate against / charge for waste • reward / pay people to recycle accept fine people for not recycling • put labels on the cans • provide recycling bags / bins / areas 1 [8] M15. (a) to remove solid / dust particles 1 (b) because at –200 °C both (water and carbon dioxide) are solids 1 this would therefore block pipes / equipment 1 (c) oxygen 1 (d) (i) helium 1 (ii) nitrogen > argon > oxygen 1 [6] M16. (a) (i) (healthiest oil is) sunflower (oil) or rapeseed (oil) sunflower (oil) is healthiest because it has less saturated fat than both olive (oil) and corn (oil) or rapeseed (oil) is healthiest because it has the lowest value of saturated fat compared with the other oils 1 sunflower (oil) is healthiest because it has the highest value of polyunsaturated fat compared with all the other oils or rapeseed (oil) is healthiest because it has more polyunsaturated fat than both olive (oil) and corn (oil) 1 no mark for the choice of oil accept the use of values from the table for these comparisons (ii) no, because hydrogen adds to the unsaturated fat or no, because hydrogen reduces the number of carbon–carbon double bonds accept no because reacting with hydrogen increases number of single bonds 1 therefore there will be less polyunsaturated fat accept therefore there will be more saturated fat 1 (b) molecules in egg yolk act as emulsifiers accept lecithin molecules act as emulsifiers 1 because molecules in egg yolk have a ‘head’ which dissolves in / attracted to water accept because molecules in egg yolk are hydrophilic 1 because molecules in egg yolk have a ‘tail’ which dissolves in / attracted to oil accept because molecules in egg yolk are hydrophobic 1 [7] M17. (a) (i) thermal decomposition 1 (ii) hydration 1 (iii) add bromine (water)/iodine solution (to K and L) 1 K will decolourise these solutions or L will not decolourise these solutions 1 (b) (i) 352 (g) for correct answer if answer is incorrect 400 + 114 – 162 gains 1 mark 2 (ii) because 2 molecules of hydrocarbon J had 25 molecules of oxygen added or because 2 molecules of hydrocarbon J produced 16 molecules of carbon dioxide allow because oxygen has been added to hydrocarbon J for 1 mark 2 (c) (i) raw materials are renewable accept does not use crude oil 1 (ii) alcohol does not need to be distilled accept alcohol produced is pure 1 process is continuous 1 [11] M18. (a) (i) because large amounts of energy would be needed to extract the copper accept because it is labour-intensive to extract copper from this land accept because copper would have to be extracted from a large area of land (owtte) 1 (ii) any one from: • produces large amounts of solid waste • atmospheric pollution from carbon dioxide / sulfur dioxide • more lorries / traffic 1 (b) (i) iron is cheap accept iron is much more abundant than copper 1 (ii) iron displaces copper from solutions of its salts accept iron is more reactive than copper 1 (c) (i) any two from: • less expensive / energy to extract the small amounts of copper • plants will remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere as they grow • can release energy when plants are burned 2 (ii) not continuous as it takes a long time for plants to grow accept supply not continuous as plants only harvested once / twice a year 1 [7] M19. (a) calcium oxide 1 calcium hydroxide 1 calcium carbonate 1 substances must be in the order shown (b) (i) strength of mortar decreases (as volume of sand increases) 1 (ii) 400 (cm3) 1 because the height the metal ball dropped from should be 42 cm and not 37 cm accept because the other results show that the height the metal ball dropped from should have an interval of 6cm 1 (c) contains aggregate allow bonding is stronger 1 [7] M20. (a) two sodium atoms (react) 1 two (bonded) chlorine atoms (react) allow one chlorine molecule (reacts) 1 two sodium ions and two chloride ions (are produced) allow two molecules of sodium chloride (are produced) or two sodium chloride particles (produced) 1 (b) (i) (2x) max 1 if candidate changes the number of electrons in the first energy level / shell 8x (in second energy level / shell) 1 1x (in outer energy level / shell) 1 (ii) sodium has 1 electron in its outer energy level / shell or chlorine has 7 electrons in its outer energy level / shell 1 [6] M21. (a) (i) the continents of South America and Africa would have fitted together like a jigsaw 1 there are matching / similar rocks / fossils on the continents of South America and Africa 1 (ii) other scientists thought that continents are fixed / cannot float or Wegener had no evidence to prove that continents can move allow Wegener was not respected by other scientists / PhD in astronomy 1 and that a land bridge could explain the matching / similar rocks / fossils on the continents of South America and Africa 1 (b) radioactive 1 mantle 1 words must be in the order shown [6] M22. (a) alkanes 1 catalyst 1 substances must be in the order shown (b) many (ethenes/monomers) 1 bond/join together 1 allow ethenes / monomers bond / join together to form very large molecules for 2 marks (c) Marks awarded for this answer will be determined by the Quality of Written Communication (QWC) as well as the standard of the scientific response. No relevant content. 0 marks There is a brief description of a positive and a negative environmental impact involved with one or more methods used to reduce the amount of plastic bags sent to landfill. Level 1 (1–2 marks) There is some description of both positive and negative environmental impacts involved with at least 2 methods used to reduce the amount of plastic bags sent to landfill. Level 2 (3–4 marks) There is a clear, balanced and detailed description of both a positive and a negative environmental impact of using each of the 3 methods used to reduce the amount of plastic bags sent to landfill. Level 3 (5–6 marks) examples of the chemistry points made in the response reuse: reuse means less bags used so: positive environmental impact • saves raw materials / crude oil • saves energy • cuts down on CO2 emissions • less global warming negative environmental impact • could cause litter • could still be sent to landfill recycle: bags bought can be recycled so: positive environmental impact • used to make new plastic bags / objects • saves raw materials / crude oil • saves energy compared to producing plastic bags from crude oil • cuts down on CO2 emissions • less global warming negative environmental impact • collection point sites cause an eyesore / litter problem • transportation to recycling plant releases carbon dioxide / causes global warming burn: bags can be burned so: positive environmental impact • could provide energy for heating buildings • could provide energy for generating electricity negative environmental impact • increases CO2 emissions • increases global warming • could release toxic gases does not conserve raw materials / crude oil [10] M23. (a) (i) both have one / 1 electron in the outer energy level / shell allow both react in a similar way 1 (ii) eleven / 11 1 (iii) twelve / 12 1 (iv) (2x) max 1 if candidate changes the number of electrons in the first energy level / shell 8x (in second energy level / shell) 1 1x (in outer energy level / shell) 1 (b) two sodium atoms (react) 1 two (bonded) chlorine atoms (react) allow one chlorine molecule (reacts) 1 two sodium ions and two chloride ions (are produced) allow two molecules of sodium chloride (are produced) or two sodium chloride particles (are produced) 1 [8] M24. (a) (i) copper 1 (ii) 50p 1 (iii) 25 (%) 1 (b) any two from: • high value of copper allow copper is expensive or contains other metals (that may have higher value now) • less copper available or copper ores exhausted / only low-grade ores available allow copper is non-renewable • high demand for copper • inflation of prices 2 [5] M25. (a) decane has the largest molecules 1 methane and butane are gases at 20 °C 1 (b) (i) water 1 (ii) carbon dioxide 1 (c) sulfur dioxide is produced when sulfur burns 1 therefore sulfur must be removed from these fuels because sulfur dioxide causes acid rain 1 [6] M26. (a) causes dust pollution 1 increases traffic 1 (b) (i) decomposition 1 (ii) 44(g) 1 (c) (calcium) hydroxide 1 (calcium) carbonate 1 substances must be in the order shown [6] M27. (a) (i) nitrogen 1 (ii) carbon dioxide 1 (iii) because water boils at 100°C and the temperature on Venus is 460°C 1 therefore any water on the surface would boil to form steam / water vapour / gas 1 (b) any three from: • by photosynthesis • by dissolving in oceans • by the formation of (calcium) carbonate or limestone • by the formation of oil or coal accept by the formation of fossil fuels 3 (c) (i) 0.0317 (%) 1 (ii) the percentage of carbon dioxide has increased 1 (iii) any one from: • burning of fossil fuels • deforestation • release of ‘locked up’ carbon dioxide 1 [10] M28. (a) D 1 C 1 A 1 letters must be in the order shown (b) (i) floats 1 (ii) an emulsion 1 [5] M29. [4] M30. (a) (i) 3 / three 1 (ii) 5 / five 1 (b) any one from: • less / no transport accept less / no distance • less / no (fossil) fuel used ignore references to carbon dioxide / carbon emissions 1 (c) (i) carbon dioxide / CO2 for a correct emission 1 (causes) global warming / climate change / greenhouse gas explanation must be correct for named emission ignore ozone layer or (cement) particles / smoke (1) (causes) asthma / dust / (global) dimming (1) accept breathing problems or sulfur dioxide / SO2 / nitrogen oxides / NOx (1) (causes) acid rain (1) do not accept nitrogen or water vapour for emissions do not accept no named emission 1 (ii) absorb / trap / capture / filter / pass through water / scrub / electrostatic attraction ignore condense / off setting / different fuel 1 [6] M31. (a) (i) calcium oxide / quicklime allow calcium monoxide do not accept calcium dioxide ignore chemical formulae 1 (ii) any three from: • carbon dioxide / CO2 • (carbon dioxide) reacts (with the calcium hydroxide / slaked lime / plaster) allow reaction 3 identified do not allow incorrect reaction ignore mixes, unless they state the correct product • limestone / calcium carbonate / CaCO3 forms allow marble / chalk • water is lost / evaporates it = plaster allow moisture ignore dries 3 (b) (i) as the amount / volume of sand decreases the strength of the mortar increases accept as sand decreases the mortar is stronger / harder to crack allow as sand decreases the mortar increases allow converse ignore references to height of metal ball 1 (ii) any two from: • 400 / 5th result is anomalous accept two results (36 and 37 / 400 and 500 / 4th and 5th) are almost the same accept result at 400 should be 42 • the interval between the others is similar or the interval is about 6/7 allow the other results fit a pattern / are on a straight line • he has only one set of results allow he has only done it once ignore reliable 2 [7] M32. (a) (i) (gases from) volcanoes 1 (ii) 100 allow 99 1 (iii) any two from: • photosynthesis • carbon dioxide used allow carbon dioxide decreased • oxygen produced allow oxygen increased ignore nitrogen / respiration they = plants 2 (b) (i) any one from: • sea floor spreading accept oceanic ridges / magnetic stripes • periodic measurements between continents accept continents move a few centimetres each year • evidence from rocks / fossils on different continents accept continents fit together • new mountain ranges accept new islands 1 (ii) in the mantle any two from: • convection (currents) / movement do not accept movement of the plates • radioactivity / radioactive decay / nuclear reactions 1 • releases heat / thermal energy accept heat from core 2 [8] M33. (a) (i) reacts with carbon / C accept burns / oxidises carbon 1 carbon dioxide / CO2 / gas is formed / given off accept carbon monoxide / CO accept correctly balanced equation for 2 marks ignore state symbols 1 (ii) change / improve properties accept any specific property accept to make alloys / special steels ignore brittle 1 (b) any two from: • to conserve ores / iron accept ores / iron are non-renewable / nonsustainable allow less quarrying / mining • to prevent the use of landfills allow reduce waste • to conserve energy / fuel accept fossil fuels are non-renewable • to reduce carbon / carbon dioxide emissions • to meet EU / International targets ignore costs / demand 2 [5] (a) yes (there is the general trend) ‘as the iodine value increases the melting point decreases’ or ‘as the hardness decreases the mp decreases’ accept converse statement do not accept boiling point M34. or no melting points are in random order / go up and down 1 one specific use of comparative data from the table either showing the trend or an anomaly can be gained from yes or no answer ignore bp 1 (b) the iodine turns colourless 1 this would be difficult to see (if the oil was dark coloured) allow similar colour as iodine or iodine is brown 1 (c) (consumer may think that) the company (scientists) would be biased 1 consumer more likely to trust independent scientists allow independent scientists not biased 1 (d) add (measured amount of) hydrogen accept hydrogenation 1 any two from: • (nickel) catalyst • hot / 60°C temperature • hardened accept add a hard / hydrogenated fat / oil or make an emulsion 2 [9] M35. (a) (i) many ethene / molecules / monomers accept double bonds open / break 1 join to form a long hydrocarbon / chain / large molecule accept addition polymerisation ignore references to ethane correct equation gains 2 marks 1 (ii) (can be deformed but) return to their original shape (when heated or cooled) ignore ‘it remembers its shape’ 1 (iii) cross links / extra bonds in PEX accept inter-molecular bonds ignore inter-molecular forces 1 molecules / chains in PEX are held in position accept rigid structure 1 molecules / chains in PEX unable to slide past each other / move it = PEX throughout 1 (b) any four from: • less (hydrocarbon) fuels used allow less energy • less / no electrical energy used allow no electrolysis • reduce carbon / carbon dioxide emissions allow less global warming • reduce / no pollution by sulfur dioxide / acid rain • continuous process allow less / no transportation • conserve copper which is running out or only low-grade ores available • reduce the amount of solid waste rock that needs to be disposed allow less waste • reduce the need to dig large holes (to extract copper ores) allow less mining ignore costs / sustainability / non-renewable 4 [10] M36. (a) (i) made up of one sort of atom accept it is in the periodic table or has its own symbol 1 (ii) nitrogen / N / N2 or oxygen / O / O2 do not accept argon or helium do not accept oxide 1 (b) (i) compound 1 carbon 1 (ii) bond 1 [5] M37. (i) unsaturated 1 (ii) hydrogen 1 higher 1 [3] M38. (a) (i) monomers 1 (ii) crude oil 1 (b) any three from: • metal may not corrode away / remains • plastic remains / does not break down (decay) / not affected by microorganisms accept non-biodegradable • should recycle / conserve resources / mend the kettle / burn (plastic) as a fuel accept it is a waste of materials / resources • landfill sites are limited / filling up • water pollution ignore harms wildlife / habitats or problems caused by burning the kettle 3 [5] M39. (a) curve of best fit drawn through or close to all of the points 1 (b) (i) 313 1 (ii) 1989 +/– 1 1 (c) concentration / amount of carbon dioxide has increased 1 recently the rate of increase is increasing 1 [5] M40. (a) good (electrical) conductor allow low reactivity / resistance to corrosion do not accept heat conductor 1 (b) a mixture of metals accept contains more than one type of metal 1 (c) (i) any one from: • eyesore • destruction of habitats • pollution of water • dust pollution • noise • traffic pollution 1 (ii) acid rain allow sulfur dioxide is a pollutant 1 (d) (i) running out of copper (ores) 1 (ii) any two from: • any specific example of using less copper • reuse / recycle allow do not throw copper / brass away • use low-grade copper ores • use other metals / materials in place of copper 2 [7] M41. (a) (i) old animals / fossils / rocks match (when the continents are put together) or (continents) fit together ignore ‘they are the same shape’ 1 (ii) any two from: • continents / plates cannot move (thousands of kilometres) accept the continents / plates are attached to the Earth or continents / plates cannot drift / float • modern / new animals are different • a land bridge (could explain the matching fossils / rocks) ignore ‘no evidence’ ‘no proof’ ‘no reputation’ 2 (b) crust allow lithosphere 1 mantle 1 year 1 [6] M42. (a) any three from: • resources / aluminium / ores are conserved accept converse argument • less / no mining or less associated environmental problems eg quarrying / eyesore / dust / traffic / noise / loss of land / habitat ignore just pollution • less / no waste (rock) / landfill do not accept ‘wastes 50% of the ore’ • no purification / separation (of aluminium oxide) • (aluminium extraction / production) has high energy / electricity / heat / temperature requirements • less carbon dioxide produced accept no carbon dioxide produced ignore references to cost 3 (b) statement ignore density 1 linked reason eg (pure) Al / it is weak / soft (1) as layers / rows can slide (over each other) (1) or alloy / other metals / they make it stronger / harder (1) stops layers / rows sliding over each other (1) accept disrupts the structure owtte if no other mark awarded accept to form an alloy or to change properties for 1 mark 1 [5] M43. (a) (i) acid rain accept consequences of acid rain allow asthma / bronchitis ignore toxic gas 1 (ii) global dimming accept dimming alone 1 (b) (i) sustainable: maximum two from: • crops (that produce oil) can be grown in most places owtte • renewable • use less fossil fuels / diesel • use (refined) waste oils low pollution: maximum two from: ignore references to CO2 here • most emissions are lower or any two named emissions from CO / SO2 / PM10 are lower • much / lot less SO2 emissions (than the others) owtte • accept spillages / waste is biodegradable • less new CO2 or (more) carbon neutral 3 (ii) plants / photosynthesis use carbon (dioxide) from the air* 1 it / biodiesel releases carbon (dioxide) from plants / crops / photosynthesis* (*) allow 1 mark for biodiesel is (more) carbon neutral 1 (fossil) diesel releases ‘locked up’ / new carbon (dioxide) / doesn’t absorb CO2 / absorbed it millions of years ago 1 [8] M44. (a) any two from: • naphtha has a different / low(er) boiling point accept different volatility • condenses at a different temperature / height / place in the column / when it reaches it’s boiling point • different size of molecules 2 (b) (i) C10H22 → C6H14 + 2C2H4 allow multiples 1 (ii) (hydrocarbon) heated / vapours 1 (passed over a) catalyst / alumina / porous pot ignore other catalysts 1 (iii) it / ethene is unsaturated or decane and hexane / they are saturated accept decane and hexane are alkanes / CnH2n+2 or ethene is an alkene / CnH2n or different homologous series / general formula 1 ethene has a double (carbon carbon) bond or decane and hexane have only single (carbon carbon) bonds accept ethene has a reactive double (carbon carbon) bond for 2 marks 1 (c) all bonds drawn correctly 1 (d) economic argument against recycling any one from: • poly(ethene) / plastic must be collected / transported / sorted / washed • this uses (fossil) fuels which are expensive 1 environmental argument against recycling any one from: • uses (fossil) fuels that are non-renewable / form CO2 / CO / SO2 / NOx / particulates ignore pollution / harmful gases / etc • washing uses / pollutes water 1 counter arguments any two from: • collect / transport alongside other waste • use biofuels (instead of fossil) • landfill is running out • landfill destroys habitats • incinerators are expensive to build • saves raw materials / crude oil • saves energy needed to make new plastic • incinerators may produce harmful substances • incinerator ash goes to landfill • poly(ethene) is non-biodegradable • poly(ethene) can be made into other useful items • more jobs / employment for people 2 [12] M45. (a) electron words must be in correct position 1 nucleus 1 (b) (i) oxygen / O2 ignore air 1 (ii) any one from: • (water) does not pollute accept no harmful gas(es) • (only) water is produced • no carbon dioxide (is produced) accept no greenhouse gas(es) / effect • no sulfur dioxide (is produced) accept no acid rain • no nitrogen oxides (are produced) • no carbon / no particles (are produced) 1 [4] M46. (a) (i) sulfur dioxide / SO2 1 (ii) global dimming 1 (iii) carbon dioxide / CO2 ignore ozone 1 increases the levels (of carbon dioxide) accept it is a greenhouse gas or causes global warming / greenhouse effect 1 (b) gas / oil bar correct length 1 coal bar correct length 1 [6] M47. (a) tectonic words must be in correct places 1 radioactive 1 (b) (i) any two from: • records not available / made / accurate • bodies not found • affected many islands / large area 2 (ii) any two from: • cannot predict earthquakes / plate movement • (cannot) accurately (predict earthquakes) • (earthquakes / tsunamis) are random / not regular / sudden • do not know what is happening below / in the Earth’s crust / in the mantle • very slow / thousands of years build up of pressure ignore references to technology / equipment 2 [6] M48. (a) (i) crushed if line blank allow crushed circled in the box 1 (ii) any one from: • ‘costs’ less / cheaper • easier / faster • less complicated equipment • does not need heating / energy • distilling could decompose the oil 1 (b) (i) any one from: • do not mix / dissolve • (stay) separate • form layers • are immiscible 1 (ii) mix words must be in correct places 1 emulsion 1 [5] M49. (a) (i) hydrogen must be name 1 (ii) a line of four or more ethene molecules joined to the original two with single bonds at least two other ethene molecules joined to the original two in a chain gains 1 mark 2 (b) (i) any two from: • non-biodegradable accept remains a long time • landfill sites are filling up / limited accept land / space used up • waste of a resource / could be recycled / reused ignore references to tablets / animals 2 (ii) any one from: • (two) different polymers / plastics / materials • need to be separated • limited collection points / many need to be collected • tablets may still be present 1 [6] M50. (a) (an alloy) that can return to its original shape (after being deformed / bent / twisted) accept (on heating / cooling) it returns to its shape 1 (b) any two from: • brass / it is a mixture accept brass / it is not pure • zinc changes structure / disrupts patterns or layers • copper metal atoms / layers able to slide over each other accept zinc prevents atoms / layers sliding over each other 2 (c) (i) oxygen / O2 / O 1 (ii) lead remains (in furnace) because of its high boiling point 1 zinc boils / evaporates (out of furnace) because of its low boiling point 1 if neither mark awarded then allow 1 mark for different boiling points ignore references to melting points 1 [6] M51. (a) (i) calcium oxide / CaO 1 carbon dioxide / CO2 products can be in either order ignore chemical names other than calcium oxide or carbon dioxide 1 (ii) (thermal) decomposition accept endothermic 1 (b) (i) (chemical) reaction / react accept calcium hydroxide / slaked lime produced ignore incorrect products 1 energy / heat released / exothermic ignore gets hot / heats up if neither mark awarded then allow ‘mixing the chemicals heats up the coffee’ for 1 mark 1 (ii) any two from: • foil has been broken(*) • ring pull used(*) (*)if neither mark awarded accept ‘cannot / difficult to repair’ for 1 mark ignore button pushed • quicklime and / or water mixed / reacted accept reaction not reversible accept cannot / difficult to replace quicklime / water / chemicals 2 [7] M52. (a) any one from: • gasoline / petrol / it contains short(er) chains / hydrocarbons or small(er) molecules or contains few(er) carbons accept fuel oil contains long(er) chain length / large(r) molecules or contains many carbons ignore particles • gasoline / petrol / it has weak(er) / small(er) intermolecular forces accept fuel oil has strong(er) / great(er) intermolecular forces 1 (b) only accept figures if used in a comparative statement any two from: • gasoline / petrol / it is in high demand accept fuel oil is in low demand • gasoline / petrol / it is in short supply accept fuel oil is plentiful accept answers such as ‘gasoline / petrol / its supply is less than demand for 2 marks or gasoline / petrol / its percentage in crude oil is less than demand for 2 marks • (high) tax / duty • cracking costs in terms of money / energy accept cracking expensive 2 (c) any two from: ignore particles • (fuel oil / it) heated / vaporised • with catalyst accept a named catalyst if first two bullet points are not awarded ‘cracking’ gains 1 mark • (to give / form / produce) short(er) chains / hydrocarbons or small(er) molecules or contains few(er) carbons if wrong process named max 1 mark 2 [5] M53. (a) any one from: • light(er) / less dense ignore stronger • resistant to acids / alkalis / chemical accept resistant to corrosion 1 (b) any two from: it must be clear list principle applies allow reverse argument ignore reference to temperature • magnesium is more reactive than titanium magnesium is above titanium in the reactivity series • titanium is more reactive than carbon • magnesium is more reactive than carbon • magnesium is most reactive • carbon is least reactive 2 (c) any three from: it = titanium ignore references to cost / easier / usefulness alone or references to incorrect processes • takes a long time to process • low abundance (of ore) • small amount produced • batch process used or blast furnace is continuous • more stages used to manufacture titanium allow ≥ 3 / many / several • more energy used (per tonne of titanium) allow high energy requirement ignore references to temperature • magnesium / chlorine is expensive • labour intensive 3 [6] M54. (i) turns colourless accept colour disappears ignore fading 1 (ii) any two from: • unsaturated fat content / healthiness about the same / similar to maize accept about the same number of double carbon bonds as maize accept ‘a bit less’ for similar • less unsaturated / less healthy than soya accept fewer / less double bonds than soya ignore ‘more saturated’ • more unsaturated / more healthy than olive / palm accept more double bonds than olive / palm ignore ‘less saturated’ if no other mark awarded accept sunflower oil has (about) the same result as maize oil for 1 mark ignore comments about saturated fats 2 [3] M55. (a) any two environmental problems with linked explanations • global warming (1) accept effects of global warming caused by (formation of) carbon dioxide / greenhouse gas (1) ignore greenhouse effect • acid rain (1) accept effects of acid rain ignore respiratory problems caused by ( formation of) sulfur dioxide (1) accept sulfur oxide ignore sulfuric acid • global dimming (1) ignore respiratory problems caused by ( formation of) particles / particulates / fires / smoke / carbon / pm 10 (1) • scarring of landscape (1) caused by mining / quarrying of coal (1) ignore ozone layer max 4 (b) any three from: • replant the trees / renewable / sustainable ignore reusable • carbon dioxide is used by the trees / photosynthesis accept trees absorb carbon dioxide as they grow do not allow respiration • it’s a (continuous carbon) cycle accept ‘carbon dioxide goes back into the air’ accept trees use CO2 which is released when trees are burnt • no ‘new’ carbon (dioxide) is produced or no locked up carbon (dioxide) is released accept no carbon (dioxide) from fossil fuels is produced 3 [7] M56. (a) any two from: asks for cause therefore no marks for just describing the change must link reason to a correct change in a gas carbon dioxide has decreased due to: accept idea of ‘used’ to indicate a decrease • plants / micro organisms / bacteria / vegetation / trees • photosynthesis ignore respiration • ‘locked up’ in (sedimentary) rocks / carbonates / fossil fuels • dissolved in oceans ignore volcanoes oxygen has increased due to: accept idea of ‘given out / produced’ • plants / bacteria / micro organisms / vegetation / trees • photosynthesis ignore respiration nitrogen increased due to: accept idea of ‘given out / produced’ • ammonia reacted with oxygen • bacteria / micro organisms ignore (increase in) use of fossil fuels / deforestation 2 (b) (because methane’s) boiling point is greater than the average / surface temperature or Titan’s (average / surface) temperature is below methane’s boiling point ignore references to nitrogen or water 1 any methane that evaporates will condense accept boils for evaporates accept cooling and produce rain for condensing 1 (c) (i) bonds must be displayed correctly ignore bond angles 1 (ii) poly(propene) / polypropene / polypropylene do not allow polypropane any two from: • double bonds open up / break / become single(*) • propene molecules / monomers / they join / undergo addition polymerisation(*) 1 • form chains / long molecules(*) (*)correct chemical equation gains 2 marks ignore large using monomer incorrectly max 2 marks 2 [8] M57. (a) made of one sort of atom accept it is in the periodic table accept it only has lithium atoms 1 (b) nucleus labelled correctly 1 electron labelled correctly 1 [3] M58. (a) pressing 1 (b) (i) water accept hydrogen oxide / H2O 1 (ii) filtration or description of this process accept decanting or similar description of a means of separating the seeds and skins from the liquids accept sieving do not accept distillation / evaporation 1 [3] M59. (a) tungsten 1 has the high(est) melting point accept that metals other than tungsten are likely to melt 1 (b) argon 1 is an unreactive gas accept that gases other than argon are reactive accept that argon is a noble gas or in Group 0 1 [4] M60. (a) 1 / one 1 3 / three 1 (b) (i) (wear safety) glasses / masks / gloves accept do not handle hot objects / use tongs or accept other safety points such as, ‘tie hair back’ 1 (ii) calcium oxide accept quicklime 1 (iii) carbon dioxide / CO2 is given off accept a gas is given off 1 (d) (i) any two from: • dust / atmospheric pollution • noise • eyesore • destroys habitats • (extra) traffic • any other named pollution or description of pollution 2 (ii) any one from: • employment • increases local trade / makes money • future development of quarry recreation / park / lake / reservoir do not accept cheaper houses / land / new roads 1 [8] M61. (a) (i) poly(ethene) accept polythene 1 (ii) cracking 1 (iii) hydrogen 1 (b) (i) bar labelled 9 1 bar drawn to correct height 1 (ii) (boiling point) increases 1 (iii) heat / evaporate (the crude oil) accept separate by boiling point 1 cool / condense (hydrocarbons at different temperatures) accept smaller molecules go to top / larger molecules stay at bottom accept fractional distillation for two marks or distillation / fractionation for one mark 1 (c) yes any two from: • because plastic does not biodegrade or running out of space for landfills or land cannot be used for a long time • it provides heat energy • which can be used to generate electricity / heat homes or greenhouses • any other advantage of burning • any other disadvantage of landfill or no • burning plastic produces carbon dioxide / carbon emissions / toxic gases accept landfill does not produce carbon dioxide / carbon emissions • causes global warming / climate change / increase greenhouse effect / global dimming / acid rain • any other disadvantage of burning • any other advantage of landfill 2 [10] M62. (a) radioactivity (keeps the core hot) accept half-life of radioactive elements has proved the Earth is older than 400 million years accept the Earth is not cooling do not accept fossil / rock evidence 1 (b) any two from: • the shapes of the two continents fit together (like a jigsaw) OWTTE\ do not accept the continents / they are the same shape • the same type of rocks have been found accept ‘rocks match’ • the same fossils have been found accept ‘fossils match’ • rising magma rising through a gap under the Atlantic 2 (c) any two from: • earthquakes accept seismic waves • volcanoes • idea of distance between America and Europe / Africa is increasing e.g. continental drift • oceanic ridges accept ocean floor spreading • formation of (new) mountain ranges accept fold mountains or mountains increasing in height • formation of (new) islands • magnetic stripes • tsunamis 2 [5] M63. (a) oxygen and nitrogen 1 20 – 21 % and 78 – 80 % accept any two correct responses in the correct space for one mark 1 (b) (i) acid rain accept toxic gas or consequence of acid rain 1 (ii) idea of the removal or use of sulfur dioxide gas (from the waste gases) do not accept remove sulfur from coal 1 (iii) oxygen accept O2 1 water accept H2O accept hydrogen oxide / steam 1 (c) any two from: • it’s a ‘greenhouse gas’ or increase greenhouse effect accept action of a ‘greenhouse gas’ • causes global warming or increase in the Earth’s temperature • sea-levels rise or flooding • climate change • (polar) ice-caps melt • extension of deserts mention of ozone / acid rain / global dimming = max 1 mark 2 (d) idea trap / store / lock the carbon dioxide 1 in the oil reservoir or under the sea bed do not accept ‘into the oil’ / ‘under the sea’ 1 [10] M64. (a) (i) contain enough metal to make it economical / worth while to extract 1 (ii) reduction accept displacement accept redox 1 (iii) Fe + CO2 do not accept Fe2 / Fe4 1 correct balancing accept multiples and halves 2Fe2O3 + 3C → 4Fe + 3CO2 allow Fe2 / Fe4 as ecf 1 (b) Pure Iron (in pure metal all the atoms are the same size and) able to slip / slide over each other – (property soft) OWTTE ignore references to molecules / particles if they say ‘move’ both times, allow one mark but ‘crack’ or ‘split’ is wrong.. 1 Cast iron (in cast iron) different sized atoms / larger atoms or structure is distorted / disrupted OWTTE 1 so it is difficult for layers of atoms to slip / slide over each other OWTTE 1 (c) any three from: • conserves / saves resources / metal ores • saves energy resources (used for extraction / processing) accept cheaper / saves money • decreases waste materials • decreases a named pollution do not accept acid rain 3 [10] M65. (i) (poly)unsaturated accept monounsaturated 1 (ii) (turns) colourless or colour disappears / decolourises do not accept clear 1 stays the same colour / orange / no change allow yellow-orange / orange-brown / redorange 1 (iii) (react) with hydrogen / H2 / hydrogenation 1 any one from: • heated / 60 °C • catalyst / nickel 1 [5] M66. (a) (i) heat / evaporate the crude oil / change to gas or vapour do not accept heat with catalyst 1 cool / condense (hydrocarbons) allow small molecules at top and / or large molecules at bottom 1 at different temperatures / boiling points if the answer describes cracking ‘ no marks 1 (ii) C4H10 1 (b) H │ H ─C ─ │ H H H │ │ C─ C─H │ │ H H 1 (c) (i) C5 to C8 fraction are fuels or easier to burn or petrol (fraction) accept C21 to C24 fraction not useful as fuels do not accept produce more energy 1 (ii) C2H4 do not accept C4H8 1 (iii) any three from: • use different / lighter crude oils • develop markets for low demand fractions • develop new techniques / equipment to use low demand fractions as fuels • cracking • convert low demand fractions to high demand fractions or bigger molecules to smaller molecules • develop alternative / bio fuels do not accept price 3 [10] M67. (a) hydrogen ignore formulae 1 (b) any two from: • different sized molecules / more or less (carbon) atoms (in molecules) ignore different densities • fuels have different boiling points • fuels condense at different temperatures 2 (c) all three correct = 3 marks two correct = 2 marks one correct = 1 mark 3 [6] M68. (a) (i) any one from: • iron ore is a limited resource / non-renewable • iron is in high demand • provide jobs • economic advantage 1 (ii) any two from: • would damage (wildlife) habitats / countryside / greenfield sites • extra traffic • visual (pollution) / eyesore • noise (pollution) / sound (pollution) • dust (pollution) • river (pollution) • carbon dioxide (from traffic) / adds to greenhouse effect / global warming • damage roads / buildings by vibrations / shockwaves 2 (b) (i) carbon monoxide / carbon accept formulae CO / C 1 (ii) atoms accept (particles) are all the same (size) / type for one mark 1 are all the same (size) / type 1 (iii) any two from: • impurities / carbon / different (sized) atoms or elements or metals • changes the structure / disrupts the pattern or layers • prevents layers sliding over each other • it is an alloy 2 [8] M69. (a) core ignore outer or inner 1 mantle 1 (b) (i) carbon dioxide accept formula CO2 1 oxygen accept formulae O2 / O 1 (ii) 4% 1 (iii) carbon dioxide has decreased / from 95% to 0% 1 oxygen has increased / from 0% to 21% 1 any one from: (carbon dioxide decrease) • carbon dioxide used during photosynthesis / by plants • carbon dioxide dissolves in oceans • carbon dioxide is locked up in rocks / carbonates / fossil fuels (oxygen increase) • oxygen released during photosynthesis / by plants 1 [8] M70. (a) any two from: • nitrogen accept formulae N / N2 • carbon dioxide accept formula CO2 ignore CO • water (vapour) / steam accept formula H2O 2 (b) any three from: no mark for ‘limestone’ or ‘concrete’ on first line – mark advantages only limestone • abundant / local ignore ideas of speed of production or easier to use • natural material or no ‘processing’ needed • relatively easy to cut • appearance better concrete • raw materials are abundant • can be reinforced (by steel rods) / strong(er) / supported (by steel rods) accept ‘can build higher’ • concrete mixture can be poured / moulded / constructed on site • less reactive with acid rain / weathering / erosion ignore density / extraction / quarrying / pollution / cost 3 [5] M71. (a) (i) Cu2S + 2O2 2CuO + SO2 accept fractions and multiple 1 (ii) any two from: • sulfur dioxide accept sulphur dioxide / sulphur oxide / SO2 • causes acid rain ignore other comments eg global warming / ozone / global dimming / greenhouse effect • consequence of acid rain eg kills fish / plants 2 (b) any two from: • heat (copper oxide with carbon) • oxygen is removed by carbon accept copper (oxide) loses oxygen or carbon gains oxygen accept carbon oxide or carbon monoxide / carbon dioxide is produced or carbon displaces copper accept a correct word or balanced symbol equation • because carbon is more reactive than copper allow a correct comparison of reactivity 2 (c) (i) electrolysis accept electroplating 1 (ii) (electrical) wiring / appliances / coins / pipes / cladding for buildings / jewellery / making alloys 1 or named alloys (d) any three explanations from: for recycling • less acid rain (pollution) • copper reserves last longer / conserved or do not run out • energy for extraction (saved) or less energy required • less mining / quarrying • less waste (copper) / electrical appliances dumped or less landfill against recycling • collection problems • transport problems • difficult to separate copper from appliances • energy used to melt the collected copper ignore electrolysis / pollution ignore ideas about less machinery / plant ignore idea of cost 3 [10] M72. (a) (i) core 1 (ii) plate (boundaries) accept parts of the crust ignore crust alone 1 sudden movement / colliding accept movement but ignore movement apart or normally move a few centimetres per year accept continental drift 1 convection currents / driven by heat from radioactive processes / decay idea of source of energy for the movement 1 the idea of uncertainty with an explanation eg scientists do not know (with any certainty) • what happens under the crust • where the forces / pressure are building up • we cannot measure the forces • when the forces reach their limit ignore references to volcanoes 1 (b) (i) 78 (ii) marks awarded for any 2 gases from the following 3 gases max 3 marks from CO2 1 any four from: ignore references to respiration carbon dioxide has decreased: • used by plants / bacteria (stromatolites) • during photosynthesis (must be linked to CO2 decrease) • ‘locked up’ in (sedimentary) rocks / carbonates / fossil fuels • dissolved in oceans and / or oxygen has increased because: • released by plants / bacteria (stromatolites) • during photosynthesis (must be linked to O2 increase) and / or nitrogen has increased because • ammonia reacted with oxygen (to release nitrogen) • nitrogen is released by bacteria 4 [10] M73. (a) (i) water and oil do not mix / are immiscible ignore density 1 or don’t dissolve each other ignore emulsifier alone 1 (ii) any two from: • emulsifier • forms an emulsion accept description of an emulsion • holds the two components together accept stops them separating / they mix allow bonds / binds for holds • by lowering the surface tension accept a description of how an emulsifier works for two marks eg ‘tadpole’ diagram or dispersal of oil drops 2 (b) (i) (because they contain) a double (carbon carbon) bond accept unsaturated ignore poly or mono 1 (ii) results suggest sunflower oil is best or ‘the one that took the least time’ 1 because (sunflower oil) has the highest amount of unsaturation / most double bonds / least saturated ignore uses up I2 most quickly second mark is dependent on first 1 (c) (i) any one from: • have a higher melting point than (vegetable) oil • are solid at (room temperature) / hardened / harder accept useful as spreads or doesn’t soak into bread ignore hard / soft(er) 1 (ii) any two from: • hydrogen added do not accept ‘water’ • to carbon carbon double bond / to saturate • (nickel) catalyst / temperature 60 – 150 °C wrong catalyst doesn’t get this mark ignore high / warm temperature 2 [9] M74. (a) (i) by (fractional) distillation accept a description of the distillation process (heat and how separation works) eg heat and condense accept boil / vapourise etc for heat or fractionation 1 (ii) CO2 note the order of these products must be correct 1 H2O wrong way round = 1 mark 1 (b) (i) (hexane) has been broken down (into smaller hydrocarbons / molecules) 1 accept (thermal) decomposition / cracked / split / broken up owtte (ii) H H │ │ C = C │ │ H H accept CH2 = CH2 1 (iii) water / hydrogen oxide / steam accept H2O 1 (c) candidates must include both sugar cane and crude oil in their evaluation and both an advantage and a disadvantage to gain full marks. if they do not then the maximum mark is three any four from: advantages of using sugar • country has no wealth to buy (large quantities of) crude oil not ‘expensive’ alone • country has limited technological development or underdeveloped / third world country • able / suitable climate to grow sugar cane • enough land to grow sugar cane / land cannot be used to grow food / deforestation • sugar is a renewable source or crude oil is a non-renewable resource / finite resource / limited resources • CO2 / carbon neutral advantages of using alkanes: • economic costs are low • continuous process • country has large oil resources • country has oil refineries / cracking plants • very pure product • faster process 4 [10] M75. (a) hydrocarbons 1 (b) evaporation 1 condensation 1 distillation allow fractional distillation 1 (c) lower and more 1 [5]