Properties of Solids
advertisement
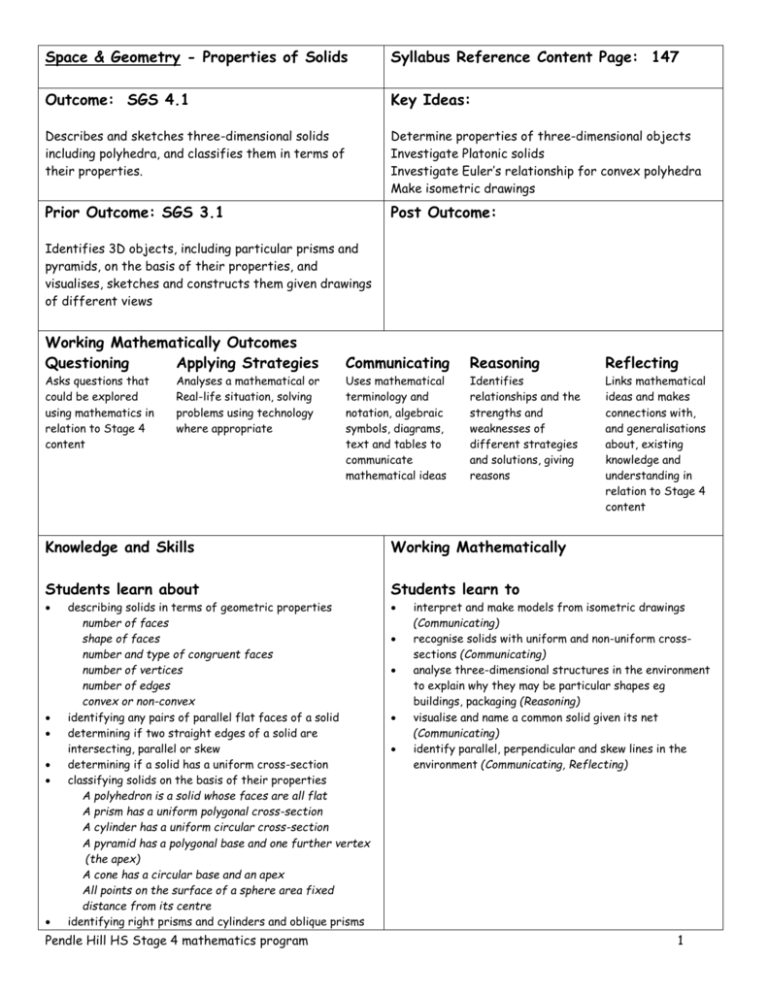
Space & Geometry - Properties of Solids Syllabus Reference Content Page: 147 Outcome: SGS 4.1 Key Ideas: Describes and sketches three-dimensional solids including polyhedra, and classifies them in terms of their properties. Determine properties of three-dimensional objects Investigate Platonic solids Investigate Euler’s relationship for convex polyhedra Make isometric drawings Prior Outcome: SGS 3.1 Post Outcome: Identifies 3D objects, including particular prisms and pyramids, on the basis of their properties, and visualises, sketches and constructs them given drawings of different views Working Mathematically Outcomes Questioning Applying Strategies Asks questions that could be explored using mathematics in relation to Stage 4 content Analyses a mathematical or Real-life situation, solving problems using technology where appropriate Communicating Reasoning Reflecting Uses mathematical terminology and notation, algebraic symbols, diagrams, text and tables to communicate mathematical ideas Identifies relationships and the strengths and weaknesses of different strategies and solutions, giving reasons Links mathematical ideas and makes connections with, and generalisations about, existing knowledge and understanding in relation to Stage 4 content Knowledge and Skills Working Mathematically Students learn about Students learn to describing solids in terms of geometric properties number of faces shape of faces number and type of congruent faces number of vertices number of edges convex or non-convex identifying any pairs of parallel flat faces of a solid determining if two straight edges of a solid are intersecting, parallel or skew determining if a solid has a uniform cross-section classifying solids on the basis of their properties A polyhedron is a solid whose faces are all flat A prism has a uniform polygonal cross-section A cylinder has a uniform circular cross-section A pyramid has a polygonal base and one further vertex (the apex) A cone has a circular base and an apex All points on the surface of a sphere area fixed distance from its centre identifying right prisms and cylinders and oblique prisms Pendle Hill HS Stage 4 mathematics program interpret and make models from isometric drawings (Communicating) recognise solids with uniform and non-uniform crosssections (Communicating) analyse three-dimensional structures in the environment to explain why they may be particular shapes eg buildings, packaging (Reasoning) visualise and name a common solid given its net (Communicating) identify parallel, perpendicular and skew lines in the environment (Communicating, Reflecting) 1 and cylinders identifying right pyramids and cones and oblique pyramids and cones sketching on isometric grid paper shapes built with cubes representing three-dimensional objects in two dimensions from different views confirming, for various convex polyhedra, Euler’s formula F+V=E+2 relating the number of faces (F), the number of vertices (V) and the number of edges (E) exploring the history of Platonic solids and how to make them making models of polyhedra Technology Links Resources 3D solid models, centicubes, multilinks straws, plasticine, scissors, glue, sticky tape card match activity card for vortex, trihexaflexagon, stellated icosahedra models geodesic dome Pendle Hill HS Stage 4 mathematics program measurement-surface area, volume trigonometry Language Many terms need to be defined: prism, pyramid, face, edge, vertex, parallel, skew 2 Learning Experiences and Assessment Opportunities Assessment for learning Students complete cardmatch activity to match a solid with its net and name Students brainstorm in small groups all they know about solids. Posters are displayed in class. Teacher observes product and listens to class discussion At Stage 2 students are expected to be able to: Name, describe, sort make and sketch prisms, pyramids, cylinders, cones and spheres. Create nets from everyday packages. Describe cross-sections of 3-dimensional objects. At Stage 3 students are expected to be able to: Identify 3-dimensional objects, including particular prisms and pyramids, on the basis of their properties. Construct 3-dimensional models given drawings of different views. Investigating 3D Solids It is important that students use, make and describe 3D solids in a variety of situations. They should have access to various building materials. Students could: build 3D models using multilinks, centicubes, . . . . investigate packaging of everyday items explore and make nets to create 3D solids use 3D models to describe solids in terms of the number of faces, shapes of faces, number and type of congruent faces, number of vertices, number of edges use skeletal solids to define parallel intersecting and skewlines use solids to develop Euler’s formula draw diagrams of solids on isometric dot paper or some form of grid with perspective draw diagrams to show 2D views of solids. Use the geometry unit from Teaching Literacy in Mathematics in Year 7 to build and share knowledge about t solids and develop skills in both group work and literacy use barrier activities to promote speaking and listening skills using appropriate mathematical language. eg one student with a picture of a solid made from blocks describes it to a second student, who attempts to build the solid. Students reverse roles and repeat process for another shape. use card matching activities to develop language skills and clarify understanding eg in small groups, students match one set of cards containing the nets of various solids to a second set of cards containing the picture of the solids. Use the geodesic dome to build the platonic solids and the dome itself use cooperative logic activities - Point of View 1, 2, 3, 4 Extension Activities Students could: make the vortex make the trihexaflexagon make the stellated icosahedron Pendle Hill HS Stage 4 mathematics program 3