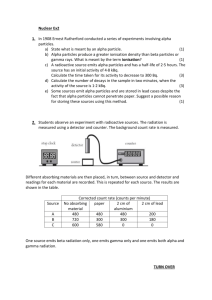
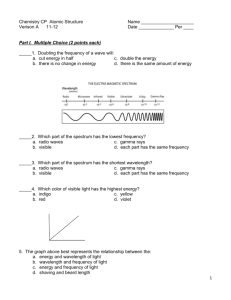
Nuclear Chem
advertisement
AP Exam Review: Nuclear 1984 30. When 214 Po decays, the emission consists consecutively of an alpha particle, then two beta particles, and 84 finally another alpha particle. The resulting stable nucleus is a) 206 Bi d) 208 Pb 83 82 210 210 b) 83Bi e) 81Tl 206 c) 82Pb 38. The radioactive decay of 146C to a) beta particle emission b) alpha particle emission c) positron emission 14 N 7 occurs by the process of d) electron capture e) neutron capture 1989 18. For the types of radiation given, which of the following is the correct order of increasing ability to penetrate a piece of lead? a) Alpha particles<gamma rays<beta particles d) Beta particles<gamma rays<alpha particles b) Alpha particles<beta particles<gamma rays e) Gamma rays<alpha particles<beta particles c) Beta particles<alpha particles<gamma rays 38. 251 98 Xe + Cf 2 n + 131 54 ___ What is the missing product in the nuclear reaction represented above? (A) 118 Mo (D) 120 Ru 44 44 118 122 (B) 44Ru (E) 46Pd 120 (C) 42Mo 1994 21. Correct statements about alpha particles include which of the following? I. They have a mass number of 4 and a charge of +2. II. They are more penetrating than beta particles. III. They are helium nuclei. (A) I only (D) I and III (B) III only (E) II and I (C) I and II 72. The nuclide 245Cm is radioactive and decays by the loss of one beta (-) particle. The product nuclide is (A) 245Pu (D) 250Cm (B) 95Am (E) 97Bk 248 (C) Cm 1999 48. If 87.5 percent of a sample of pure 131I decays in 24 days, what is the half-life of 131I? a) 6 days d) 14 days b) 8 days e) 21 days c) 12 days APReviewNuclear.doc 1 2002 235 92 U + 01 n 141 55 Cs + 3 01 n + X 23. Neutron bombardment of uranium can induce the reaction represented above. Nuclide X is which of the following? d. 92 Rb 37 a. 92 Br 35 94 e. 37Rb b. 94 Br c. 35 91 Rb 37 43. The atomic mass of copper is 63.55. Given that there are only two naturally occurring isotopes of copper, 63 Cu and 65Cu, the natural abundance of the 65Cu isotope must be approximately a) 90% d) 25 % b) 70% e) 10% c) 50% Free Response Questions 1997 8. Answer each of the following questions regarding radioactivity. (a) Write the nuclear equation for decay of 239 94 Pu by alpha emission. (b) Account for the fact that the total mass of the products of the reaction in part (a) is slightly less than that of the original 239 . 94 Pu (c) Describe how , , and rays each behave when they pass through an electric field. Use the diagram below to illustrate your answer. (d) Why is it not possible to eliminate the hazard of nuclear waste by the process of incineration? 2003 Form B 8. The decay of the radioisotope I-131 was studied in a laboratory. I-131 is known to decay by beta ( -10 e ) emission. (a) Write a balanced nuclear equation for the decay of I-131. (b) What is the source of the beta particle emitted from the nucleus? APReviewNuclear.doc 2 Multiple Choice Answers 1984 30. c) 38. a) 1989 18. b) 38. b) 1994 21. (D) 72. (E) 1999 48. b) 2002 23. d) 43. d) Answer 1997 #8 (a) 239 94 Pu 24a + 235 92 U (b) The mass defect has been converted into energy: ∆E = ∆m c2 (c) An alpha particle, or He nuclei, has a 2+ charge and would be attracted to the (-) side of the electric field. A beta particle, , or electron, has a single negative charge and is attracted to the positive side of the electric field, but since it is much lighter and faster than an alpha it would not be as strongly deflected. Gamma, , rays are not charged and, therefore, not deflected by the electric field. (d) The half-life of a radionuclide is independent of its environment. Incineration will neither accelerate its decay nor render it non-radioactive. Half-life is a function of its nucleus, incineration is a function of its electrons. Answer 2003 Form B 8. (a) 131 53 0 I ® 131 54 Xe + -1 e (b) A neutron spontaneously decays to an electron and a proton. APReviewNuclear.doc 3