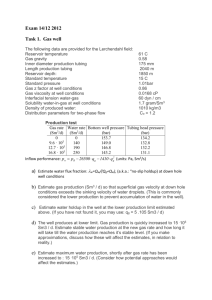
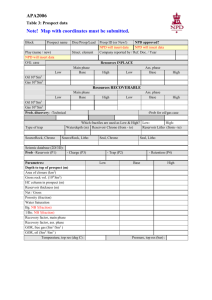
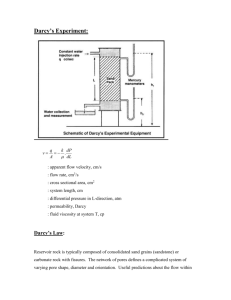
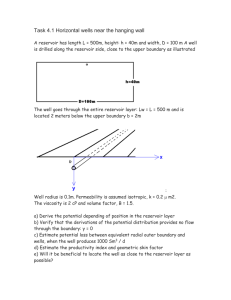
Exercise 3.1 Formation damage A well is producing 670 Sm3/d at a
advertisement

Exercise 3.1 Formation damage A well is producing 670 Sm3/d at a wellbore pressure of 170 bara. The well is producing 450 Sm3/d at a bottom -hole pressure of 180 bara. The drainage volume is cylindrical shaped. The following data is given: - outer radius wellradius : Layer thickness Formation volume factor porosity viscosity, reservoir oil 150 m 0.1 m 50 m 1.5 m3/Sm3 20% 5 cP The logs indicate 1m invasion of drilling fluid filtrate. The skinfactor is estimated from a transient test to be 3. a) Estimate the productivity index. b) Estimate the inflow efficiency. c) What is the well able to produce if the bottom hole pressure is kept at 180 bar, and you are able to remove the skin factor? d) Estimate the permeability in the damaged zone. e) Estimate the permeability in the part of the formation that has not been affected by the drilling fluid. Exercise 3.2 Geometric skin A well is producing 670 Sm3/d with a bottom hole pressure at 170 bara. At a bottom -hole pressure of 180 bar, the production is 450 Sm3/d. From these observations we get a productivity index J = 22 Sm3/d/bar. The following data is given: - outer radius wellradius : perforated interval perforation skin formation volume factor porosity viscosity, reservoir oil 150 m 0.1 m 50 m -1 1.5 m3/Sm3 20% 5 cP From transient test, the skin factor is estimated to be of the value 3. The logs indicate a drilling fluid filtrate invasion of 1 m. The logs also give indications that the productive interval may be 100 m, but only the top 50 is completed. a) Estimate the geometric skin factor due to partial completion. b) Estimate the total geometric skin factor. c) Evaluate if the observed skin factor is due to geometric conditions only. d) If we perforate the whole reservoir layer, what is the well able to produce if the bottom hole pressure is 180 bara? e) Estimate the permeability in the undamaged part of the formation. Exercise 3-3 Inflow efficiency A vertical well is producing from a cylindrical shaped volume. The following data is given: Reservoir Pay : Reservoir permeability: Wellbore radius: Drainage radius: h = 20 m k = 0.15 2 rw = 0.8 m re = 200 m Drilling fluid is being filtrated and invades 10 cm into the formation and reduces the permeability by 60 % in the nearby region. a. Estimate the inflow efficiency. b. Express the skin factor as a function of invasion radius and permeability in the damaged zone. Task 3.4 Lamination The picture shows the lamination in a sandstone layer (ref. Geo-Expro, Oct.2007). Roughly, we can say that 80% of the cross section consists of horizontal laminations of clean sandstone, with porosity: 0.15 and permeability: 1 D. The remaining 20% of the cross section consists of clayey sandstone with porosity of 0.05 and permeability: 0.01 D. Both the clean sandstone and argillaceous is isotropic (same permeability in all directions, within the lamina). a) Estimate the effective permeability for a vertical well, complemented through the reservoir layer illustrated b) Estimate the effective vertical permeability c) Estimate the anisotropy factor Task 3.5 Vertical well in anisotropic reservoir The reservoir lyer is 20 m high. Horizontal permeability is measured: kh = 0.2m2 vertical : kv = 0.05m2. A vertical well is planned completed in the upper 10 meters. Well radius: rw = 0.1m . The well is planned perforated with 6 shots per meter, penetration depth : Lp = 0.25 m Estimate : a) Skin factor due to partial completion b) Skin factor due to perforation c ) Total skin factor Task 3.6: 2nd-order flow characteristics The following information is available about the well and reservoir - Viscosity, reservoir oil: 2 cP - Length of the completed interval: 50 m - Formation factor: 1.5 m3/Sm3 - Well radius: 0.1 m - Equivalent radius to the outer limit of 200 m - Reservoir pressure: 200 bar - Density, reservoir oil: 700 kg/m3 - Skin factor by viscous influx .5 A well test gave the following results Production (Sm3 / d) 0 200 400 Bottom hole pressure (bar) 200 196 189 a) Estimate the linear productivity index, based on the measured data b) Predict bottom hole pressure to produce 800 Sm3 / d c) Estimate second order flow characteristic d) Predict bottom hole pressure to produce 800 Sm3 / d. Task 3.7 Vogels flow characteristics (The task uses the same data as 3.6 above. But we have now learned that the reservoir oil is near the saturation pressure.) - Viscosity , reservoir oil : - Length of the completed interval : - Formation factor: - Well radius: - Equivalent radius to the outer limit - Reservoir pressure: - Density , reservoir oil : - Skin factor 2 cP 50 m 1.5 m3/Sm3 0.1 m 200 m 200 bar 700 kg/m3 0.5 A well test gave the following results Production (Sm3 / d) 0 200 400 Bottom hole pressure (bar) 200 196 189 a) Estimate Vogel’s inflow characteristic , from the measured data b) Predict bottom hole pressure to produce 800 Sm3 / d c ) Consider the choice of linear, 2 order , or Vogel’s inflow characteristics.