ISE442: Design of Experiments
advertisement
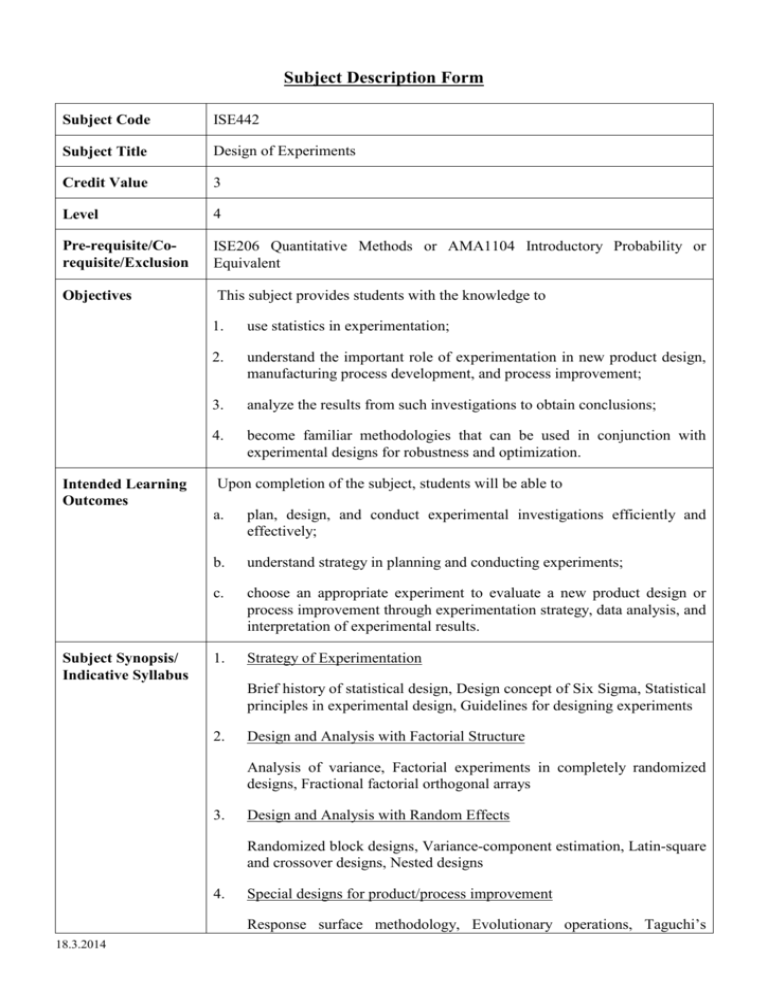
Subject Description Form Subject Code ISE442 Subject Title Design of Experiments Credit Value 3 Level 4 Pre-requisite/Corequisite/Exclusion ISE206 Quantitative Methods or AMA1104 Introductory Probability or Equivalent Objectives This subject provides students with the knowledge to Intended Learning Outcomes Subject Synopsis/ Indicative Syllabus 1. use statistics in experimentation; 2. understand the important role of experimentation in new product design, manufacturing process development, and process improvement; 3. analyze the results from such investigations to obtain conclusions; 4. become familiar methodologies that can be used in conjunction with experimental designs for robustness and optimization. Upon completion of the subject, students will be able to a. plan, design, and conduct experimental investigations efficiently and effectively; b. understand strategy in planning and conducting experiments; c. choose an appropriate experiment to evaluate a new product design or process improvement through experimentation strategy, data analysis, and interpretation of experimental results. 1. Strategy of Experimentation Brief history of statistical design, Design concept of Six Sigma, Statistical principles in experimental design, Guidelines for designing experiments 2. Design and Analysis with Factorial Structure Analysis of variance, Factorial experiments in completely randomized designs, Fractional factorial orthogonal arrays 3. Design and Analysis with Random Effects Randomized block designs, Variance-component estimation, Latin-square and crossover designs, Nested designs 4. Special designs for product/process improvement Response surface methodology, Evolutionary operations, Taguchi’s 18.3.2014 robust product design approach, Parameter design, Customer tolerance, Types of quality loss functions; Tolerance design Teaching/Learning Methodology A mixture of lectures and tutorials is used to achieve the objectives of this subject. Students also have the opportunity to use the computer package to perform data analysis. The lectures are aimed at providing students with the integrated knowledge required to hone expertise and master procedures necessary to perform, evaluate, and arrive at decisions using designed experiments. The tutorials are aimed at enhancing design and analysis techniques. Tutorials and case studies are based on real-world applications of experimental design and are drawn from a number of different fields of engineering. The software packages are introduced in lectures and are used in tutorials and cases studies to handle the analysis of experiments. Assessment Methods in Alignment with Intended Learning Outcomes Specific assessment methods/tasks % weighting Intended subject learning outcomes to be assessed a b c 1.Examination 60% 2. Assignments 30% 3.Test 10% Total 100% The continuous assessment comprises of two components: a test (10%) and three tutorials (30%). The test is aimed at assessing the knowledge gained by the students. The tutorials are designed to assess students’ ability to design experiments and analyze results of the experiment. The examination, which covers all the intended learning outcomes, is used to assess the knowledge and skills acquired by the students. Student Study Effort Expected Class contact: Lecture 2 hours/week for 13 weeks 26 Hrs. Tutorial & Test 1 hour/week for 13 weeks 13 Hrs. Other student study effort: Assignments 26 Hrs. Self Study 52 Hrs. Total student study effort 18.3.2014 117 Hrs. Reading List and References 18.3.2014 1. C.F. Jeff Wu & Michael Hamada 2009, Experiments-Panning, Analysis, and Parameter Design Optimization, 2nd edn, John Wiley & Sons. Inc. 2. D.C. Montgomery 2013, Design and Analysis of Experiments, 7th edn, John Wiley & Sons. Inc. 3. R. L. Mason, R. F. Gunst & J.L. Hess 2003, Statistical Design and Analysis of Experiments with Applications to Engineering and Science, 2nd edn, John Wiley & Sons. Inc.