CHEMISTRY 150 - Seattle Central College
advertisement
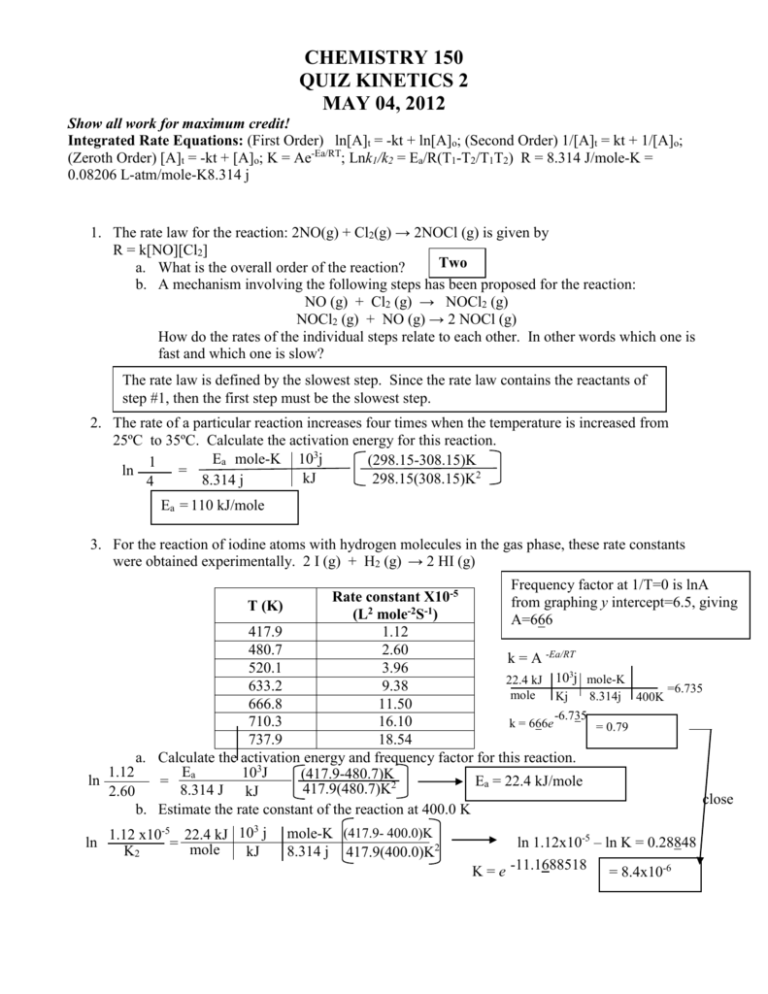
CHEMISTRY 150 QUIZ KINETICS 2 MAY 04, 2012 Show all work for maximum credit! Integrated Rate Equations: (First Order) ln[A]t = -kt + ln[A]o; (Second Order) 1/[A]t = kt + 1/[A]o; (Zeroth Order) [A]t = -kt + [A]o; K = Ae-Ea/RT; Lnk1/k2 = Ea/R(T1-T2/T1T2) R = 8.314 J/mole-K = 0.08206 L-atm/mole-K8.314 j 1. The rate law for the reaction: 2NO(g) + Cl2(g) → 2NOCl (g) is given by R = k[NO][Cl2] Two a. What is the overall order of the reaction? b. A mechanism involving the following steps has been proposed for the reaction: NO (g) + Cl2 (g) → NOCl2 (g) NOCl2 (g) + NO (g) → 2 NOCl (g) How do the rates of the individual steps relate to each other. In other words which one is fast and which one is slow? The rate law is defined by the slowest step. Since the rate law contains the reactants of step #1, then the first step must be the slowest step. 2. The rate of a particular reaction increases four times when the temperature is increased from 25ºC to 35ºC. Calculate the activation energy for this reaction. Ea mole-K 103j (298.15-308.15)K 1 ln = kJ 298.15(308.15)K2 8.314 j 4 Ea = 110 kJ/mole 3. For the reaction of iodine atoms with hydrogen molecules in the gas phase, these rate constants were obtained experimentally. 2 I (g) + H2 (g) → 2 HI (g) Frequency factor at 1/T=0 is lnA Rate constant X10-5 from graphing y intercept=6.5, giving T (K) (L2 mole-2S-1) A=666 417.9 1.12 480.7 2.60 k = A -Ea/RT 520.1 3.96 3 22.4 kJ 10 j mole-K 633.2 9.38 =6.735 mole Kj 8.314j 400K 666.8 11.50 -6.735 710.3 16.10 k = 666e = 0.79 737.9 18.54 a. Calculate the activation energy and frequency factor for this reaction. 1.12 Ea 103J (417.9-480.7)K ln = Ea = 22.4 kJ/mole 417.9(480.7)K2 8.314 J kJ 2.60 close b. Estimate the rate constant of the reaction at 400.0 K -5 22.4 kJ 103 j ln 1.12 x10 = mole K2 kJ mole-K (417.9- 400.0)K 8.314 j 417.9(400.0)K2 ln 1.12x10-5 – ln K = 0.28848 K = e -11.1688518 = 8.4x10-6