Jump Lab
advertisement

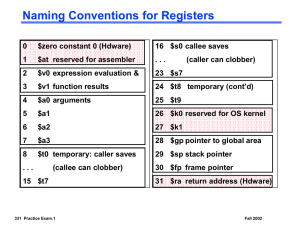
Vertical Jump Lab Due: Friday, January 26th Open Hu-m-an and select a jump trial from the list Select Options: Instant Calculation Follow directions to determine aspect ratio and scaling factors Measure vertical jump height _____ *Explain how you measured vertical jump height Relative Angles Select Help: Hu-m-an Manual Scroll down to Chapter 3 and click on “Natural Relative Angles” Observe how relative angles are determined for the hip, knee, ankle, shoulder, and elbow joints. Keep that window available for reference and determine relative angles at those joints for the: First Frame Maximum flexion of the hip, knee, and ankle joints (lowest point) Take-off Digitizing sequence (click-on the joint centers or axes of rotation for each joint): Shoulder: shoulder-hip-shoulder-elbow _____ _____ _____ Elbow: elbow-wrist-elbow-shoulder _____ _____ _____ Hip: hip-knee-hip-shoulder _____ _____ _____ Knee: knee-hip-knee-ankle _____ _____ _____ Ankle: heel-ball-heel-ankle _____ _____ _____ Digitizing (click-on the joint centers or axes of rotation for each joint) Selection Options: Digitize from the first frame until subject lands from their jump Calculations Exit the digitizing window Calculate: System C. of G. (center of gravity) for Y Display the graph and smooth Click-on the graph to display the C. of G. values at take-off and at the peak of the vertical jump Determine the difference in C. of G. at take-off and the peak of the vertical jump _____ *How does this compare with the vertical jump height you calculated earlier? Calculate relative angles at the hip, knee, and ankle Calculate velocity at the hip, knee, and ankle Display the angular velocity graphs for each of these joints and smooth Observe the angular velocity graphs for the hip, knee, and ankle and compare when peak angular velocity occurs at each joint. Describe the temporal relationship between these three joints and how it functions to maximize vertical jump height. Graphs Display each graph one at a time. Then select Utilities, Copy, Graph Window, and paste into a Word document. Additional Questions Vertical jump height is decreased if subjects perform the jumps with their hands placed on their hips. Which of Newton’s laws best explains the positive effect that the upward swing of the arms has on vertical jump height? The vertical jump you observed for this lab is classified as a countermovement jump because the subject flexed their hip, knee, and ankle joints before immediately and powerfully extending those same joints. Vertical jump height is decreased if no or minimal countermovements are performed. Explain how countermovements increase vertical jump height. Please do some research before answering this question.