EE 572 OPTIMIZATION THEORY
advertisement

EE 572 OPTIMIZATION THEORY
HOMEWORK II
Due: 22 Jan 2009
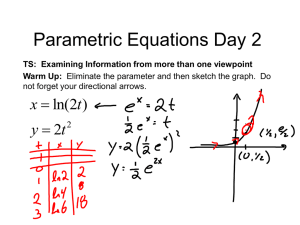
1-) Consider the iterative process
1
a
xk 1 xk
2
xk
where a > 0. Assuming that the process converges, to what does it converge? What is the
order of convergence?
2-) In the steepest descent algorithm applied to the quadratic problem
min
x
1 T
x Qx bT x
2
show that the successive gradient vectors are orthogonal, i.e. gTk1gk 0 , k 0,1,... .
3-) Let e1 , e2 ,..., en denote the eigenvectors of the symmetric positive definite n×n matrix
Q. For the quadratic problem
min
x
1 T
x Qx bT x
2
Suppose x0 is chosen so that g0 belongs to a subspace M spanned by a subset of the ei’s.
Show that for the method of steepest descent g k M for all k. Find the rate of
convergence for this case.
4-) Use the steepest descent method to find the minimum of the following non-quadratic
function. Take x0 = (1.0 1.0)T as the initial point and perform a line search at each step.
f (x) 2x14 x24 x12 x23 6x1 8
5-) Apply Newton’s method with line search to the problem in Q.4:
1
xk 1 xk k F(xk ) f (xk )T
where k minimizes f (xk gk ), gk f (xk )T and F is the Hessian matrix.
SOLUTION
1-) If x* is the convergence point, then
1
a
x* x* *
2
x
x* a
Consider
lim
k
xk 1 a
xk a
p
Let xk a .
1
a
xk 1 a xk
2
xk
lim
k
2
2 a
xk 1 a
xk a
p
1
1
a
a
1
2
a
1
2
a
1
1
2
a 1
...
2
a a
2
.....
2
lim
2 a
p
lim
1
2 a
p 2
if p 2
order of convergence is 2.
2-)
xk 1 xk k g k
k
g kT g k
g kT Qg k
g k 1 Qxk 1 b Qxk k Qxk b g k k Qg k
3-)
g kT1 g k ( g kT k g kT Q) g k g kT g k k g kT Qg k g kT g k
g 0 M Sp e j , j I M ,
Suppose g n Qxn b M
g 0 Qx0 b
gn
g k Qxk b
ae
jI M
g kT g k T
g k Qg k 0
g kT Qg k
j
j
gT g
gT g
g n 1 Qxn 1 b Qxn Qg n Tn n b g n Qg n Tn n
g n Qg n
g n Qg n
1
y Qg n PP g n
P (e1 e2 ... en )
a
0
T
T
e1
e1 g n
T
T a j1
e
e g
Pg n 2 g n 2 n
T
T a jM
en
en g n
0
0
j1 a j1
P 1 g n
jM a jM
0
ekT g n ak
Now,
PP 1 g n
ae
jI M
j
j
k IM ,
I M j1, j 2,
yM
j
, jM
g n 1 M
Convergence rate:
( g kT g k )2
E ( xk 1 ) 1 T
E ( xk )
T
1
(
g
Qg
)(
g
Q
g
)
k
k
k
k
Let x M , x a j e j Qx a j Qe j
jI M
xT Qx
a
jI M
j
jI M
Q PP 1
2
j
ae
jI M
j
j
j
Q 1 P 1 P 1 Q 1 x P 1 ( PT x)
0
0
e a j e j
jI M
1 a j1
T
a j1
j1
e2 a j e j
1
j
I
M
Px
(
P
x
)
1
a
jM
jM a jM
T
en a j e j
jI M
0
0
T
1
P 1 ( PT x)
1
jI M
a je j
j
xT Q 1 x
1
jI M
a 2j
j
2
2
a
j
jI
( xT x ) 2
M
T
T
1
( x Qx)( x Q x)
2
j a j
j
jI M
I M
2
1
j
a
2
j
4min max
(min max ) 2
where min min j , j I M , max max j , j I M
min
rM 1
E{xk 1} max
E{xk } convergence rate =
rM 1
max min
(QM ) : eigenvalues of Q restricted to the subspace M .
2
where rM
max (QM )
min (QM )
4-) 5-)
% EE 572 HW2 Q4 and Q5 solution ; Fall 2008-2009
syms x1 x2
f=2*x1^4+x2^4+x1^2*x2^3-6*x1+8;
g1=diff(f,x1);
g2=diff(f,x2);
alf=0.001;
kmax=20;
x1=1.25; x2=1.25;
x=[x1 x2];
g=[g1 g2];
%-----------------------------% Steepest descent
%-----------------------------for k=1:kmax
k
gn=subs(g);
fn0=subs(f);
flag=0;
l(k)=0;
% line search in small steps of alf
while flag == 0
x=x-alf*gn;
x1=x(1); x2=x(2);
fn=subs(f);
if(fn < fn0)
fn0=fn;
xl=x;
l(k)=l(k)+1;
else
flag=1;
end
end
x=xl;
end
fmin=subs(f);
%-----------------------------% Newton's method
%-----------------------------f11=diff(g1,'x1'); f12=diff(g1,'x2'); f21=f12; f22=diff(g2,'x2');
F=[f11 f12 ; f21 f22];
kmax=10;
for k=1:kmax
k
gn=subs(g);
Fn=subs(F);
fn0=subs(f);
flag=0;
l(k)=0;
% line search in small steps of alf
while flag == 0
x=x-alf*(inv(Fn)*gn')';
x1=x(1); x2=x(2);
fn=subs(f);
if(fn < fn0)
fn0=fn;
xl=x;
l(k)=l(k)+1;
else
flag=1;
end
end
x=xl;
end
fmin=subs(f);