Table 1 Summary Statistics
advertisement
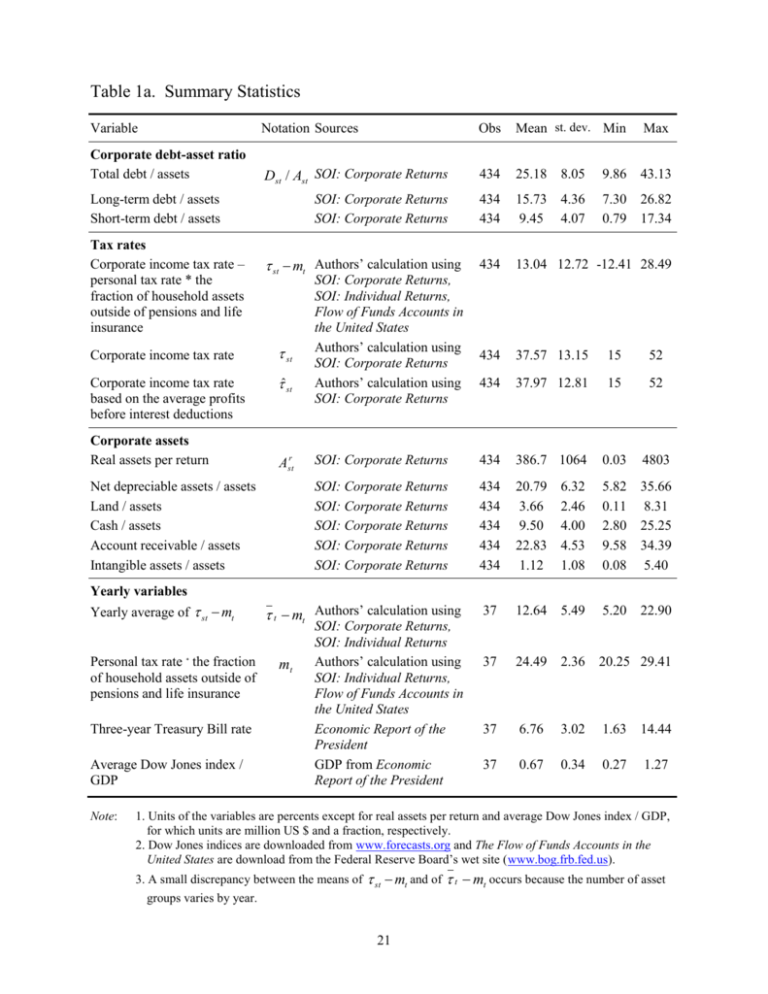
Table 1a. Summary Statistics Variable Notation Sources Obs Mean st. dev. Min Max Corporate debt-asset ratio Total debt / assets Dst / Ast SOI: Corporate Returns 434 25.18 8.05 9.86 43.13 SOI: Corporate Returns SOI: Corporate Returns 434 434 15.73 9.45 4.36 4.07 7.30 0.79 26.82 17.34 434 13.04 12.72 -12.41 28.49 434 37.57 13.15 15 52 434 37.97 12.81 15 52 SOI: Corporate Returns 434 386.7 1064 0.03 4803 SOI: Corporate Returns SOI: Corporate Returns SOI: Corporate Returns SOI: Corporate Returns SOI: Corporate Returns 434 434 434 434 434 20.79 3.66 9.50 22.83 1.12 6.32 2.46 4.00 4.53 1.08 5.82 0.11 2.80 9.58 0.08 35.66 8.31 25.25 34.39 5.40 37 12.64 5.49 5.20 22.90 37 24.49 2.36 20.25 29.41 37 6.76 3.02 1.63 14.44 37 0.67 0.34 0.27 1.27 Long-term debt / assets Short-term debt / assets Tax rates Corporate income tax rate – personal tax rate * the fraction of household assets outside of pensions and life insurance st mt Authors’ calculation using Corporate income tax rate st Corporate income tax rate based on the average profits before interest deductions ˆ st Corporate assets Real assets per return Astr Net depreciable assets / assets Land / assets Cash / assets Account receivable / assets Intangible assets / assets SOI: Corporate Returns, SOI: Individual Returns, Flow of Funds Accounts in the United States Authors’ calculation using SOI: Corporate Returns Authors’ calculation using SOI: Corporate Returns Yearly variables Yearly average of st mt Personal tax rate * the fraction of household assets outside of pensions and life insurance Three-year Treasury Bill rate Average Dow Jones index / GDP Note: t mt Authors’ calculation using mt SOI: Corporate Returns, SOI: Individual Returns Authors’ calculation using SOI: Individual Returns, Flow of Funds Accounts in the United States Economic Report of the President GDP from Economic Report of the President 1. Units of the variables are percents except for real assets per return and average Dow Jones index / GDP, for which units are million US $ and a fraction, respectively. 2. Dow Jones indices are downloaded from www.forecasts.org and The Flow of Funds Accounts in the United States are download from the Federal Reserve Board’s wet site (www.bog.frb.fed.us). 3. A small discrepancy between the means of st mt and of t mt occurs because the number of asset groups varies by year. 21 Table 1b. Summary Statistics by Size of Firm Large firms with real assets larger than $25m (n=182) Medium firms Small firms with real with real assets assets smaller between $5m than $5m and $25m (n=186) (n=66) Variable Mean st. dev. Mean st. dev. Mean st. dev. Corporate debt-asset ratio Total debt / assets 16.93 3.48 28.79 6.13 31.98 2.93 Long-term debt / assets 11.46 2.02 16.81 2.92 19.54 2.11 Short-term debt / assets 5.47 2.09 11.98 3.32 12.44 1.92 5.13 21.52 4.50 1.49 10.55 6.19 45.85 5.73 26.01 11.00 6.18 45.28 6.74 27.21 11.26 Tax rates Corporate income tax rate – personal tax rate * the fraction of household assets outside of 21.76 pensions and life insurance Corporate income tax rate 46.37 Corporate income tax rate based on the average 46.31 profits before interest deductions Corporate assets Real assets per return 916.4 1491.4 13.11 5.72 1.00 1.11 Net depreciable assets / assets 14.86 3.93 20.34 2.63 26.75 2.32 Land / assets 1.22 0.60 3.67 0.96 6.04 1.36 Cash / assets 6.78 1.97 8.29 1.48 12.60 3.92 Account receivable / assets 24.56 4.13 25.44 2.04 20.21 4.20 Intangible assets / assets 0.88 1.06 1.11 0.93 1.37 1.10 22 Table 2a. D/A Ratio on Corporate Marginal Tax Rate, OLS Dependent variables are the ratio of total debt to total assets in percent. Estimation method st mt (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) OLS OLS OLS OLS OLS -0.419** -0.393** 0.110** 0.302** 0.067** (0.018) (0.020) (0.033) (0.025) (0.019) -2.243** -0.773** 2.227** (0.120) (0.192) (0.351) log( Astr ) r st 2 r st 3 (log( A )) -0.712** (0.146) (log( A )) -0.572** (0.068) (log( Astr )) 4 0.088** (0.009) (log( Astr )) 5 0.019** (0.004) r st 6 r st 7 (log( A )) -0.004** (0.001) (log( A )) 0.00021** (0.000038) Net dep. assets / total assets Land / total assets Accounts receivable / total assets Intangible assets / total assets r st (Dow Jones index / GDP)* log( A ) Year dummies included? No. of observations R2 0.347** (0.069) (0.066) 1.463 Cash / total assets Constant 0.639** ** 0.156 (0.289) (0.295) -0.156 -0.414** (0.113) (0.086) -0.036 -0.072 (0.046) (0.044) 1.237 1.406** * (0.581) (0.354) -0.224 -0.245 (0.132) (0.125) 30.646** 25.572** 23.143** -0.349 22.049** (0.243) (1.289) (1.013) (2.308) (2.379) No 434 0.437 Yes 434 0.433 Yes 434 0.726 Yes 434 0.932 Yes 434 0.972 White-corrected standard errors in parentheses. * significant at 5% level; ** significant at 1% level. Data come from the U.S. Statistics of Income: Corporate Tax Returns, for 1954 – 1995 except for 1962 and 1966-9, reported separately each year for around 14 different size categories of firms, based on assets. 23 Table 2b. D/A Ratio on Corporate Marginal Tax Rate, IV Dependent variables are the ratio of debt to total assets in percent.. (1) (2) (3) (4)a Dependent variable Total Dst / Ast short-term Dst / Ast long-term Dst / Ast Total Dst / Ast st mt 0.047* 0.029 0.019 0.057* (0.023) (0.019) (0.015) (0.027) 2.406** 0.921** 1.486** 2.415** (0.379) (0.319) (0.246) (0.376) -0.724** -0.097 -0.627** -0.724** (0.147) (0.100) (0.092) (0.147) -0.590** -0.390** -0.200** -0.590** (0.071) (0.055) (0.045) (0.071) 0.090** 0.037** 0.052** 0.090** (0.009) (0.007) (0.005) (0.009) 0.020** 0.014** 0.006** 0.020** (0.004) (0.003) (0.002) (0.004) -0.004** -0.002** -0.002** -0.004** (0.001) (0.001) (0.000) (0.001) 0.00022** 0.00011** 0.00011** 0.00022** (0.00004 ) (0.00003) (0.00002) (0.00004) 0.356 0.029 0.327 0.357** (0.067) (0.035) (0.059) r st log( A ) (log( Astr )) 2 (log( Astr )) 3 r st (log( A )) 4 (log( Astr )) 5 (log( Astr )) 6 r st (log( A )) 7 Net depreciable assets / total assets Land / total assets Cash / total assets Accounts receivable / total assets Intangible assets / total assets r st (Dow Jones index / GDP)* log( A ) Constant Year dummies included? No. of observations R2 ** ** (0.067) 0.077 -0.117 0.194 0.085 (0.303) (0.212) (0.236) (0.304) -0.423** -0.616** 0.193** -0.415** (0.087) (0.063) (0.066) (0.088) -0.073 -0.108 0.035 -0.073 (0.044) (0.035) (0.023) (0.044) 1.381 -0.085 1.465 1.380** (0.360) (0.284) (0.214) (0.360) -0.275* -0.228* -0.047 -0.276* (0.128) (0.092) (0.074) (0.127) 22.56** 19.81** 2.75 21.70** (2.435) (1.931) (1.565) (2.583) Yes 434 0.972 Yes 434 0.931 Yes 434 0.967 Yes 434 0.972 ** ** ** Data come from the U.S. Statistics of Income: Corporate Tax Returns, for 1954 – 1995 except for 1962 and 1966-9, reported separately each year for around 14 different size categories of firms, based on assets. 24 All regressions use IV, to correct for possible endogeneity in st . White-corrected standard errors in parentheses. * significant at 5% level; ** significant at 1% level. Note: a tax variable in column (4) is st mt (1 st ) * z st instead of st mt . 25 Table 3. Yearly Variation Unexplained by Non-tax Factors, OLS and IV. Sample years are from 1954 to 1995 except 1962 and 1966-69. Dependent variables are the average value of Dst / Ast each year, corrected for the effects of the nontax variables using coefficients from column (1) of Table 2b. Estimation method t mt (1) (2) (3) (4) (5)a (6)a OLS OLS IV IV IV IV -0.241** 0.330* 0.362* (0.045) (0.100) (0.103) 0.305** 0.257* 0.249* (0.104) (0.100) (0.092) -0.603** -0.395** -0.210** (0.133) (0.128) (0.070) t mt Three year Treasury Bill rate 0.523 Dow Jones index / GDP Dummy for post 1986 Constant No. of observations R2 0.253 0.245 (0.161) 0.540 (0.159) (0.130) (0.158) (0.164) -3.840* -4.060* -4.724** -3.289** -1.384 (1.586) (1.613) (1.251) (0.952) (0.909) 3.369 3.583 ** ** 0.483 ** 1.845 1.955 1.591* (0.750) (0.758) (1.004) (0.676) (0.706) 8.569** -0.507 -0.933 8.390* 36.516** -3.124 (0.641) (2.172) (2.157) (3.992) (3.925) (4.206) 37 0.42 37 0.75 37 0.75 37 0.79 25 0.54 25 0.51 ** ** ** Data come from the U.S. Statistics of Income: Corporate Tax Returns, for 1954 – 1995 except for 1962 and 1966-9, averaged each year over 14 different size categories of firms, based on assets. The tax incentive variable, t mt , and its instrument, ˆst mt , are unweighted yearly averages. White-corrected standard errors in parentheses. * significant at 5% level; ** significant at 1% level. Note: a m t in column (5) is a weighted average, weighting by the size of taxable income. m t in column (6) is a weighted average, weighting by the size of assets. These two columns use just the IMF data, so include 1964 and 1970-93. 26 Table 4. Actual Yearly Variation of D/A, IV Sample years are 37 years from 1954 to 1995 except 1962 and 1966-69. (1) Dependent variable t mt (2) (3) (4) unweighted average of debtassets ratio, ( Dst / Ast ) / S Asset-weighted average of debtassets ratio, Dst / Ast s s s 0.130 0.110 (0.113) (0.136) t mt 0.035 0.066 (0.066) (0.058) -0.533** -0.553** (0.115) Three year Treasury Bill rate Dow Jones index / GDP Dummy for post 1986 Constant No. of observations R2 (0.122) 0.505 0.411 (0.173) (0.096) (0.177) (0.102) -3.002 -4.109 -2.563 -4.066** (1.529) (1.053) (1.462) (0.941) 5.724 2.827 3.829 1.308* (0.957) (0.609) (1.155) (0.497) 20.84** 36.39** 15.42** 30.28** (2.424) (3.051) (3.287) (2.935) 37 0.91 37 0.95 37 0.80 37 0.88 ** ** ** ** ** 0.363 * ** 0.304** Data come from the U.S. Statistics of Income: Corporate Tax Returns, for 1954 – 1995 except for 1962 and 1966-9, reported separately for around 14 different size categories of firms, based on assets. White-corrected standard errors in parentheses. * significant at 5% level; ** significant at 1% level. Note: For columns (1) and (2), the tax incentive variable, t mt , and its instrument, ˆst mt , are unweighted yearly averages. Since in columns (3) and (4) the dependent variable is an assetweighted average of the debt-asset ratios, the tax incentive variable, t mt , is now a weighted average corporate tax rate, weighting by the size of corporate assets in each category. The instrument is also constructed as an asset-weighted average of ˆst mt . 27 Figure 1. US Corporate Tax Rate Structure, 1954-1995 51 52 50 52.8 48 50 48 49.2 46 46 46 48 48 46 40 40 40 40 Marginal tax rate 40 38 40 42.5 39 39 35 35 34 37 34 30 30 30 30 30 34 30 27.5 20 25 22 22 22 24.2 22.5 22 19 20 18 18 16.5 16 15 15 15 15 15 & 19 54 - 50 bt 25 bt & 50 25 Year w lo be 19 63 1 19 96 65 4 19 -19 68 67 -1 96 9 19 19 7 71 0 19 -19 75 74 19 19 79 78 -1 98 1 19 82 19 198 84 3 -1 98 6 19 198 7 88 19 199 2 93 -1 99 5 0 33 ,3 3 0 18 ,33 ,00 e 18 15 ov 00 ab 5 & 0 & ,0 1 0 10 ,0 bt & 05 10 4 5 1, bt 40 & 1, 0 00 0 bt 00 1, 1, & 5 bt 5 33 33 & bt 0 0 10 10 bt & 75 75 bt 17 10 25 20 Taxable income, thousand dollars Note: Surtaxes have been imposed in a certain range of taxable income since 1984. Marginal tax rates for taxable income more than $25,000 in years 1965-67 were 48%, and those in 1964 were 50%. All figures represent nominal income. Inflation corrections would lead to further variation across years. 28 Figure 2. Debt-Asset Ratios on Size of Firm, 1954-1995 45 88 Debt / Assets, % 40 30 20 10 90 89 90 86 89 91 91 90 88 91 84 88 86 92 87 87 85 85 86 8985 87 78 95 84 92 73 84 79 77 82 94 93 83 92 91 7674 93 78 81 89 79 74 80 93 75 77 94 73 75 76 9572 58 95 71 59 90 82 81 90 84 83 7065 72 83 80 83 90 85 6056 94 89 928884 83 91 86 91 89 64 78 77 76 87 74 88 91 8257 59 71 75 86 8092 89 63 92 73 9590 55 85 79 71 65 60 95 72 63 94 87 82 82 94 81 84 95 81 94 87 95 94 88 93 64 92 85 79 70 70 81 80 78 93 60 87 61 54 77 86 59 73 60 61 86 7674 77 80 888280 93 59 60 59 61 93 79 78 58 83 5975 72 65 63 58 63 79 78 75 71 81 64 76 58 60 57 85 58 74 57 73 63 71 57 61 58 70 56 72 57 57 56 77 84 64 55 65 56 65 64 70 6355 55 56 65 55 75 56 90 54 7674 61 64 54 55 54 89 60 91 83 63 54 73 59 54 57 95 88 82 58 72 93 92 94 87 85 63 86 81 71 80 7079 84 90 90 56 91 89 89 55 54 61 60 78 83 9288 9188 86 777482 95 59 93 87 94 87 85 92 85 7573 72 86 58 65 76 84 74 70 84 73 82 72 748095 93 83 94 64 81 80 71 71 57 70 63 79 56 83 79 75 80 81 81 82 73 74 78 61 77 78 7370 75 72 55 60 70 57 76 71 58 65 59 54 65 56 76 75 72 77 55 7179 64 54 63 64 78 60 59 76 63 63 77 64 61 61 60 65 65 63 57 58 64 58 61 60 59 57 61 59 56 55 56 55 57 54 56 60 58 54 57 56 59 55 54 58 55 54 .025 .05 .1 .25 .5 1 2.5 5 10 25 50 Avg Assets per Return / CPI 100 250 Note: Log scale is used for the x-axis. The label is the year of the observation. Source: Authors’ calculation using SOI Corporate Returns. 29 500 90 89 88 9187 92 86 9484 9585 93 74 70 83 827571 72 7673 80 79 78 81 77 60 61 65 59 57 63 58 64 56 55 54 Figure 3. The Estimated Tax Effect as a Function of Asset Size 0.6 Estimated tax coefficient 0.5 0.4 tax coefficient 0.3 95% confidence interval 0.2 0.1 0 $10 $100 $1,000 $10,000 -0.1 Real assets on log scale, thousand dollars 30 $100,000 $1,000,000